Abstract
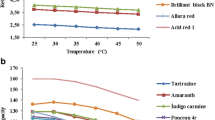
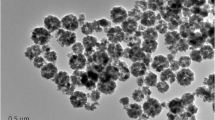
A new automated magnetic solid-phase extraction (MSPE) method was developed and combined with high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and spectrophotometry for off-line and on-line quantitative enrichment and determination of synthetic food colorants in food samples. Fe3O4-poly (ionic liquid) core-shell microspheres were prepared as a sorbent to quickly extract analytes from aqueous samples. The entire MSPE process, including extraction, separation, elution, and cleaning, was automated using common equipment. The main parameters affecting the performance of MSPE and the automated process, such as absorbent, sample pH, eluent, flow rate, elution time, etc., were investigated in detail. Under the optimum experimental conditions, the limits of detection ranged between 4.1 and 14 ng/mL by off-line HPLC and were 220 ng/mL for the determination of amaranth by on-line spectrophotometry, with excellent reproducibility (intra- and inter-day relative standard deviations were less than 3.2 %). The developed method was successfully applied to the determination of colorants in food samples.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguilar-Arteaga K, Rodriguez JA, Barrado E (2010) Magnetic solids in analytical chemistry: a review. Anal Chim Acta 674:157–165
Al-Degs YS (2009) Determination of three dyes in commercial soft drinks using HLA/GO and liquid chromatography. Food Chem 117:485–490
Alves SP, Brum DM, de Andrade ÉCB, Netto ADP (2008) Determination of synthetic dyes in selected foodstuffs by high performance liquid chromatography with UV-DAD detection. Food Chem 107:489–496
Berzas JJ, Flores JR, Llerena MV, Farinas NR (1999) Spectrophotometric resolution of ternary mixtures of Tartrazine, Patent Blue V and Indigo Carmine in commercial products. Anal Chim Acta 391:353–364
Bianchi F, Bisceglie F, Dugheri S, Arcangeli G, Cupelli V, del Borrello E, Sidisky L, Careri M (2014) Ionic liquid-based solid phase microextraction necklaces for the environmental monitoring of ketamine. J Chromatogr A 1331:1–9
Bonan S, Fedrizzi G, Menotta S, Elisabetta C (2013) Simultaneous determination of synthetic dyes in foodstuffs and beverages by high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with diode-array detector. Dyes Pigments 99:36–40
Chanlon S, Joly-Pottuz L, Chatelut M, Vittori O, Cretier JL (2005) Determination of Carmoisine, Allura red and Ponceau 4R in sweets and soft drinks by Differential Pulse Polarography. J Food Compos Anal 18:503–515
Chen QC, Mou SF, Hou XP, Riviello JM, Ni ZM (1998) Determination of eight synthetic food colorants in drinks by high-performance ion chromatography. J Chromatogr A 827:73–81
Chen B, Heng S, Peng H, Hu B, Yu X, Zhang Z, Zhu Y (2010) Magnetic solid phase microextraction on a microchip combined with electrothermal vaporization-inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry for determination of Cd, Hg and Pb in cells. J Anal At Spectrom 25:1931–1938
Combeau S, Chatelut M, Vittori O (2002) Identification and simultaneous determination of Azorubin, Allura red and Ponceau 4R by differential pulse polarography: application to soft drinks. Talanta 56:115–122
Deng M, Jiang C, Jia L (2013) N-Methylimidazolium modified magnetic particles as adsorbents for solid phase extraction of genomic deoxyribonucleic acid from genetically modified soybeans. Anal Chim Acta 771:31–36
Dossi N, Toniolo R, Pizzariello A, Susmel S, Perennes F, Bontempelli G (2007) A capillary electrophoresis microsystem for the rapid in-channel amperometric detection of synthetic dyes in food. J Electroanal Chem 601:1–7
Fontanals N, Borrull F, Marcé RM (2012) Ionic liquids in solid-phase extraction. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 41:15–26
Galán-Cano F, del Carmen A-LM, Lucena R, Cárdenas S, Valcárcel M (2013) Ionic liquid coated magnetic nanoparticles for the gas chromatography/mass spectrometric determination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in waters. J Chromatogr A 1300:134–140
Gao H, Kan T, Zhao S, Qian Y, Cheng X, Wu W, Wang X, Zheng L (2013) Removal of anionic azo dyes from aqueous solution by functional ionic liquid cross-linked polymer. J Hazard Mater 261:83–90
Gao N, Wu H, Chang Y, Guo X, Zhang L, Du L, Fu Y (2015) Mixed micelle cloud point-magnetic dispersive μ-solid phase extraction of doxazosin and alfuzosin. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 134:10–16
Ge D, Lee HK (2012) Ionic liquid based hollow fiber supported liquid phase microextraction of ultraviolet filters. J Chromatogr A 1229:1–5
Giakisikli G, Anthemidis AN (2013) Automated magnetic sorbent extraction based on octadecylsilane functionalized maghemite magnetic particles in a sequential injection system coupled with electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry for metal determination. Talanta 110:229–235
He L, Zhang K, Wang C, Luo X, Zhang S (2011) Effective indirect enrichment and determination of nitrite ion in water and biological samples using ionic liquid-dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction combined with high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr A 1218:3595–3600
Ho TD, Canestraro AJ, Anderson JL (2011) Ionic liquids in solid-phase microextraction: a review. Anal Chim Acta 695:18–43
Huang YF, Li Y, Jiang Y, Yan XP (2010) Magnetic immobilization of amine-functionalized magnetite microspheres in a knotted reactor for on-line solid-phase extraction coupled with ICP-MS for speciation analysis of trace chromium. J Anal At Spectrom 25:1467–1474
Hutchinson JP, Setkova L, Pawliszyn J (2007) Automation of solid-phase microextraction on a 96-well plate format. J Chromatogr A 1149:127–137
Kucharska M, Grabka J (2010) A review of chromatographic methods for determination of synthetic food dyes. Talanta 80:1045–1051
Lan H, Gan N, Pan D, Hu F, Li T, Long N, Qiao L (2014) An automated solid-phase microextraction method based on magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer as fiber coating for detection of trace estrogens in milk powder. J Chromatogr A 1331:10–18
Lee PL, Sun YC, Ling YC (2009) Magnetic nano-adsorbent integrated with lab-on-valve system for trace analysis of multiple heavy metals. J Anal At Spectrom 24:320–327
Minioti KS, Sakellariou CF, Thomaidis NS (2007) Determination of 13 synthetic food colorants in water-soluble foods by reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with diode-array detector. Anal Chim Acta 583:103–110
Morlock GE, Oellig C (2009) Rapid planar chromatographic analysis of 25 water-soluble dyes used as food additives. J AOAC Int 92:745–756
Ni Y, Gong X (1997) Simultaneous spectrophotometric determination of mixtures of food colorants. Anal Chim Acta 354:163–171
Ni Y, Bai J, Jin L (1997) Multicomponent chemometric determination of colorant mixtures by voltammetry. Anal Lett 30:1761–1777
Pandey S (2006) Analytical applications of room-temperature ionic liquids: a review of recent efforts. Anal Chim Acta 556:38–45
Poole CF, Poole SK (2010) Extraction of organic compounds with room temperature ionic liquids. J Chromatogr A 1217:2268–2286
Ruiz-Aceituno L, Sanz ML, Ramos L (2013) Use of ionic liquids in analytical sample preparation of organic compounds from food and environmental samples. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 43:121–145
Ryvolová M, Táborský P, Vrábel P, Krásenský P, Preisler J (2007) Sensitive determination of erythrosine and other red food colorants using capillary electrophoresis with laser-induced fluorescence detection. J Chromatogr A 1141:206–211
Šafařı́ková M, Šafařı́k I (1999) Magnetic solid-phase extraction. J Magn Magn Mater 194:108–112
Sayar S, Özdemir Y (1998) First-derivative spectrophotometric determination of ponceau 4R, sunset yellow and tartrazine in confectionery products. Food Chem 61:367–372
Tang S, Chia GH, Chang Y, Lee HK (2014) Automated dispersive solid-phase extraction using dissolvable Fe3O4-layered double hydroxide core–shell microspheres as sorbent. Anal Chem 86:11070–11076
Trujillo-Rodríguez MJ, Rocío-Bautista P, Pino V, Afonso AM (2013) Ionic liquids in dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 51:87–106
Vidal L, Riekkola ML, Canals A (2012) Ionic liquid-modified materials for solid-phase extraction and separation: a review. Anal Chim Acta 715:19–41
Vidotti EC, Costa WF, Oliveira CC (2006) Development of a green chromatographic method for determination of colorants in food samples. Talanta 68:516–521
Wang Y, Luo X, Tang J, Hu X, Xu Q, Yang C (2012a) Extraction and preconcentration of trace levels of cobalt using functionalized magnetic nanoparticles in a sequential injection lab-on-valve system with detection by electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry. Anal Chim Acta 713:92–96
Wang Y, Wang L, Tian T, Hu X, Yang C, Xu Q (2012b) Automated solid-phase extraction hyphenated to voltammetry for the determination of quercetin using magnetic nanoparticles and sequential injection lab-on-valve approach. Analyst 137:2400–2405
Wierucka M, Biziuk M (2014) Application of magnetic nanoparticles for magnetic solid-phase extraction in preparing biological, environmental and food samples. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 59:50–58
Wu H, Guo JB, Du LM, Tian H, Hao CX, Wang ZF, Wang JY (2013) A rapid shaking-based ionic liquid dispersive liquid phase microextraction for the simultaneous determination of six synthetic food colourants in soft drinks, sugar-and gelatin-based confectionery by high-performance liquid chromatography. Food Chem 141:182–186
Yoshioka N, Ichihashi K (2008) Determination of 40 synthetic food colors in drinks and candies by high-performance liquid chromatography using a short column with photodiode array detection. Talanta 74:1408–1413
Zhang Q, Yang F, Tang F, Zeng K, Wu K, Cai Q, Yao S (2010) Ionic liquid-coated Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles as an adsorbent of mixed hemimicelles solid-phase extraction for preconcentration of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in environmental samples. Analyst 135:2426–2433
Zheng X, He L, Duan Y, Jiang X, Xiang G, Zhao W, Zhang S (2014) Poly (ionic liquid) immobilized magnetic nanoparticles as new adsorbent for extraction and enrichment of organophosphorus pesticides from tea drinks. J Chromatogr A 1358:39–45
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Shanxi Province Natural Science Foundation for Youths (No. 2014021018-3). Helpful suggestions by anonymous referees are also gratefully acknowledged.
Conflict of interest
Hao Wu declares that he has no conflict of interest. Nannan Gao declares that she has no conflict of interest. Lizhen Zhang declares that she has no conflict of interest. Yunrong Li declares that she has no conflict of interest. Yating Shi declares that she has no conflict of interest. Liming Du declares that he has no conflict of interest. This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, H., Gao, N., Zhang, L. et al. Automated Magnetic Solid-Phase Extraction for Synthetic Food Colorant Determination. Food Anal. Methods 9, 614–623 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-015-0219-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-015-0219-2