Abstract
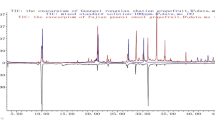
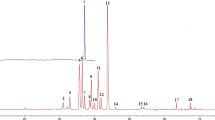
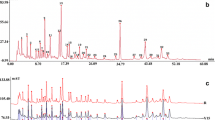
A newly validated HPLC fingerprint method has been developed for the identification and quality assessment of Exocarpium Citri Grandis. Twenty-three batches of Exocarpium Citri Grandis collected or purchased from different localities in China were investigated. The analyses were conducted on a Diamonsil C18 column (250 mm × 4.6 mm, 5-μm particle) preceded by a Diamonsil C18 guard column (10 mm × 4.6 mm, 5-μm particle). Mobile phases were composed of 0.5 % acetic acid (A) and methanol (B), with a flow rate of 1 mL/min under a gradient elution. The wavelength was set at 254 nm. The common fingerprint profile was established with professional analytical software. Common peaks were further identified using LC-DAD-MS/MS. Chemometric methods including similarity calculation and hierarchical clustering analysis were performed to differentiate the 23 batches of Exocarpium Citri Grandis samples. Fifteen batches of samples had a high similarity (more than 0.9) and the overall 23 batches of samples were divided into two clusters. This method presented good precision, repeatability, and stability; therefore, it would be a reliable and useful approach for the quality control of Exocarpium Citri Grandis.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen ZX, Lin L, Sun DM (2003) HPLC fingerprint of flavonoids in Exocarpium Citri Grandis. Chin Tradit Herbal Drug 7:657–661
Chen ZX, Lin L, Sun DM (2005) TLC fingerprints of coumarins in Exocarpium citri grandis. Cent South Pharm 1:9–11
Commission CP (2010) Chinese pharmacopoeia, 1st edition, vol 1. China Medical Science, Beijing, p 69
Goyeneche R, Roura S, Scala K (2014) Principal component and hierarchical cluster analysis to select hurdle technologies for minimal processed radishes. LWT–Food Sci Technol 57:522–529
Huang FL, Ma SM (2007) Analysis methods of main effective components in Exocarpium citri Grandis. Anhui Agric Sci Bull 13:26–28
Huang LZ, Liang ZH, Lin L, Gao DX, Ou JF (2005) Influence of different processing technique on the content of naringin in Exocarpium citri Grandis. Tradit Chin Drug Res Clinic Pharmacol 1:59–61
Liang YZ, Xie PS, Chan K (2004) Quality control of herbal medicines. J Chromatogr, B 812:53–70
Liu EH, Qi LW, Li K, Chu C, Li P (2010) Recent advances in quality control of traditional Chinese medicines. Comb Chem High T Scr 10:869–884.6
Mo XL, Cai YW, Zeng QQ (2007) Research advance on Citrus grandis ‘Tomentosa’. Food Drug 6:39–41
Rhourrhi-Frih B, West C, Pasquier L, André P, Chaimbault P, Lafosse M (2012) Classification of natural resins by liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry and gas chromatography–mass spectrometry using chemometric analysis. J Chromatogr A 1256:177–190
Xiao WQ, Zhang CH, Huang BX, Dai HF, Xie LS, Wang XR (2010) High performance liquid chromatography fingerprint of tomentose pummelo peel. Food Sci 22:318–321
Zhang JL, Cui M, He Y, Yu HL, Guo DA (2005) Chemical fingerprint and metabolic fingerprint analysis of Danshen injection by HPLC-UV and HPLC-MS methods. J Pharmaceut Biomed 36:1029–1035
Zhou X, Zhao Y, Lei PH, Cai ZW, Liu H (2010) Chromatographic fingerprint study on Evodia rutaecarpa (Juss.) Benth by HPLC/DAD/ESI-MSn technique. J Sep Sci 33:2258–2265
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Guangdong Province Special Major Science and Technology Project (no. 2011A080503001) and the Industry/University Research Cooperation Program from Science and Technology Department of Qingyuang City (no. 2012D021211001).
Conflict of Interest
Xiaoxue Yu has no conflict of interest. Qundi Liu has no conflict of interest. Zhisheng Xie has no conflict of interest. Shingchung Lam has no conflict of interest. Xinjun Xu has no conflict of interest. This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, X., Liu, Q., Xie, Z. et al. Chromatographic Fingerprint Analysis of Exocarpium Citri Grandis by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Coupled with Diode-Array Detector. Food Anal. Methods 8, 1868–1875 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-014-0071-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-014-0071-9