Abstract
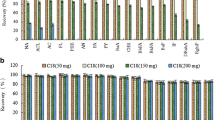
In this study, dispersive solid phase extraction (DSPE) combined with dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction (DLLME) method was developed for the determination of triazole fungicide residues in tea samples. DSPE with ODS C18, primary secondary amine, and florisil as sorbents was applied to clean up and minimize matrix interference from tea samples; it was followed with the enrichment of target compounds in the DLLME procedure and detection with liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS). The effects of various experimental parameters on the DSPE and DLLME procedures were studied systematically, such as the kinds and volume of sorbents, extraction and dispersive solvents, and extraction time. Under optimum conditions, the method was validated in a tea matrix. The matrix-matched calibration curves of three triazoles had good linearity in the range of 0.0125–50 μg kg−1, and the linear regression coefficients (r) ranged from 0.9998 to 0.9999. The limits of quantification (S/N = 10) for penconazole, tebuconazole, and triadimenfon were 4.0, 7.8, and 31.6 ng kg−1, respectively. The intra-day and inter-day relative standard deviations varied from 3.6 to 18.6 %. Recoveries in three concentration levels were between 91 and 118 %. The obtained results show that the proposed DSPE-DLLME-LC-MS method has the potential to analyze trace fungicides in a complex sample matrix.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DSPE:
-
Dispersive solid phase extraction
- DLLME:
-
Dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction
- LC-MS/MS:
-
Liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry
- RSD:
-
Relative standard deviation
- LOQs:
-
Limits of quantification
- MRLs:
-
Maximum residue limits
- LLE:
-
Liquid–liquid extraction
- SPE:
-
Solid phase extraction
- SPME:
-
Solid phase microextraction
- PSA:
-
Primary secondary amine
References
Aktas O, Ceçen F (2007) J Hazard Mater 141:769
Anastassiades M, Lehotay SJ, Stajnbaher D, Schenck FJ (2003) J AOAC Int 86:412
Bellido GG, Hatcher DW (2011) Food Chem 125:813
Cajka T (2012) Anal Chim Acta 743:51
Carabias-Martínez R, Rodríguez-Gonzalo E, Herrero-Hernández E, Hernández-Méndez J (2004) Anal Chim Acta 517(71)
Commission Regulation (EC) (2008a) Commission Regulation (EC) No. 149/2008 of 29 January 2008 amending Regulation (EC) No. 396/2005 of the European Parliament and of the Council by establishing Annexes II,III and IV setting maximum residue levels for products covered by Annex I. European Union, Brussels
Commission Regulation (EC) (2008b) Commission Regulation (EC) No. 839/2008 of 31 July 2008 amending Regulation (EC) No. 396/2005 of the European Parliament and of the Council as regards Annexes II, III and IV on maximum residue levels of pesticides in or on certain products. European Union, Brussels
Font N, Hernández F, Hogendoorn EA, Baumann RA, van Zoonen P (1998) J Chromatogr A 798:179
Gervais G, Brosillon S, Laplanche A, Helen C (2008) J Chromatogr A 1202:163
Gilbert-López B, García-Reyes JF, Lozano A, Fernández-Alba AR, Molina-Díaz A (2010) J Chromatogr A1217(A. Molina-Díaz):6022
Hamer M (2007) Nutr Res 27:373
Herrero M, Mendiola JA, Cifuentes A, Ibáñez E (2010) J Chromatogr A 1217:2495
Li Y, Chen X, Fan CL, Pang GF (2012) J Chromatogr A 1266:131
Lozano A, Rajski L, Belmonte-Valles N, Ucles A, Ucles S, Mezcua M, Fernandez-Alba AR (2012) J Chromatogr A 1268:109
Poole CF (2003) Trends Anal Chem 22:362
Poole CF, Gunatilleka AD, Sethuraman R (2000) J Chromatogr A 885:17
Rajski L, Lozano A, Belmonte-Valles N, Ucles A, Ucles S, Mezcua M, Fernandez-Alba AR (2013) Analyst 138:921
Rezaee M, Assadi Y, Hosseini MRM, Aghaee E, Ahmadi F, Berijani S (2006) J Chromatogr A 1116:1
Sanagi MM, See HH, Ibrahim WAW, Naim AA (2004) J Chromatogr A 1059:95
Sannino A (2004) J AOAC Int 87:991
Schermerhorn PG, Golden PE, Krynitsky AJ, Leimkuehler WM (2005) J AOAC Int 88:1491
Tang KJ, Chen SW, Gu XH, Wang HJ, Dai J, Tang J (2008) Anal Chim Acta 614:112
Taxvig C et al (2007) Toxicol Sci 100:464
Wu QH, Wang C, Liu ZM, Wu CX, Zeng X, Wen JL, Wang Z (2009) J Chromatogr A 1216:5504
Zhao PY, Wang L, Zhou L, Zhang FZ, Kang S, Pan CP (2012) J Chromatogr A 1225:17
Acknowledgments
The project was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 21175052), “Chen Guang” project of Wuhan (no. 201050231065), and Scientific and Technological Brainstorm Project of Wuhan (no. 201060623259).
Conflict of Interest
The authors indicate that they have no financial relationship with the organization that sponsored the research. Hui Xu declares that she has no conflict of interest. Yu Zhang declares that she has no conflict of interest. This article does not contain any studies with human and animal subjects.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Xu, H. Determination of Triazoles in Tea Samples Using Dispersive Solid Phase Extraction Combined with Dispersive Liquid–Liquid Microextraction Followed by Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Food Anal. Methods 7, 189–196 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-013-9617-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-013-9617-5