Abstract
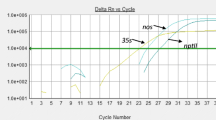
Two real-time PCR approaches for the detection of genetically modified (GM) rice were tested: (1) a combination of SYBR® Green real-time PCR methods detecting the 35S promoter (P-35S) of Cauliflower Mosaic Virus, the nopaline synthase terminator (T-nos) of Agrobacterium tumefaciens and the Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) CryIAb/Ac toxins and (2) a P-35S/T-nos duplex TaqMan® real-time PCR system. Both systems correctly recognized their respective targets in control samples of Bt63, Kefeng6 and KMD1 insect-resistant and LLRice62 and LLRice601 herbicide-resistant rice. Due to its lesser specificity but broader genetically modified organism (GMO) coverage capacity, the SYBR® Green real-time PCR approach was further tested in more detail. Melting curve, capillary and agarose gel electrophoresis analyses indicated that the P-35S, T-nos and CryIAb/Ac targets in the GM rice events are similar to the corresponding targets present in many known GMOs. High-resolution melting analysis showed that the CryIAb/Ac targets of the GM rice events Bt63 and Kefeng6 matched best the corresponding Bt11 CryIAb sequence. Digital PCR analysis on genomic DNA from the GM rice Bt63 and Kefeng6 events indicated that both GMO contained multiple inserts. Sensitivity tests showed that all SYBR® Green real-time PCR methods could detect their targets at less than an estimated five copies per reaction. Finally, it was shown that these SYBR® Green real-time PCR methods could detect low levels of their targets in rice consignments originating from China. Together, these results demonstrated that a ‘P-35S and T-nos and CryIAb/Ac’ combinatory SYBR® Green real-time PCR screening is highly suited to trace the respective targets including the possible presence of Bt63, Kefeng6 and KMD1 GM rice materials in food products.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arumugunathan K, Earle ED (1991) Mol Biol Rep 9:208–218
Babekova R, Funk T, Pecoraro S, Engel K-H, Busch U (2008) Eur Food Res Technol 228:707–716
Barbau-Piednoir E, Lievens A, Mbongolo-Mbella EG, Roosens N, Sneyers M, Leunda-Casi A, Van den Bulcke M (2010) Eur Food Res Technol 230:383–393
Barbau-Piednoir E, Lievens A, Vandermassen E, Mbongolo-Mbella EG, Leunda-Casi A, Roosens N, Sneyers M, Van den Bulcke M (2012) Eur Food Res Technol 234:13–23
Callwood S (2009) DEFRA Foodmatters - Literature review 1308
Chen M, Shelton A, Ye G (2011) Annu Rev Entomol 56:81–101
Gu S, Wu Y, Li S, Li L, Yang J (2009) J Sci Food Agric 89:1101–1106
ISO (2005) International Standard 21571, Foodstuffs—methods of analysis for the detection of genetically modified organisms and derived products—nucleic acid extraction. International Organization for Standardization, Geneva
James C (2010) ISAAA Brief No. 42. ISAAA, Ithaca
Lu C (2010) GM Crops 1:3, 113–115
Mbongolo-Mbella EG, Lievens A, Barbau-Piednoir E, Sneyers M, Leunda-Casi A, Roosens N, Van den Bulcke M (2011) Eur Food Res Technol 232:485–496
Reiting R, Grohmann L, Mäde D (2010) Journal für Verbraucherschutz und Lebensmittelsicherheit 5:185–188
Su C, Xie J, Wang X, Peng Y (2011) Eur Food Res Technol 232:351–359
Van den Bulcke M, Lievens A, Barbau-Piednoir E, Mbongolombella EG, Roosens N, Sneyers M, Leunda-Casi A (2010) Anal Bioanal Chem 396:2113–2123
Van den Eede G (2010) Compendium of reference methods for GMO analyses. http://publications.jrc.ec.europa.eu/repository/handle/111111111/15068. Accessed 1 June 2011
Waiblinger HU, Ernst B, Anderson A, Pietsch K (2008) Eur Food Res Technol 226:1221–1228
Waiblinger HU, Grohmann L, Mankertz J, Engelbert D, Pietsch K (2010) Anal Bioanal Chem 396(6):2165–2172
Yang L et al (2005) J Agric Food Chem 53:6222–6229
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank Alex Patak for his support with the bioinformatic analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kluga, L., Folloni, S., Kagkli, D.M. et al. Combinatory SYBR® Green Real-Time PCR Screening Approach for Tracing Materials Derived from Genetically Modified Rice. Food Anal. Methods 6, 361–369 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-012-9493-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-012-9493-4