Abstract
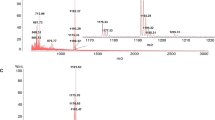
Cereulide is the heat-stable toxin produced by certain strains of Bacillus cereus. It is the main virulence factor of emetic B. cereus strains, which causes the emetic food poisoning syndrome, including rare fatal cases of food intoxications. Due to presumably low intoxication doses, a sensitive, specific, and robust technique is needed for its detection. In 2002, a LC–MS method was developed which allowed absolute quantification of cereulide using valinomycin as standard. This study describes the validation, according to the Commission Decision 2002/657/EC, of the LC–MS² method, a tandem mass spectrometry technique, which guarantees lower detection limit and higher specificity. The LC–MS² method, calibrated with valinomycin, was validated in rice and tested on various matrices (i.e., red beans, spices, and chili con carne) containing cereulide. The process combines a simple extraction step from the food matrix followed by LC–MS² analysis and detection by ion trap mass spectrometer. The detection limit for cereulide in rice was 0.5 ng eq/g, which is 20 to 2,500 times lower than currently understood intoxicative doses between 10 and 1.280 ng/g previously reported for cereulide. The validated method was specific, sensitive, repeatable, and reproducible with recoveries ranging from 77% to 101%.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agata N, Mori M, Ohta M, Suwan S, Ohtani I, Isobe M (1994) A novel dodecadepsipeptide, cereulide, isolated from Bacillus cereus causes vacuole formation in HEp-2 cells. FEMS Microbiol Lett 121:31–34
Agata N, Ohta M, Mori M, Isobe M (1995) A novel dodecadepsipeptide, cereulide, is an emetic toxin of Bacillus cereus. FEMS Microbiol Lett 129:17–19
Agata N, Ohta M, Yokoyama K (2002) Production of Bacillus cereus emetic toxin (cereulide) in various foods. Int J Food Microbiol 73:23–27
Altayar M, Sutherland AD (2006) Bacillus cereus is common in the environment but emetic toxin producing isolates are rare. J Appl Microbiol 100:7–14
Andersson MA, Mikkola R, Helin J, Andersson MC, Salkinoja-Salonen M (1998) A novel sensitive bioassay for detection of Bacillus cereus emetic toxin and related depsipeptide ionophores. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:1338–1343
Andersson MA, Shaheen R, Pirhonen T, Wijnands LM (2004) Sperm bioassay for rapid detection of cereulide-producing Bacillus cereus in food and related environments. Int J Food Microbiol 94:175–183
Andersson MA, Hakulinen P, Honkalampi-Hämäläinen U, Hoornstra D, Lhuguenot JC, Mäki-Paakkanen J, Savolainen M, Severin I, Stammati AL, Turco L, Weber A, von Wright A, Zucco F (2007) Toxicological profile of cereulide, the Bacillus cereus emetic toxin, in functional assays with human, animal and bacterial cells. Toxicon 49:351–367
Bauer T, Stark T, Hofmann T, Ehling-Schulz M (2010) Development of a stable isotope dilution analysis for the quantification of the Bacillus cereus toxin cereulide in foods. J Agr Food Chem 58:1420–1428
Beattie SH, Williams AG (1999) Bacillus detection of toxins. In: Richard KR (ed) Encyclopedia of food microbiology. Elsevier, Oxford, pp 141–149
Biesta-Peters EG, Reij MW, Blaauw RH, In ’t Veld PH, Rajkovic A, Ehling-Schulz M, Abee T, Rajkovic A, Ehling-Schulz M, Abee T (2010) Quantification of the emetic toxin cereulide in food products by liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry using synthetic cereulide as a standard. Appl Environ Microbiol 76:7466–7472
Ceuppens S, Rajkovic A, Heyndrickx M, Tsilia V, De Wiele TV, Boon N, Uyttendaele M (2011) Regulation of toxin production by Bacillus cereus and its food safety implications. Crit Rev Microbiol 37:188–213
Delbrassinne L, Andjelkovic M, Rajkovic A, Bottledoorn N, Mahillon J, Van Loco J (2011) Follow-up of the Bacillus cereus emetic toxin production in penne pasta under household conditions using liquid chromatography coupled with mass spectrometry. Food Microbiol 28:1105–1109
Dierick K, Van Collie E, Swiecicka I, Meyfroidt G, Devlieger H, Meulemans A, Hoedemaekers G, Fourie L, Heyndrickx M, Mahillon J (2005) Fatal family outbreak of Bacillus cereus-associated food poisoning. J Clin Microbiol 43:4277–4279
European Commission Decision 2002/657/EC (2002) Official Journal of the European Communities L221 8
European Commission Decision 333/2007/EC (2007) Official Journal of the European Communities L88/35
European Community Council Directive 93/88/EC (1993) Official Journal of the European Communities L268/71-82
Fretz R, Schmid D, Brueller W, Girsch L, Pichler AM, Riediger K, Safer M, Allerberger F (2007) Food poisoning due to Jimson weed mimicking Bacillus cereus food intoxication in Austria, 2006. Int J Infect Dis 11:557–558
Granum PE, Lund T (1997) Bacillus cereus and its food poisoning toxins. FEMS Microbiol Lett 157:223–228
Granum PE, Baird-Parker TC (2000) Bacillus spp. In: Lund B, Baird-Parker TC, Gould G (eds) Microbiological safety and quality of food. Aspen, Frederick, pp 1029–1039
Häggblom MM, Apetroaie C, Andersson MA, Salkinoja-Salonen MS (2002) Quantitative analysis of cereulide, the emetic toxin of Bacillus cereus, produced under various conditions. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:2479–2483
Hughes S, Bartholomew B, Hardy JC, Kramer JM (1988) Potential application of a HEp-2 cell assay in the investigation of Bacillus cereus emetic-syndrome food poisoning. FEMS Microbiol Lett 52:7–11
Horwitz W, Albert R (2006) The Horwitz ratio (HorRat): a useful index of method performance with respect to precision. J AOAC Int 89:1095–1109
In’t Veld PH, Fitz-James IA, Nuppunen M, Kankare M, Johansson T (2010) Quantification of cereulide from food poisoning outbreaks caused by Bacillus cereus, Proceedings of FoodMicro Symposium, poster nb PEB1.26
ISO 5725–2 (1994) Accuracy (trueness and precision) of measurement methods and results-basic method for the determination of repeatability and reproducibility of a standard measurement method
Isobe M, Ishikawa T, Suwan S, Agata N, Ohta M (1995) Synthesis and activity of cereulide, a cyclic dodecadepsipeptide ionophore as emetic toxin from Bacillus cereus. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 5:2855–2858
Jääskeläinen EL, Teplova V, Andersson MA, Andersson LC, Tammela P, Andersson MC, Pirhonen TI, Saris NEL, Vuorela P, Salkinoja-Salonen MS (2003a) In vitro assay for human toxicity of cereulide, the emetic mitochondrial toxin produced by food poisoning Bacillus cereus. Toxicol in Vitro 17:737–744
Jääskeläinen EL, Häggblom MM, Andersson MA, Vanne L, Salkinoja-Salonen MS (2003b) Potential of Bacillus cereus for producing an emetic toxin, cereulide, in bakery products: quantitative analysis by chemical and biological methods. J Food Protect 66:1047–1054
Jääskeläinen EL, Häggblom MM, Andersson MA, Salkinoja-Salonen MS (2004) Atmospheric oxygen and other conditions affecting the production of cereulide by Bacillus cereus in food. Int J Food Microbiol 96:75–83
Kawamura-Sato K, Hirama Y, Agata N, Ito H, Torii K, Takeno A, Hasegawa T, Shimomura Y, Ohta M (2005) Quantitative analysis of cereulide, an emetic toxin of Bacillus cereus, by using rat liver mitochondria. Microbiol Immunol 49:25–30
Magnus M (2008) Essential readings in infectious disease epidemiology. Jones & Bartlett Learning, Sudbury
Mahler H, Pasi A, Kramer JM, Schulte P, Scoging AC, Bar W, Krahenbuhl S (1997) Fulminant liver failure in association with the emetic toxin of Bacillus cereus. New England J Med 336:1142–1148
Mandel J (1964) The statistical analysis of experimental data. Wiley, New York
Mead PS, Slutsker L, Dietz V, Mccaig LF, Bresee JS, Shapiro C, Griffin PM, Tauxe RV (1999) Food-related illness and death in the United States. Emerg Infect Dis 5:607–625
Melling J, Capel BJ (1978) Characteristics of Bacillus cereus emetic toxin. FEMS Microbiol Lett 4:133–135
Nelms PK, Larson O, Barnes-Josiah D (1997) Time to B. cereus about hot chocolate. Public Health Rep 112:240–244
Nissen H, Rosnes JT, Brendehaug J, Kleiberg GH (2002) Safety evaluation of sous vide-processed ready meals. Lett Appl Microbiol 35:433–438
Paananen A, Mikkola R, Sareneva T, Matikainen S, Hess M, Andersson MA, Julkunen I, Salkinoja-Salonen MS, Timonen T (2002) Inhibition of human natural killer cell activity by cereulide, an emetic toxin from Bacillus cereus. Clin Exp Immunol 129:420–428
Pirhonen TI, Andersson MA, Jääskeläinen EL, Salkinoja-Salonen MS, Honkanen-Buzalski T, Johansson TM (2005) Biochemical and toxic diversity of Bacillus cereus in a pasta and meat dish associated with a food-poisoning case. Food Microbiol 22:87–91
Rajkovic A, Uyttendaele M, Deley W, Van Soom A, Rijsselaere T, Debevere J (2006) Dynamics of boar semen motility inhibition as a semi-quantitative measurement of Bacillus cereus emetic toxin (cereulide). J Microbiol Meth 65:525–534
Rajkovic A, Uyttendaele M, Debevere J (2007) Computer aided boar semen motility analysis for cereulide detection in different food matrices. Int J Food Microbiol 114:92–99
Rajkovic A, Uyttendaele M, Vermeulen A, Andjelkovic M, Fitz-James I, In’t Veld P, Denon Q, Verhe R, Debevere J (2008) Heat resistance of Bacillus cereus emetic toxin, cereulide. Lett Appl Microbiol 46:536–541
Schoeni JL, Wong AC (2005) Bacillus cereus food poisoning and its toxins. J Food Protect 68:636–648
Shaheen R, Andersson MA, Apetroaie C, Schulz A, Ehling-Schulz M, Ollilainen VM (2006) Potential of selected infant food formulas for production of Bacillus cereus emetic toxin, cereulide. Int J Food Microbiol 107:287–294
Shinagawa K, Konuma H, Sekita H, Sugii S (1995) Emesis of rhesus monkeys induced by intragastric administration with the HEp-2 vacuolation factor (cereulide) produced by Bacillus cereus. FEMS Microbiol Lett 130:87–90
Shiota M, Saitou K, Mizumoto H, Matsusaka M, Agata N, Nakayama M, Kage M, Tatsumi S, Okamoto A, Yamaguchi S, Ohta M, Hata D (2010) Rapid detoxification of cereulide in Bacillus cereus food poisoning. Pediatrics 125:951–955
Turnbull PC (1981) Bacillus cereus toxins. Pharmacol and Therapeut 13:453–505
Willoughby R, Sheehan E, Mitrovich S (1998) A global view of LC–MS: how to solve your most challenging analytical problems. In: Global View Publishing First (ed). Chem-Space Associates Inc., Pittsburgh
Acknowledgments
Financial support by the Federal Public Service of the Belgian Science Policy is gratefully acknowledged. The authors would like to thank Jacques Lhermitte for able technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Delbrassinne, L., Andjelkovic, M., Rajkovic, A. et al. Determination of Bacillus cereus Emetic Toxin in Food Products by Means of LC–MS². Food Anal. Methods 5, 969–979 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-011-9340-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-011-9340-z