Abstract
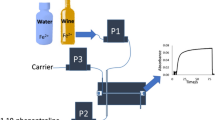
A new and expeditious automated procedure for the determination of ethanol content in alcoholic beverages (distilled liquors and wine) by using a single interface flow analysis (SIFA) system with spectrophotometric detection is presented. The developed approach was simply based on refractive index gradient measurements, known as Schlieren effect, produced when acidified beverages samples were introduced in a single-line SIFA system that used deionized water as carrier (trailing) stream and a computer-controlled spectrophotometer as detector. In the implemented SIFA system, no chromogenic reagent is used, being the refractive index gradient a consequence of the mutual interdispersion of sample and carrier zones at the formed single interface, and no predefined volumes of both sample and carrier are required, which greatly simplifies system operation and optimization. The proposed methodology allowed the determination of ethanol concentrations between 4% and 24% (v/v) with good precision (RSD < 5.2%, n = 3) and a sampling frequency of about 58 h−1 with consumption of 400 μl of sulfuric acid 0.5 mol l−1 and 400 μl of sample per measurement. The developed procedure was applied to whisky, gin, rum, vodka, the sugar cane-based beverage “cachaça,” and white wine, and the obtained results were in a good agreement with those provided by the reference method (RD < 5.0%). Recovery values acquired in the analysis of spiked ethanol samples (between 90.0% and 111.0% of the added amount) were also satisfactory.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander PW, Di Benedetto LT, Hibbert DB (1998) Field Anal Chem Technol 2:135
Betteridge D, Bacan S, Beetlestone D, Sweet P (1978) Analyst 103:897
Caputi AJ, Mooney DP (1983) J Assoc Off Anal Chem 66:1152
Cañizares P, Luque de Castro MD (1995) Analyst 120:2837
Costa RS, Santos SRB, Almeida LF, Nascimento ECL, Pontes MJC, Lima RAC, Simões SS, Araújo MCU (2004) Microchem J 78:27
Dias ACB, Borges EP, Zagatto EAG, Worsfold PJ (2006) Talanta 68:1076
Fletcher PJ, Staden JF (2003) Anal Chim Acta 499:123
Gallignami M, Carlos A, Brunetto MR, Burguera JL, Burguera M (2005) Talanta 68:470
González-Rodríguez J, Pérez-Juan P, Luque de Castro MD (2003) Talanta 59
Hanning A, Roeraade J (1997) Anal Chem 69:1496
Iwachido T, Ishimaruk K, Toei K (1986) Anal Sci 2:495
Kiranas ER, Karayannis MI, Tzouwara-Karayanni SM (1997) Anal Lett 30:537
Krugg FJ, Zagatto EAG, Reis BF (1983) Anal Chim Acta 145:179
Kokovkin VV, Smolyakov BS (1995) J Anal Chem 50:569
Lázaro F, Luque de Castro MD, Válcarcel M (1987) Anal Chem 59:1859
Leach RA, Ruzicka J, Harris JM (1983) Anal Chem 55:1669
Martin E, Iadaresta V, Giacometti JC, Vogel J (1986) Mitt Geb Lebensmittelunters Hyg 77:528
Mason M (1983) Am J Enol Vitic 34:173
Mattos IL, Fernandez-Romero JM, Luque de Castro MD, Valcárcel M (1995) Analyst 120:179
Naviglio D, Romano R, Attanasiv G (2001) Italian Food Bever Technol 24:19
Norma Portuguesa (1987) Bebidas Alcoólicas e Espirituosas, Determinação do teor alcoólico em volume (grau alcoólico volumétrico), NP-2143
Office International de la Vigne et du Vin (OIV) (2005) Recueil des methodes internationales d’analyse des vins et des mouts, Titre alcoome’ trique volumique, OIV, Paris, France , MA-F-AS312-01-TALVOL
Ribeiro MFT, Santos JLM, Lima JLFC, Dias ACB, Zagatto EAG (2005) Talanta 68:351
Santos SRB, Araújo MCU, Barbosa RA (2002) Analyst 127:324
Santos JR, Santos JLM, Lima JLFC (2010) Talanta 80:1326
Segundo MA, Rangel AOSS (2002) Anal Chim Acta 458:131
Silvestre CIC, Santos JLM, Lima JLFC, Zagatto EAG (2008) Talanta 77:518
Silvestre CIC, Santos JLM, Lima JLFC, Zagatto EAG (2009) Talanta 79:1117
Silvestre CIC, Santos JLM, Lima JLFC, Zagatto EAG (2010) Talanta 81:1847
Skoog DA, Holler FJ, Nieman TA (1998) Principles of instrumental analysis, 5th edn. Harcourt Brace, Philadelphia
Van den Berg FWJ, Van Osenbruggen WA, Smilde AK (1997) Proc Contr Qual (1997) 9:51
Yamane T, Saito M (1992) Talanta 39:215
Zagatto EAG, Arruda MAZ, Jacintho AO (1990) Anal Chim Acta 234:153
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Fundação para a Ciência e Tecnologia for the financial support under the project PTDC/QUI-QUI/105514/2008.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
L.R.G. Abreu, V., Santos, J.L.M. & Lima, J.L.F.C. An Automated Single Interface Flow System for the Spectrophotometric Determination of Ethanol in Beverages Based on Schlieren Effect. Food Anal. Methods 5, 867–873 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-011-9322-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-011-9322-1