Abstract
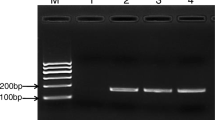
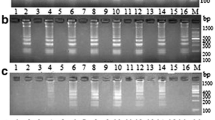
A polymerase chain reaction (PCR) method based on the RNA polymerase alpha subunit (rpoA) gene was developed for the detection of the Vibrio genus. The specific primers were designed aligning the rpoA gene sequences available in GenBank of all Vibrio species. The specificity of the primers was tested against 35 Vibrio species. In addition, 12 species phylogenetically related to the Vibrio genus were used as negative control. Moreover, in order to eliminate any false-negative results, bacterium-specific primers targeting the 16S rRNA gene were introduced in the test as a noncompetitive internal amplification control. The rpoA primers correctly amplified all the Vibrio species considered. No cross-reaction was observed when tested against closely related species. To estimate the applicability of this method, 336 Vibrio wild-type strains isolated from Italian aquaculture products and from imported seafoods were tested. The sensitivity, tested using serial dilutions of different pure cultures of certified strains, resulted to 103 colony-forming units per milliliter. The assay proved to be specific, rapid, and reliable. It can be proposed as a routine screening technique for the confirmation of Vibrio genus in isolated colonies.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbott SL, Seli LS, Catino M Jr, Hartley MA, Janda JM (1998) Misidentification of unusual Aeromonas species as members of the genus Vibrio: a continuing problem. J Clin Microbiol 36:1103–1104
Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ (1990) Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 215:403–410
Bej AK, Patterson DP, Brasher CW, Vickery MC, Jones DD, Kaysner CA (1999) Detection of total and hemolysin-producing Vibrio parahaemolyticus in shellfish using multiplex PCR amplification of tl, tdh and trh. J Microbiol Methods 36:215–225. doi:10.1016/S0167-7012(99)00037-8
Blackstone GM, Nordstrom JL, Bowen MD, Meyer RF, Imbro P, DePaola A (2007) Use of a real time PCR assay for detection of the ctxA gene of Vibrio cholerae in an environmental survey of Mobile Bay. J Microbiol Methods 68:254–259. doi:10.1016/j.mimet.2006.08.006
Blackstone GM, Nordstrom JL, Vickery MC, Bowen MD, Meyer RF, DePaola A (2003) Detection of pathogenic Vibrio parahaemolyticus in oyster enrichments by real time PCR. J Microbiol Methods 53:149–155. doi:10.1016/S0167-7012(03)00020-4
Brauns LA, Hudson MC, Oliver JD (1991) Use of the polymerase chain reaction in detection of culturable and nonculturable Vibrio vulnificus cells. Appl Environ Microbiol 57:2651–2655
Cavallo RA, Acquaviva MI, Stabili L (2009) Culturable heterotrophic bacteria in seawater and Mytilus galloprovincialis from a Mediterranean area (Northern Ionian Sea–Italy). Environ Monit Assess 149:465–475. doi:10.1007/s10661-008-0223-8
Chakraborty R, Sinha S, Mukhopadhyay AK, Asakura M, Yamasaki S, Bhattacharya SK, Nair GB, Ramamurthy T (2006) Species-specific identification of Vibrio fluvialis by PCR targeted to the conserved transcriptional activation and variable membrane tether regions of the toxR gene. J Med Microbiol 55:805–808. doi:10.1099/jmm.0.46395-0
Crosa JH, Actis LA, Tolmasky ME (2006) The biology and pathogenicity of Vibrio anguillarum and V. ordalii. In: Thompson FL, Austin B, Swings JG (eds) The biology of vibrios. ASM, Washington, DC, pp 253–266
Dewettinck T, Hulsbosch W, Van Hege K, Top EM, Verstraete W (2001) Molecular fingerprinting of bacterial populations in groundwater and bottled mineral water. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 57:412–418. doi:10.1007/s002530100797
Di Pinto A, Ciccarese G, Tantillo G, Catalano D, Forte VT (2005) A collagenase-targeted multiplex PCR assay for identification of Vibrio alginolyticus, Vibrio cholerae and Vibrio parahaemolyticus. J Food Prot 68:150–153
Fedio W, Blackstone GM, Kikuta-Oshima L, Wendakoon C, McGrath TH, DePaola A (2007) Rapid detection of the Vibrio cholerae ctx gene in food enrichments using real-time polymerase chain reaction. J AOAC Int 90:1278–1283
Ferrini AM, Mannoni V, Suffredini E, Cozzi L, Croci L (2008) Evaluation of antibacterial resistance in Vibrio strains isolated from imported seafood and Italian aquaculture settings. Food Anal Methods 1:164–170. doi:10.1007/s12161-007-9011-2
Ghittino C, Latini M, Agnetti F, Panzieri C, Lauro L, Ciappelloni R, Petracca G (2003) Emerging pathologies in aquaculture: effects on production and food safety. Vet Res Commun 27:471–479. doi:10.1023/B:VERC.0000014204.37722.b6
Higgins DG, Bleasby AJ, Fuchs R (1992) CLUSTAL V: improved software for multiple sequence alignment. Comput Appl Biosci 8:189–191
Hong GE, Kim DG, Bae JY, Ahn SH, Bai SC, Kong IS (2007) Species-specific PCR detection of the fish pathogen, Vibrio anguillarum, using the amiB gene, which encodes N-acetylmuramoyl-l-alanine amidase. FEMS Microbiol Lett 269:201–206. doi:10.1111/j.1574-6968.2006.00618.x
Hoorfar J, Malorny B, Abdulmawjood A, Cook N, Wagner M, Fach P (2004) Practical considerations in design of internal amplification controls for diagnostic PCR assays. J Clin Microbiol 42:1863–1868. doi:10.1128/JCM.42.5.1863-1868.2004
Kim YB, Okuda J, Matsumoto C, Takahashi N, Hashimoto S, Nishibuchi M (1999) Identification of Vibrio parahaemolyticus strains at the species level by PCR targeted to the toxR gene. J Clin Microbiol 37:1173–1177
Kumar HS, Parvathi A, Karunasagar I (2006) A gyrB-based PCR for the detection of Vibrio vulnificus and its application for direct detection of this pathogen in oyster enrichment broths. Int J Food Microbiol 111:216–220. doi:10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2006.05.007
Kwok AY, Wilson JT, Coulthart M, Ng LK, Mutharia L, Chow AW (2002) Phylogenetic study and identification of human pathogenic Vibrio species based on partial hsp60 gene sequences. Can J Microbiol 48:903–910. doi:10.1139/w02-089
Lee CY, Panicker G, Bej AK (2003) Detection of pathogenic bacteria in shellfish using multiplex PCR followed by CovaLink NH microwell plate sandwich hybridization. J Microbiol Methods 53:199–209. doi:10.1016/S0167-7012(03)00032-0
Nandi B, Nandy RK, Mukhopadhyay S, Nair GB, Shimada T, Ghose AC (2000) Rapid method for species-specific identification of Vibrio cholerae using primers targeted to the gene of outer membrane protein OmpW. J Clin Microbiol 38:4145–4151
Nhung PH, Ohkusu K, Miyasaka J, Sun XS, Ezaki T (2007) Rapid and specific identification of 5 human pathogenic Vibrio species by multiplex polymerase chain reaction targeted to dnaJ gene. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 59:271–275. doi:10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2007.05.016
Noguerola I, Blanch AR (2008) Identification of Vibrio spp. with a set of dichotomous keys. J Appl Microbiol 105:175–185. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2672.2008.03730.x
Panicker G, Call DR, Krug MJ, Bej AK (2004) Detection of pathogenic Vibrio spp. in shellfish by using multiplex PCR and DNA microarrays. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:7436–7444. doi:10.1128/AEM.70.12.7436-7444.2004
Rip D, Gouws PA (2009) Development of an internal amplification control using multiplex PCR for the detection of Listeria monocytogenes in food products. Food Anal Methods . doi:10.1007/s12161-009-9081-4
Singh DV, Isac SR, Colwell RR (2002) Development of a hexaplex PCR assay for rapid detection of virulence and regulatory genes in Vibrio cholerae and Vibrio mimicus. J Clin Microbiol 40:4321–4324. doi:10.1128/JCM.40.11.4321-4324.2002
Tarr CL, Patel JS, Puhr ND, Sowers EG, Bopp CA, Strockbine NA (2007) Identification of Vibrio isolates by a multiplex PCR assay and rpoB sequence determination. J Clin Microbiol 45:134–140. doi:10.1128/JCM.01544-06
Thompson FL, Gevers D, Thompson CC, Dawyndt P, Naser S, Hoste B, Munn CB, Swings J (2005) Phylogeny and molecular identification of vibrios on the basis of multilocus sequence analysis. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:5107–5115. doi:10.1128/AEM.71.9.5107-5115.2005
Thompson FL, Iida T, Swings JG (2004) Biodiversity of vibrios. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 68:403–431. doi:10.1128/MMBR.68.3.403-431.2004
Urakawa H, Kita-Tsukamoto K, Ohwada K (1998) A new approach to separate the genus Photobacterium from Vibrio with RFLP patterns by HhaI digestion of PCR-amplified 16S rDNA. Curr Microbiol 36:171–174. doi:10.1007/PL00006762
Acknowledgements
The research has been supported by a grant of the Italian Ministry of University and Research (MIUR-PRIN 2004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dalmasso, A., La Neve, F., Suffredini, E. et al. Development of a PCR Assay Targeting the rpoA Gene for the Screening of Vibrio Genus. Food Anal. Methods 2, 317–324 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-009-9089-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-009-9089-9