Abstract
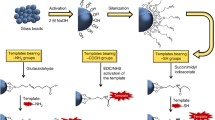
The method of hierarchical imprinting was used for the first time in order to synthesize polymers with a high affinity for nisin. The concept of this approach is demonstrated by filling the pores of silica particles, which contain immobilized peptidic templates, with a mixture of monomers/initiator, followed by polymerization and subsequent dissolution of the silica template. This method leaves imprinted polymers with binding sites located at the surface that are capable of recognizing larger molecules with the same immobilized epitope. The results of the high-performance liquid chromatography analyses illustrate that the highest retention factors and imprinting factors of nisin on nisin C-terminal analogously imprinted polymers could be obtained with acetonitrile/water mixtures containing more than 80% water. Furthermore, nisin was strongly retained on polymers that were imprinted with a longer amino acid sequence because of better sterical accessibility of the binding sites for the C terminus of nisin. The retention of nisin (k = 21.65) under aqueous elution conditions results from selective ionic interactions and hydrophobic interactions. Furthermore, the polymers exhibited selectivity for the template Lys-Ala and the structurally related dipeptide Ala-Lys. The results of the present work show that these hierarchically imprinted polymers could be used for the chromatographic separation of the polypeptide nisin in aqueous solutions.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aranha S, Gupta, Reddy KVR (2004) Contracept 69:333. doi:10.1016/j.contraception.2003.11.002
Berger T, Bütikofer U, Muralt L, Rieder K, Rhyn P, Züst C (2005) Mitt Lebensm Hyg 96:336
Bouksamin M, Fliss I, Meghrous J, Simard R, Lacroix C (1998) J Appl Microbiol 84:176. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2672.1998.00315.x
Cormack PAG, Elorza AZ (2004) J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci 804:173. doi:10.1016/j.jchromb.2004.02.013
Falahee MB, Adams MR, Dale JW, Morris BA (1990) Int J Food Sci Technol 25:590
Hakovirta J, Reunanen J, Saris PEJ (2006) Appl Environ Microbiol 72:1001. doi:10.1128/AEM.72.2.1001-1005.2006
Hansen JN (1997) In: Strohl WR (ed) Biotechnology of antibiotics. Marcell Dekker, New York, p 437
Hurst A (1981) Appl Microbiol 27:85. doi:10.1016/S0065-2164(08)70342-3
Leung PP, Khadre M, Shellhammer TH, Yousef AE (2002) Lett Appl Microbiol 34:199. doi:10.1046/j.1472-765x.2002.01072.x
Nandakumar R, Nandakumar MP, Mattiasson B (2000) Biosens Bioelectron 15:241. doi:10.1016/S0956-5663(00)00083-X
Pfeiffer P, Orben C (1997) Dtsch Lebensm–Rundsch 93:47
Rachkov A, Minoura N (2000) J Chromatogr A 889:111. doi:10.1016/S0021-9673(00)00568-9
Rachkov A, Minoura N (2001) Biochim Biophys Acta 1544:255
Rachkov A, Hu M, Bulgarvich E, Matsumoto T, Minoura N (2004) Anal Chim Acta 504:191. doi:10.1016/S0003-2670(03)00764-5
Reunanen J, Saris PEJ (2003) Appl Environ Microbiol 69:4214. doi:10.1128/AEM.69.7.4214-4218.2003
Rossano R, Del Fiore A, D’Elia A, Pesole G, Parente E, Riccio P (1998) Biotechnol Tech 12:783. doi:10.1023/A:1008820803070
Schirmer C, Meisel H (2006) J Chromatogr A 1132:325. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2006.09.032
Sellergren J (2001) Chromatogr A 906:227. doi:10.1016/S0021-9673(00)00929-8
Suárez AM, Azcona JI, Rodríguez JM, Sanz B, Hernández PE (1997) Appl Environ Microbiol 63:4990
Titirici MM, Sellergren B (2004) Anal Bioanal Chem 378:1913. doi:10.1007/s00216-003-2445-5
Titirici MM, Hall AJ, Sellergren B (2002) Chem Mater 14:21. doi:10.1021/cm011207 +
Titirici MM, Hall AJ, Sellergren B (2003) Chem Mater 15:822. doi:10.1021/cm025770j
Tramer J, Fowlers JI (1964) J Sci Food Agric 15:522. doi:10.1002/jsfa.2740150802
Turner SR, Love RM, Lyons KM (2004) Int Endod J 37:664. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2591.2004.00846.x
Wolf CE, Gibbons WR (1996) J Appl Bacteriol 80:453
Ye L, Mosbach K (2001) J Incl Phenom Macrocycl Chem 41:107. doi:10.1023/A:1014498404292
Yilmaz E, Haupt K, Mosbach K (2000) Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 39:2115. doi:10.1002/1521-3773(20000616)39:12<2115::AID-ANIE2115>3.0.CO;2-V
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Horst Neve, Max Rubner-Institute, Federal Research Institute of Nutrition and Food, Department of Microbiology and Biotechnology, for recording the SEM micrographs.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schirmer, C., Meisel, H. Synthesis and Evaluation of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers (MIP) with Affinity for the Polypeptide Nisin. Food Anal. Methods 2, 257–263 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-008-9061-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-008-9061-0