Abstract
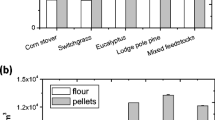
Lignocellulosic biorefineries have tonnage and throughput requirements that must be met year round, and there is no single feedstock available in any given region that is capable of meeting the price and availability demands of the biorefineries. Ionic liquid (IL) pretreatment with certain ILs is receiving significant attentions as a potential process that enables fractionation of a wide range of feedstocks and produces high yields of fermentable sugars suitable for biofuel production. Building on the large-scale demonstration of a single herbaceous feedstock (switchgrass), this work extends scale-up of IL pretreatment to woody (eucalyptus) and mixed feedstock (mixtures of two) by 30-fold, relative to the bench scale (6 vs 0.2 L) at 10 % solid loading. The mixed feedstock recovered similar yields of glucan (99.7 %), xylan (62.8 %), and lignin (59.9 %) as switchgrass and eucalyptus at 6-L scale operation, and results of all three feedstocks are better than those obtained from small-scale studies. By integrating the process of IL pretreatment with efficient and scalable homogenization, washing, and product recovery system, IL contents in the recovered materials were decreased to 0.2 %, mitigating the risk to downstream enzymatic saccharification and microbial fermentation. Results indicate that mixed feedstock are viable and valuable resource to consider when assessing biomass availability and affordability for lignocellulosic biorefineries. This scale-up evaluation demonstrates that IL pretreatment technology is feedstock agnostic and can be effectively scaled to larger operations.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Johnson JM, Coleman MD, Gresch R, Jaradat A, Mitchell R, Reicosky D, Wilhelm WW (2007) Biomass-bioenergy crops in the United States: a changing paradigm. Am J Plant Sci Biotechnol 1(1):1–28
Eranki PL, Dale BE (2011) Comparative life cycle assessment of centralized and distributed biomass processing systems combined with mixed feedstock landscapes. GCB Bioenergy 3(6):427–438
Corton J, Buhle L, Wachendorf M, Donnison IS, Fraser MD (2013) Bioenergy as a biodiversity management tool and the potential of a mixed species feedstock for bioenergy production in Wales. Bioresour Technol 129:142–149
Banerjee G, Car S, Liu TJ, Williams DL, Meza SL, Walton JD, Hodge DB (2012) Scale-up and integration of alkaline hydrogen peroxide pretreatment, enzymatic hydrolysis, and ethanolic fermentation. Biotechnol Bioeng 109(4):922–931
Singh S, Arora R, Li C, Mathews IP, Simmons BA (2013) Mixed feedstocks processing using an ionic liquid. US 20130183739 A1
George A, Brandt A, Zahari S, Klein-Marcuschamer D, Parthasarathi R, Sun N, Sathitsuksanoh N, Shi J, Stavila V, Tran K, Singh S, Holmes BM, Welton T, Simmons B, Hallett J (2014) Design of low-cost ionic liquids for biomass pretreatment. Green Chem. doi:10.1039/C4GC01208A
Wyman CE, Dale BE, Elander RT, Holtzapple M, Ladisch MR, Lee YY, Mitchinson C, Saddler JN (2009) Comparative sugar recovery and fermentation data following pretreatment of poplar wood by leading technologies. Biotechnol Prog 25(2):333–339
Wyman C, Dale B, Elander R, Holtzapple M, Ladisch M, Lee Y (2005) Comparative sugar recovery data from laboratory scale application of leading pretreatment technologies to corn stover. Bioresour Technol 96:2026–2032
Li C, Sun L, Simmons BA, Singh S (2012) Comparing the recalcitrance of eucalyptus, pine, and switchgrass using ionic liquid and dilute acid pretreatments. Bioenerg Res 6(1):14–23
Shi J, Thompson VS, Yancey NA, Stavila V, Simmons BA, Singh S (2013) Impact of mixed feedstocks and feedstock densification on ionic liquid pretreatment efficiency. Biofuels 4(1):63–72
Li C, Tanjore D, He W, Wong J, Gardner JL, Sale KL, Simmons BA, Singh S (2013) Scale-up and evaluation of high solid ionic liquid pretreatment and enzymatic hydrolysis of switchgrass. Biotechnol Biofuels 6(1):154
Ouellet M, Datta S, Dibble DC, Tamrakar PR, Benke PI, Li C, Singh S, Sale KL, Adams PD, Keasling JD, Simmons BA, Holmes BM, Mukhopadhyay A (2011) Impact of ionic liquid pretreated plant biomass on Saccharomyces cerevisiae growth and biofuel production. Green Chem 13(10):2743–2749
Dibble D, Li C, Sun L, George A, Cheng A, Cetinkol O, Benke P, Holmes B, Singh S, Simmons B (2011) A facile method for the recovery of ionic liquid and lignin from biomass pretreatment. Green Chem 13:3255–3264
Datta S, Holmes B, Park JI, Chen ZW, Dibble DC, Hadi M, Blanch HW, Simmons BA, Sapra R (2010) Ionic liquid tolerant hyperthermophilic cellulases for biomass pretreatment and hydrolysis. Green Chem 12(2):338–345
Shi J, Gladden JM, Sathitsuksanoh N, Kambam P, Sandoval L, Mitra D, Zhang S, George A, Singer SW, Simmons BA, Singh S (2013) One-pot ionic liquid pretreatment and saccharification of switchgrass. Green Chem 15(9):2579–2589
Li C, Cheng G, Balan V, Kent MS, Ong M, Chundawat SPS, Ld S, Melnichenko YB, Dale BE, Simmons BA, Singh S (2011) Influence of physico-chemical changes on enzymatic digestibility of ionic liquid and AFEX pretreated corn stover. Bioresour Technol 102(13):6928–6936
Li C, Knierim B, Manisseri C, Arora R, Scheller HV, Auer M, Vogel KP, Simmons BA, Singh S (2010) Comparison of dilute acid and ionic liquid pretreatment of switchgrass: Biomass recalcitrance, delignification and enzymatic saccharification. Bioresour Technol 101(13):4900–4906
Lee SH, Doherty TV, Linhardt RJ, Dordick JS (2009) Ionic liquid-mediated selective extraction of lignin from wood leading to enhanced enzymatic cellulose hydrolysis. Biotechnol Bioeng 102(5):1368–1376
Sun N, Rahman M, Qin Y, Maxim ML, Rodriguez H, Rogers RD (2009) Complete dissolution and partial delignification of wood in the ionic liquid 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium acetate. Green Chem 11(5):646–655
Tan SSY, MacFarlane DR, Upfal J, Edye LA, Doherty WOS, Patti AF, Pringle JM, Scott JL (2009) Extraction of lignin from lignocellulose at atmospheric pressure using alkylbenzenesulfonate ionic liquid. Green Chem 11(3):339–345
Wu H, Mora-Pale M, Miao J, Doherty TV, Linhardt RJ, Dordick JS (2011) Facile pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass at high loadings in room temperature ionic liquids. Biotechnol Bioeng 108(12):2865–2875
Sluiter A, Hames B, Ruiz R, Scarlata C, Sluiter J, Templeton D (2004) Determination of structural carbohydrates and lignin in biomass.LAP-002 NREL Analytical Procedure. National Renewable Energy Laboratory, Golden, CO
Sluiter A, Hames B, Ruiz R, Scarlata C, Sluiter J, Templeton D (2004) Determination of ash in biomass. LAP-005 NREL Analytical Procedure. National Renewable Energy Laboratory, Golden, CO
Sathitsuksanoh N, Zhu ZG, Wi S, Zhang YHP (2011) Cellulose solvent-based biomass pretreatment breaks highly ordered hydrogen bonds in cellulose fibers of switchgrass. Biotechnol Bioeng 108(3):521–529
Modenbach AA, Nokes SE (2012) The use of high-solids loadings in biomass pretreatment—a review. Biotechnol Bioeng 109(6):1430–1442
Tanjore D, Wong J, Li C, Gardner JL, Baez J (2013) Inline rheometry to identify mass transfer issues in enzymatic hydrolysis of biomass at high solids concentration. In: 2013 AICHE Annual Meeting San Francisco, California, USA
Arora R, Manisseri C, Li C, Ong M, Scheller HV, Vogel K, Simmons BA, Singh S (2010) Monitoring and analyzing process streams towards understanding ionic liquid pretreatment of switchgrass (Panicum virgatum L.). BioEnergy Research 3:134–145
Cruz A, Scullin C, Mu C, Cheng G, Stavila V, Varanasi P, Xu D, Mentel J, Chuang Y-D, Simmons B, Singh S (2013) Impact of high biomass loading on ionic liquid pretreatment. Biotechnology for Biofuels 6(1):52
Sun N, Liu H, Sathitsuksanoh N, Stavila V, Sawant M, Bonito A, Tran K, George A, Sale K, Singh S, Simmons B, Holmes B (2013) Production and extraction of sugars from switchgrass hydrolyzed in ionic liquids. Biotechnol Biofuels 6(1):39
Varanasi P, Singh P, Auer M, Adams P, Simmons B, Singh S (2013) Survey of renewable chemicals produced from lignocellulosic biomass during ionic liquid pretreatment. Biotechnology for Biofuels 6(1):14
Gutowski K, Grant A, Willauer H, Huddleston J, Swatloski R, Holbrey J, Rogers R (2003) Controlling the aqueous miscibility of ionic liquids: aqueous biphasic systems of water-miscible ionic liquids and water-structuring salts for recycle, metathesis, and separations. J Am Chem Soc 125:6632–6633
Shill K, Padmanabhan S, Xin Q, Prausnitz JM, Clark DS, Blanch HW (2011) Ionic liquid pretreatment of cellulosic biomass: enzymatic hydrolysis and ionic liquid recycle. Biotechnol Bioeng 108(3):511–520
Brennan TCR, Datta S, Blanch HW, Simmons BA, Holmes BM (2010) Recovery of sugars from ionic liquid biomass liquor by solvent extraction. Bioenerg Res 3(2):123–133
Acknowledgments
ABPDU would like to acknowledge the funding support from Office of Biomass Program within the US DOE’s Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy and also the funding support from the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act. JBEI would like to acknowledge the funding support from US DOE’s Office of Science, Office of Biological and Environmental Research, through contract DE-AC02-05CH11231 between Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory and the US DOE. The authors would like to thank the Idaho National Laboratory for providing the switchgrass and eucalyptus used in this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, C., Tanjore, D., He, W. et al. Scale-Up of Ionic Liquid-Based Fractionation of Single and Mixed Feedstocks. Bioenerg. Res. 8, 982–991 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12155-015-9587-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12155-015-9587-0