Abstract
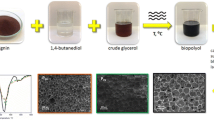
The objective of this investigation was to find a simple method for the production of phenolic-rich products and sugar derivatives via separation of liquefied lignocellulosic materials. After liquefaction, the liquefied products were separated by addition of a sufficient amount of water. It was found that those hydrophobic phenolics could be largely separated from aqueous solutions. Preparation of polyurethane foams using biopolyol and isocyanate was studied. Water was used as an environmentally friendly blowing agent. The factors influencing the cell structure of foams such as catalyst, dosage of blowing agent, and mass ratio of biopolyol to PEG were studied. The microstructure of synthesized foams was characterized by SEM.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang ZJ, Wang QW, Tripathi P, Pittman CU (2011) Catalytic upgrading of bio-oil using 1-octene and 1-butanol over sulfonic acid resin catalysts. Green Chem 13:940–949
Huber GW, Iborra S, Corma A (2006) Synthesis of transportation fuels from biomass: chemistry, catalysts, and engineering. Chem Rev 106:4044–4098
Zakzeski J, Bruijnincx PCA, Jongerius AL, Weckhuysen BM (2010) The catalytic valorization of lignin for the production of renewable chemicals. Chem Rev 110:3552–3599
Gani A, Naruse I (2007) Effect of cellulose and lignin content on pyrolysis and combustion characteristics for several types of biomass. Renew Energy 32:649–661
Alma MH, Basturk MA, Digrak M (2003) New polyurethane-type rigid foams from liquified wood powders. J Mater Sci Lett 22(17):1225–1228
Chen FG, Lu ZM (2009) Liquefaction of wheat straw and preparation of rigid polyurethane foam from the liquefaction products. J Appl Polym Sci 111(1):508–516
Lee SH, Yoshioka M, Shiraishi N (2000) Liquefaction of corn bran (CB) in the presence of alcohols and preparation of polyurethane foam from its liquefied polyol. J Appl Polym Sci 78(2):319–325
Yan YB, Pang H, Yang XX, Zhang RL, Liao B (2008) Preparation and characterization of water-blown polyurethane foams from liquefied cornstalk polyol. J Appl Polym Sci 110(2):1099–1111
Rivera-Armenta JL, Heinze T, Mendoza-Martinez AM (2004) New polyurethane foams modified with cellulose derivatives. Eur Polym J 40:2803–2812
Ge J, Shi X, Cai M, Wu R, Wang M (2003) A novel biodegradable antimicrobial PU foam from wattle tannin. J Appl Polym Sci 90:2756–2763
Kwon OJ, Yang SR, Kim DH, Park JS (2006) Characterization of polyurethane foam prepared by using starch as polyol. J Appl Polym Sci 103:1544–1553
Junming X, Jianchun J, Chungyun H, Todd FS (2012) Renewable chemical feedstocks from integrated liquefaction processing of lignocellulosic materials using microwave energy. Green Chem 14(10):2821–2830
Li XB, Cao HB, Zhang Y (2008) Properties of water blown rigid polyurethane foams with different functionality. J Wuhan Univ Technol Mater Sci 23(1):125–129
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the “Commonweal Research Foundation of Forestry” (201204801) for financial support during this investigation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Z., Xu, S., Hu, Wp. et al. Fractionation of the Biopolyols from Lignocellulosic Biomass for the Production of Rigid Foams. Bioenerg. Res. 6, 896–902 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12155-013-9320-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12155-013-9320-9