Abstract
Objective
The tumor-to-normal tissue (T/N) boron ratio is determined in a patient prior to boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT) using 4-borono-2-18F-fluoro-l-phenylalanine (18F-FBPA) positron emission tomography (PET). The T/N ratio is used as a reference parameter to calculate BNCT dose and to evaluate treatment effects. The boronophenylalanine (BPA) dosage for BNCT treatment is higher than the 18F-FBPA dosage for PET diagnosis. Therefore, we aimed to determine whether the T/N ratios between diagnosis and treatment were correlated.
Methods
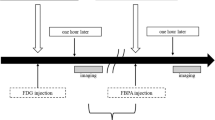
In this study, SAS tongue cancer cells were used to develop an orthotopic nude mouse model. Micro-PET was performed after the mice were injected a dose of 3.7 ± 0.74 MBq of 18F-FBPA via the tail vein. The 18F radioactivity in the tumor, muscle, and heart blood pool was calculated using AMIND software. Organs and blood were collected for boron concentration analysis using inductively coupled plasma-atomic emission spectroscopy after the mice were injected with 400 mg/kg BPA at 15, 30, 45, and 60 min.
Results
Pharmacokinetics of the tumor and muscle from 45 to 60 min after 18F-FBPA and BPA injections were slightly increased, whereas that of blood was slightly decreased. Median T/N ratios at 60 min after 18F-FBPA and BPA injections were 3.5 and 3.43, respectively. Median value of the T/N ratio between them was 3.49 at 60 min. The T/N ratio at 60 min after 18F-FBPA injection was similar to that after BPA injection. However, median tumor-to-blood (T/B) boron ratios of 18F-FBPA and BPA at 60 min were 1.63 and 3.35, respectively. Median value between them was 1.83 at 60 min.
Conclusions
In this study, the T/B ratios demonstrate the spread of a distribution between 18F-FBPA and BPA injections. At 60 min, the T/N ratio of the 18F-FBPA injection was similar to that of the BPA injection. Boron concentration in normal tissue was almost equal to that in blood. Therefore, the representative T/N ratio could be obtained at 60 min after 18F-FBPA injection, and it was used as a reference parameter for calculating accurate radiation dose.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barth RF, Coderre JA, Vicente MG, Blue TE. Boron neutron capture therapy of cancer: current status and future prospects. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11:3987–4002.
Mehta SC, Lu DR. Targeted drug delivery for boron neutron capture therapy. Pharm Res. 1996;13:344–51.
Barth RF, Soloway AH, Fairchild RG, Brugger RM. Boron neutron capture therapy for cancer. Realities and prospects. Cancer. 1992;70:2995–3007.
Aihara T, Morita N, Kamitani N, Kumada H, Ono K, Hiratsuka J, et al. Boron neutron capture therapy for advanced salivary gland carcinoma in head and neck. Int J Clin Oncol. 2014;19:437–44.
Imahori Y, Ueda S, Ohmori Y, Sakae K, Kusuki T, Kobayashi T, et al. Positron emission tomography-based boron neutron capture therapy using boronophenylalanine for high-grade gliomas: part II. Clin Cancer Res. 1998;4:1833–41.
Aihara T, Hiratsuka J, Morita N, Uno M, Sakurai Y, Maruhashi A, et al. First clinical case of boron neutron capture therapy for head and neck malignancies using 18F-BPA PET. Head Neck. 2006;28:850–5.
Takahashi Y, Imahori Y, Mineura K. Prognostic and therapeutic indicator of fluoroboronophenylalanine positron emission tomography in patients with gliomas. Clin Cancer Res. 2003;9:5888–95.
Imahori Y, Ueda S, Ohmori Y, Kusuki T, Ono K, Fujii R, et al. Fluorine-18-labeled fluoroboronophenylalanine PET in patients with glioma. J Nucl Med. 1998;39:325–33.
Kabalka GW, Smith GT, Dyke JP, Reid WS, Longford CP, Roberts TG, et al. Evaluation of fluorine-18-BPA-fructose for boron neutron capture treatment planning. J Nucl Med. 1997;38:1762–7.
Kato I, Fujita Y, Maruhashi A, Kumada H, Ohmae M, Kirihata M, et al. Effectiveness of boron neutron capture therapy for recurrent head and neck malignancies. Appl Radiat Isot. 2009;67:S37–42.
Suzuki M, Kato I, Aihara T, Hiratsuka J, Yoshimura K, Niimi M, et al. Boron neutron capture therapy outcomes for advanced or recurrent head and neck cancer. J Radiat Res. 2014;55:146–53.
Wang LW, Wang SJ, Chu PY, Ho CY, Jiang SH, Liu YWH, et al. BNCT for locally recurrent head and neck cancer: preliminary clinical experience from a phase I/II trial at Tsing Hua Open-Pool Reactor. Appl Radiat Isot. 2011;69:1803–6.
Linko S, Revitzer H, Zilliacus R, Kortesniemi M, Kouri M, Savolainen S. Boron detection from blood samples by ICP-AES and ICP-MS during boron neutron capture therapy. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 2008;68:696–702.
Laakso J, Kulvik M, Ruokonen I, Vahatalo J, Zilliacus R, Farkkila M, et al. Atomic emission method for total boron in blood during neutron-capture therapy. Clin Chem. 2001;47:1796–803.
Kortesniemi M, Seppala T, Auterinen I, Savolainen S. Enhanced blood boron concentration estimation for BPA-F mediated BNCT. Appl Radiat Isot. 2004;61:823–7.
Coderre JA, Chanana AD, Joel DD, Elowitz EH, Micca PL, Nawrocky MM, et al. Biodistribution of boronophenylalanine in patients with glioblastoma multiforme: boron concentration correlates with tumor cellularity. Radiat Res. 1998;149:163–70.
Hanaoka K, Watabe T, Naka S, Kanai Y, Ikeda H, Horitsugi G, et al. FBPA PET in boron neutron capture therapy for cancer: prediction of B concentration in the tumor and normal tissue in a rat xenograft model. EJNMMI Res. 2014;4:70.
Wang HE, Liao AH, Deng WP, Chang PF, Chen JC, Chen FD, et al. Evaluation of 4-borono-2-F-18-fluoro-l-phenylalanine-fructose as a probe for boron neutron capture therapy in a glioma-bearing rat model. J Nucl Med. 2004;45:302–8.
Hsieh CH, Chen YF, Chen FD, Hwang JJ, Chen JC, Liu RS, et al. Evaluation of pharmacokinetics of 4-borono-2-F-18-fluoro-l-phenylalanine for boron neutron capture therapy in a glioma-bearing rat model with hyperosmolar blood-brain barrier disruption. J Nucl Med. 2005;46:1858–65.
Watanabe T, Hattori Y, Ohta Y, Ishimura M, Nakagawa Y, Sanada Y, et al. Comparison of the pharmacokinetics between L-BPA and L-FBPA using the same administration dose and protocol: a validation study for the theranostic approach using [(18)F]-L-FBPA positron emission tomography in boron neutron capture therapy. BMC Cancer. 2016;16:859.
Bibby MC. Orthotopic models of cancer for preclinical drug evaluation: advantages and disadvantages. Eur J Cancer. 2004;40:852–7.
Lin YC, Hwang JJ, Wang SJ, Yang BH, Chang CW, Hsiao MC, et al. Macro- and microdistributions of boron drug for boron neutron capture therapy in an animal model. Anticancer Res. 2012;32:2657–64.
Chen W, Dilsizian V. PET assessment of vascular inflammation and atherosclerotic plaques: SUV or TBR? J Nucl Med. 2015;56:503–4.
Pawade TA, Cartlidge TR, Jenkins WS, Adamson PD, Robson P, Lucatelli C, et al. Optimization and reproducibility of aortic valve 18F-fluoride positron emission tomography in patients with aortic stenosis. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2016;9:e005131.
Isohashi K, Shimosegawa E, Naka S, Kanai Y, Horitsugi G, Mochida I, et al. Comparison of the image-derived radioactivity and blood-sample radioactivity for estimating the clinical indicators of the efficacy of boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT): 4-borono-2-(18)F-fluoro-phenylalanine (FBPA) PET study. EJNMMI Res. 2016;6:75.
Ishiwata K, Shiono M, Kubota K, Yoshino K, Hatazawa J, Ido T, et al. A unique in vivo assessment of 4-[10B]borono-l-phenylalanine in tumour tissues for boron neutron capture therapy of malignant melanomas using positron emission tomography and 4-borono-2-[18F]fluoro-l-phenylalanine. Melanoma Res. 1992;2:171–9.
Ishiwata K, Ido T, Honda C, Kawamura M, Ichihashi M, Mishima Y. 4-Borono-2-[18F]fluoro-D, l-phenylalanine: a possible tracer for melanoma diagnosis with PET. Int J Rad Appl Instrum B. 1992;19:311–8.
Ishiwata K, Ido T, Kawamura M, Kubota K, Ichihashi M, Mishima Y. 4-Borono-2-[18F]fluoro-D,L-phenylalanine as a target compound for boron neutron capture therapy: tumor imaging potential with positron emission tomography. Int J Rad Appl Instrum B. 1991;18:745–51.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the Biomedical Technology Research and Development Center (Tsing Hua University, Taiwan) and the Molecular and Genetic Imaging Core of the Taiwan Mouse Clinic for their technical support. And also we appreciate Enago (www.enago.tw) for the English language review.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Co-first author: Fong-In Chou.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, YC., Chou, FI., Yang, BH. et al. Similar T/N ratio between 18F-FBPA diagnostic and BPA therapeutic dosages for boron neutron capture therapy in orthotropic tongue cancer model. Ann Nucl Med 34, 58–64 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12149-019-01415-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12149-019-01415-z