Abstract
Objective
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the degree of cytological radiation damage to lymphocytes occurring after I-131 metaiodobenzylguanidine (MIBG) therapy as determined by the cytokinesis-blocked micronucleus assay. The chromosomal damage to lymphocytes induced by I-131 in vivo should result in augmentation of the number of cells with micronuclei.
Methods
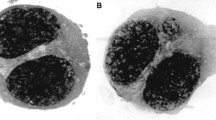
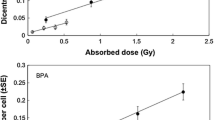
We studied 15 patients with pheochromocytoma (14/15) or ganglioneuroma (1/15), who were treated initially with 7.4 GBq of I-131-MIBG. Isolated lymphocytes collected from patients 10 days after the therapy were harvested and treated according to the cytokinesis-blocked method of Fenech and Morley. Serial blood samples were obtained periodically only from two patients for 2 years after therapy. Micronucleus number of micronuclei per 500 binucleated cells was scored by visual inspection. As controls, lymphocytes from the same patients before the therapy were also studied. In an in vitro study, lymphocytes from eight normal volunteers were exposed to doses varying from 0.5 to 2 Gy and studied with the same method.
Results
The mean number (mean ± SD) of micronuclei after treatment was significantly increased (p < 0.001) as compared to control subjects (49.4 ± 8.2 vs. 11.3 ± 6.4). Internal radiation absorbed doses estimated for the 15 patients were 1.6 ± 0.3 Gy in this external irradiation study. The frequency of micronuclei post-administration of I-131-MIBG gradually decreased to near baseline (i.e., pre-therapy) levels by 2 years.
Conclusions
The relatively low frequency of lymphocyte micronuclei induced by I-131-MIBG in vivo and reversal of the increasing frequency of lymphocyte micronuclei after therapy suggest that the short-term non-stochastic damage induced by this therapy with 7.4 GBq of I-131-MIBG in pheochromocytoma or ganglioneuroma patients is limited and reversible.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sisson JC. Radiopharmaceutical treatment of pheochromocytoma. Ann NY Acad Sci. 2002;970:54–60.
Sisson JC, Frager MS, Valk TW, Gross DM, Swanson DP, Wieland DM, et al. Scintigraphic localization of pheochromocytoma. N Engl J Med. 1981;305:12–7.
Treuner J, Feine V, Niethammer D, Muller-Sshaumberg W, Meinke J, Eibach E, et al. Scintigraphic imaging of neuroblastoma with 131-I-metaiodobenzylguanidine. Lancet. 1984;1:333–4.
Smit AS, van Essen LH, Hollema H, Muskiert FAJ, Piers OA. Meta-I-131-iodobenzylguanidine uptake in a nonsecreting paraganglioma. J Nucl Med. 1984;25:984–6.
Connel JMC, Hilditch TE, Elliott A. I-131-MIBG and medullary carcinoma of the thyroid. Lancet. 1984;2:1273–4.
Sisson JC, Hutchinson RJ, Carey JE, Shapiro B, Johnson JW, Mallette SA, et al. Toxicity from treatment of neuroblastoma with I-131-meta-iodobenzylguanidine. Eur J Nucl Med. 1988;14:337–40.
Monsieurs MA, Thierens HM, Vral A, Brans B, De Ridder L, Dierckx RA. Patient dosimetry after 131I-MIBG therapy for neuroblastoma and carcinoid tumours. Nucl Med Commun. 2001;22:367–74.
Fenech M, Morley AA. Measurement of micronuclei in lymphocytes. Mutat Res. 1983;147:29–36.
Hayashi M, Sofumi T, Ishidate M Jr. An application of acridine orange fluorescent staining to the micronucleus test. Mutat Res. 1983;120:241–7.
Heddle JA, Lue CB, Sanders EF, Benz RD. Sensitivity to five mutagens in Fanconi’s anemia as measured by the micronucleus method. Cancer Res. 1978;38:2983–8.
Krishna G, Kropko ML, Theisis JC. Dimethylnitrosamine-induced micronucleus formation in mouse bone marrow and spleen. Mutat Res. 1990;242:345–51.
Watanabe N, Yokoyama K, Kinuya S, Shuke N, Shimizu M, Futatsuya R, et al. Evaluation of radiotoxicity after iodine-131 therapy for thyroid cancer using the micronucleus assay. J Nucl Med. 1998;39:436–40.
Watanabe N, Yokoyama K, Kinuya S, Shuke N, Shimizu M, Michigishi T, et al. Radiotoxicity after strontium-89 therapy for bone metastases using the micronucleus assay. J Nucl Med. 1998;39:2077–9.
Ottesen J. On age of human white cells in peripheral blood. Acta Physiol Scand. 1954;32:75–93.
Norman A, Sasaki MS, Ottoman RE, Fingerhut AG. Lymphocyte lifetime in women. Science. 1965;147:745.
M’Kacher R, Legal JD, Schlumberger M, Aubert B, Beron-Gaillard N, Gaussen A, et al. Sequential biological dosimetry after a single treatment with iodine-131 for differentiated thyroid carcinoma. J Nucl Med. 1997;38:377–80.
Hall EJ. Repair of radiation damage and dose rate effect. In: Hall EJ, editor. Radiobiology for the radiologist. Philadelphia: JB Lippincott; 1994. p. 107–31.
Matthay KK, Panina C, Hurbery J, Price D, Glidden DV, Tang HR, et al. Correlation of tumor and whole-body dosimetry with tumor response and toxicity in refractory neuroblastoma treated with I-131-MIBG. J Nucl Med. 2001;42:1713–21.
Prosser JS, Moquet JE, Lloyd DC, Edwards AA. Radiation induction of micronuclei in human lymphocytes. Mutat Res. 1988;199:37–45.
Kormos C, Koteles GJ. Micronuclei in X-irradiated human lymphocytes. Mutat Res. 1988;199:31–5.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported in part by a Grant-in-Aid for scientific research (17591251) from the Japan Society for the promotion of Science. We have no conflict of interest with regard to our paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Watanabe, N., Yokoyama, K., Kinuya, S. et al. Evaluation of cytological radiation damage to lymphocytes after I-131 metaiodobenzylguanidine therapy by the cytokinesis-blocked micronucleus assay. Ann Nucl Med 30, 624–628 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12149-016-1105-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12149-016-1105-8