Abstract
Purpose
In proton therapy, imaging of proton-induced positrons is a useful method to monitor the proton beam distribution after therapy. Usually, a positron emission tomography (PET) system installed in or near the proton beam treatment room is used for this purpose. However, a PET system is sometimes too large and expensive for this purpose. We developed a small field-of-view (FOV) gamma camera for high-energy gamma photons and used it for monitoring the proton-induced positron distribution.
Methods
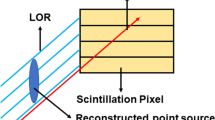
The gamma camera used 0.85 mm × 0.85 mm × 10 mm Ce:Gd3Al2Ga3O12 (GAGG) pixels arranged in 20 × 20 matrix to form a scintillator block, which was optically coupled to a 1-inch-square position-sensitive photomultiplier tube (PSPMT). The GAGG detector was encased in a 20-mm thick container and a pinhole collimator was mounted on its front. The gamma camera was set 1.2 m from the 35 cm × 35 cm × 5 cm plastic phantom in the proton therapy treatment room, and proton beams were irradiated to the phantom with two proton energies.
Results
The gamma camera had spatial resolution of ~6.7 cm and sensitivity of 3.2 × 10−7 at 1 m from the collimator surface. For both proton energies, positron distribution in the phantom could be imaged by the gamma camera with 10-min acquisition. The lengths of the range of protons measured from the images were almost identical to the simulation results.
Conclusions
These results indicate that the developed high-energy gamma camera is useful for imaging positron distributions in proton therapy.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bennett GW, Archambeau JO, Archambeau BE, Meltzer JI, Wingate CL. Visualization and transport of positron emission from proton activation in vivo. Science. 1978;200:1151–3.
Del Guerra A, Di Domenico G, Gambaccini M, Marziani M. A Monte Carlo simulation of the possible use of positron emission tomography in proton radiotherapy. Nucl Instr Methods A. 1994;345:379–84.
Oelfke U, Lam GKY, Atkins MS. Proton dose monitoring with PET: quantitative studies in Lucite. Phys Med Biol. 1996;41:177–96.
Hishikawa Y, Kagawa K, Murakami M, Sakai H, Akagi T, Abe M. Usefulness of positron-emission tomographic images after proton therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2002;53:1388–91.
Parodi K, Paganetti H, Shih EA, Michaud S, Loeffler JS, Delaney TF, et al. Patient study on in vivo verification of beam delivery and range using PET/CT imaging after proton therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2007;68:920–34.
Experimental results with proton beams, Litzenberg DW, Roberts DA, Lee MY, Pham K, Vander Molen AM, Ronninge R, et al. On-line monitoring of radiotherapy beams. Med Phys. 1999;26:992–1006.
Parodi K, Enghardt W, Haberer T. In-beam PET measurements of radioactivity induced by proton beams. Phys Med Biol. 2002;47:21–36.
Inaniwa T, Tomitani T, Kohno T, Kanai T. Quantitative comparison of suitability of various beams for range monitoring with induced activity in hadron therapy. Phys Med Biol. 2005;50:1131–45.
Iseki Y, Mizuno H, Futami Y, Tomitani T, Kanai T, Kanazawa M, et al. Positron camera for range verification of heavy-ion radiotherapy. Nucl Instrum Methods-A. 2003;515:840–9.
Nishio T, Ogino T, Nomura K, Uchida H. Dose-volume delivery guided proton therapy using beam on-line PET system. Med Phys. 2006;33(11):4190–7.
Yamaya T, Yoshida E, Inaniwa T, Sato S, Nakajima Y, Wakizaka H, et al. Development of a small prototype for a proof-of-concept of open PET imaging. Phys Med Biol. 2011;56:1123–37.
Tashima H, Yamaya T, Yoshida E, Kinouchi S, Watanabe M, Tanaka E. A single-ring open PET enabling PET imaging during radiotherapy. Phys Med Biol. 2012;57(14):4705–18.
Smeets J, Roellinghoff F, Prieels D, Stichelbaut F, Benilov A, Busca P, et al. Prompt gamma imaging with a slit camera for real-time range control in proton therapy. Phys Med Biol. 2012;57(11):3371–405.
Perali I, Celani A, Bombelli L, Fiorini C, Camera F, Clementel E, et al. Prompt gamma imaging of proton pencil beams at clinical dose rate. Phys Med Biol. 2014;59(19):5849–71.
Kamada K, Yanagida T, Endo T, Tsutsumi K, Usuki Y, Nikl M, et al. 2 inch diameter single crystal growth and scintillation properties of Ce:Gd3Al2Ga3O12. J Cryst Growth. 2012;352:88–90.
Yamamoto S, Watabe H, Kato K, Hatazawa J. Performance comparison of high quantum efficiency and normal quantum efficiency photomultiplier tubes and position sensitive photomultiplier tubes for high resolution PET and SPECT detectors. Med Phys. 2012;39(11):6667–960.
Sato T, Niita K, Matsuda N, Hashimoto S, Iwamoto Y, Noda S, et al. Particle and heavy ion transport code system PHITS, Version 2.52. J Nucl Sci Technol. 2013;50(9):913–23.
Jakoby BW, Bercier Y, Conti M, Casey ME, Bendriem B, Townsend DW. Physical and clinical performance of the mCT time-of-flight PET/CT scanner. Phys Med Biol. 2011;56(8):2375–89.
Bettinardi V, Presotto L, Rapisarda E, Picchio M, Gianolli L, Gilardi MC. Physical performance of the new hybrid PET/CT discovery-690. Med Phys. 2011;38(10):5394–411.
Bettinardi V, Danna M, Savi A, Lecchi M, Castiglioni I, Gilardi MC, et al. Performance evaluation of the new whole-body PET/CT scanner: discovery ST. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2004;31(6):867–81.
Moyer RA. A low-energy multihole converging collimator compared with a pinhole collimator. J Nucl Med. 1974;15:59–64.
Acknowledgments
Measurements of proton beam in this work were performed at the Nagoya Proton Therapy Center. We would also like to thank the clinical team for allowing beam time for our experiments, and thank all of the staff who helped us prepare and carry out the irradiations.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yamamoto, S., Toshito, T., Komori, M. et al. Monitoring of positron using high-energy gamma camera for proton therapy. Ann Nucl Med 29, 268–275 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12149-014-0936-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12149-014-0936-4