Abstract
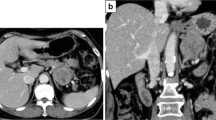
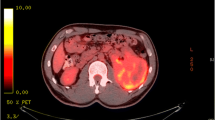
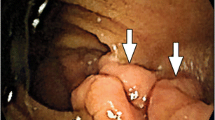
A 70-year-old woman with a submucosal gastric tumor was referred to our hospital for surgical treatment. Upon examination, it was found that she had hypertension, and abdominal computed tomography revealed swelling on both adrenal glands. The patient was examined with gamma camera imaging and iodine-123 metaiodobenzylguanidine (MIBG), because her hypertension was thought to be due to a suspected adrenomedullary tumor. The planar image showed an unexpected abnormal uptake of MIBG in the upper abdomen. On single-photon emission computed tomographic images, the area of abnormal tracer uptake was thought to correspond to the known gastric tumor. The surgical procedure and histological assessments revealed that the gastric tumor was a gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST). MIBG can accumulate in GISTs as well as in neuroendocrine tumors of the medulla of the adrenal glands. Although the cause of radiolabeled MIBG uptake in GISTs is uncertain, further studies are necessary to establish the significance of MIBG scintigraphy in GIST imaging.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sisson JC, Frager MS, Valk TW, Gross MD, Swanson DP, Wieland DM, et al. Scintigraphic localization of pheochromocytoma. N Engl J Med. 1981;305:12–7.
Balan KK, Sonoda LI, Pawaroo D. I-123 MIBG uptake in a gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST). Clin Nucl Med. 2010;35:196–7.
Frappaz D, Giammarile F, Thiesse P, Ranchere-Vince D, Louis D, Guibaud L, et al. False positive MIBG scan. Med Pediatr Oncol. 1997;29:589–92.
Rainis T, Ben-Haim S, Dickstein G. False positive metaiodobenzylguanidine scan in a patient with a huge adrenocortical carcinoma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2000;85:5–7.
Sone H, Okuda Y, Nakamura Y, Ishikawa N, Yamaoka T, Kawakami Y, et al. Radioiodinated metaiodobenzylguanidine scintigraphy for pheochromocytoma. A false-positive case of adrenocortical adenoma and literature review. Horm Res. 1996;46:138–42.
Inoue Y, Akahane M, Kitazawa T, Ijichi H, Obi S, Yoshikawa K, et al. False positive uptake of metaiodobenzylguanidine in hepatocellular carcinoma. Br J Radiol. 2002;75:548–51.
Corless CL, Fletcher JA, Heinrich MC. Biology of gastrointestinal stromal tumors. J Clin Oncol. 2004;22:3813–25.
Min KW, Leabu M. Interstitial cells of Cajal (ICC) and gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST): facts, speculations, and myths. J Cell Mol Med. 2006;10:995–1013.
Ward SM, Sanders KM. Involvement of intramuscular interstitial cells of Cajal in neuroeffector transmission in the gastrointestinal tract. J Physiol. 2006;576:675–82.
Tobes MC, Jaques S Jr, Wieland DM, Sisson JC. Effect of uptake-one inhibitors on the uptake of norepinephrine and metaiodobenzylguanidine. J Nucl Med. 1985;26:897–907.
Beierwaltes WH. Endocrine imaging: parathyroid, adrenal cortex and medulla, and other endocrine tumors. Part II. J Nucl Med. 1991;32:1627–39.
Jun JY, Choi S, Yeum CH, Chang IY, Park CK, Kim MY, et al. Noradrenaline inhibits pacemaker currents through stimulation of beta 1-adrenoceptors in cultured interstitial cells of Cajal from murine small intestine. Br J Pharmacol. 2004;141:670–7.
Kindblom LG, Remotti HE, Aldenborg F, Meis-Kindblom JM. Gastrointestinal pacemaker cell tumor (GIPACT): gastrointestinal stromal tumors show phenotypic characteristics of the interstitial cells of Cajal. Am J Pathol. 1998;152:1259–69.
Debiec-Rychter M, Pauwels P, Lasota J, Franke S, De Vos R, De Wever I, et al. Complex genetic alterations in gastrointestinal stromal tumors with autonomic nerve differentiation. Mod Pathol. 2002;15:692–8.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fukuchi, K., Suzuki, M., Sato, S. et al. Unusually increased metaiodobenzylguanidine uptake in a gastrointestinal stromal tumor of the stomach. Ann Nucl Med 26, 684–687 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12149-012-0612-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12149-012-0612-5