Abstract
Aim
The motion of the head during brain positron emission tomography (PET) acquisitions has been identified as a source of artifact in the reconstructed image. In this study, a method is described to develop an image-based motion correction technique for correcting the post-acquisition data without using external optical motion-tracking system such as POLARIS.
Method
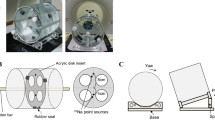
In this technique, GATE has been used to simulate PET brain scan using point sources mounted around the head to accurately monitor the position of the head during the time frames.
Result
The measurement of head motion in each frame showed a transformation in the image frame matrix, resulting in a fully corrected data set.
Conclusion
Using different kinds of phantoms and motions, the accuracy of the correction method is tested and its applicability to experimental studies is demonstrated as well.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bloomfield P, Spinks T, Reed J, Schnorr L, Westrip A, Livieratos L, et al. The design and implementation of a motion correction scheme for neurological PET. Phys Med Biol. 2003;48:959–78.
Lopresti B, Russo A, Jones W, Fisher T, Crouch D, Altenburger D, et al. Implementation and performance of an optical motion tracking system for high resolution brain pet imaging. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci. 1999;46:2059–67.
Rahmim A. Advanced motion correction methods in PET. Iran J Nucl Med. 2005;13(24):1–17. (review article).
Picard Y, Thompson C. Motion correction of PET images using multiple acquisition frames. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 1997;16:137–44.
Daube-Witherspoon ME, Yan YC, Green MV, Carson RE, Kempner KM, Herscovitch P. Correction for motion distortion in PET by dynamic monitoring of patient position. J Nucl Med. 1990;31:816. (abstract).
Fulton R, Meikle S, Eberl S, Pfeiffer J, Constable C, Fulham M. Correction for head movements in positron emission tomography using an optical motion-tracking system. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci. 2002;49:116–23.
Fulton R, Tellmann L, Pietrzyk U, Winz O, Stangier I, Nickel I, et al. Accuracy of motion correction methods for pet brain imaging. Nuclear Science Symposium Conference Record, IEEE 2004. p. 4226–30.
Mourik JEM, Lubberink M, van Velden FHP, Lammertsma AA, Boellaard R. Off-line motion correction methods for multi-frame PET data. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2009;36:2002–13.
Koshino K, Watabe H, Hasegawa S, Hayashi T, Hatazawa J, Iida H. Development of motion correction technique for cardiac 15O-water PET study using an optical motion tracking system. Ann Nucl Med. 2010;24:1–11.
Naum A, Laaksonen MS, Tuunanen H, Oikonen V, Teräs M, Kemppainen J, et al. Motion detection and correction for dynamic (15)O-water myocardial perfusion PET studies. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2005;32(12):1378–83.
Menke M, Atkins M, Buckley K. Compensation methods for head motion detected during PET imaging. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci. 1996;43:310–7.
Rahmim A, Bloomfield P, Houle S, et al. Motion compensation in histogram-mode and list-mode EM reconstructions: beyond the event-driven approach. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci. 2004;51:2588–96.
Bühler P, Just U, Will E, Kotzerke J, van den Hoff J. An accurate method for correction of head movement in PET. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2002;23:1176–85.
Qi J, Huesman RH. List mode reconstruction for PET with motion compensation: a simulation study. In: Proceedings of IEEE International Symposium on Biological Imaging, 2002. p. 413–16.
Faber TL, Raghunath N, Tudorascu D, Votaw JR. Motion correction of PET brain images through deconvolution: I. Theoretical development and analysis in software simulations. Phys Med Biol. 2009;54:797–811.
Rahmim A, Cheng JC, Dinelle K, Shilov M, Segars WP, Rousset OG, et al. System matrix modeling of externally tracked motion. Nucl Med Comm. 2008;29:574–81.
Jan S, Santin G, Strul D, Staelens S, Assié K, Autret D, et al. GATE: a simulation toolkit for PET and SPECT. Phys Med Biol. 2004;49:4543–61.
Jan S, Comtat C, Strul D, Santin G, Trébossen R. Monte Carlo simulation for the ECAT EXACT HR+ system using GATE. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci. 2005;52(3):627–33.
Brix G, Zaers J, Adam LE, Bellemann ME, Ostertag H, Trojan H, et al. Performance evaluation of a whole body PET scanner using the NEMA protocol. J Nucl Med. 1997;38(10):1614–23.
Chang LT. A method for attenuation correction in radionuclide computed tomography. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci. 1978;25:638–43.
Cherry SR, Huang Sc. Effects of scatter on model parameter estimates in 3D PET studies of the human brain. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci. 1995;42(4):1174–9.
Woo S, Watabe H, Choi Y, Min Kim K, Park CC, Bloomfield PM, et al. Sinogram-based motion correction of PET images using optical motion tracking system and list-mode data acquisition. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci. 2004;51(3):830–34.
Dennis JE Jr. Nonlinear Least-Squares. In: Jacobs D, editor. State of the art in numerical analysis. London: Academic Press; 1977. p. 269–312.
Moré JJ. The Levenberg–Marquardt algorithm: implementation and theory. In: Watson GA, editor. Numerical analysis, lecture notes in mathematics 630. Berlin: Springer; 1977. p. 105–16.
Rodgers JL, Nicewander WA. Thirteen ways to look at the correlation coefficient. Am Stat. 1988;42(1):59–66.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nazarparvar, B., Shamsaei, M. & Rajabi, H. Correction of head movements in positron emission tomography using point source tracking system: a simulation study. Ann Nucl Med 26, 7–15 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12149-011-0532-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12149-011-0532-9