Abstract
Objective
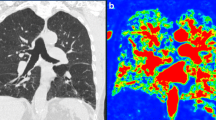
Anatomic relation between pulmonary perfusion and morphology in pulmonary emphysema was assessed on deep-inspiratory breath-hold (DIBrH) perfusion single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT)-CT fusion images.
Methods
Subjects were 38 patients with pulmonary emphysema and 11 non-smoker controls, who successfully underwent DIBrH and non-BrH perfusion SPECT using a dual-headed SPECT system during the period between January 2004 and June 2006. DIBrH SPECT was three-dimensionally co-registered with DIBrH CT to comprehend the relationship between lung perfusion defects and CT low attenuation areas (LAA). By comparing the appearance of lung perfusion on DIBrH with non-BrH SPECT, the correlation with the rate constant for the alveolar-capillary transfer of carbon monoxide (DLCO/VA) was compared between perfusion abnormalities on these SPECTs and LAA on CT.
Results
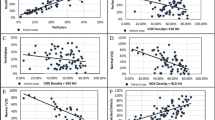
DIBrH SPECT provided fairly uniform perfusion in controls, but significantly enhanced perfusion heterogeneity when compared with non-BrH SPECT in pulmonary emphysema patients (P < 0.001). The reliable DIBrH SPECT-CT fusion images confirmed more extended perfusion defects than LAA on CT in majority (73%) of patients. Perfusion abnormalities on DIBrH SPECT were more closely correlated with DLCO/VA than LAA on CT (P < 0.05).
Conclusions
DIBrH SPECT identifies affected lungs with perfusion abnormality better than does non-BrH SPECT in pulmonary emphysema. DIBrH SPECT-CT fusion images are useful for more accurately localizing affected lungs than morphologic CT alone in this disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Briggs DD Jr. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease overview: prevalence, pathogenesis, and treatment. J Manag Care Pharm 2004;10:3–10.
Muzykantov VR. Delivery of antioxidant enzyme proteins to the lung. Antioxid Redox Signal 2001;3:39–62.
Petty TL. COPD in perspective. Chest 2002;121:116–120.
Sala R, Moriggi E, Corvasce G, Morelli D. Protection by N-acetylcysteine against pulmonary endothelial cell damage induced by oxidant injury. Eur Respir J 1993;6:440–446.
Bae KT, Slone RM, Gierada DS, Yusen RD, Cooper JD. Patients with emphysema: quantitative CT analysis before and after lung volume reduction surgery-work in progress. Radiology 1997;203:705–714.
Berger P, Laurent F, Begueret H, Perot V, Rouiller R, Raherison C, et al. Structure and function of small airways in smokers: relationship between air trapping at CT and airway inflammation. Radiology 2003;228:85–94.
Eidelman D, Saetta MP, Ghezzo H, Wang NS, Hoidal JR, King M, et al. Cellularity of the alveolar walls in smokers and its relation to alveolar destruction: functional implications. Am Rev Respir Dis 1990;141:1547–1552.
Noma S, Moskowitz GW, Herman PG. Pulmonary scintigraphy in elastase-induced emphysema in pigs: correlation with high-resolution computed tomography and histology. Invest Radiol 1992;27:429–435.
Jamadar DA, Kazerooni EA, Martinez FJ, Wahl RL. Semi-quantitative ventilation/perfusion scintigraphy and single-photon emission tomography for evaluation of lung volume reduction surgery candidates: description and prediction of clinical outcome. Eur J Nucl Med 1999;26:734–742.
Sando Y, Inoue T, Nagai R, Endo K. Ventilation/perfusion ratios and simultaneous dual-radionuclide single-photon emission tomography with krypton-81m and technetium-99m macroaggregated albumin. Eur J Nucl Med 1997;24:1237–1244.
Sandek K, Bratel T, Lagerstrand L, Rosell H. Relationship between lung function, ventilation-perfusion inequality and extent of emphysema as assessed by high-resolution computed tomography. Respir Med 2002;96:934–943.
Goerres GW, Kamel E, Heidelberg TN, Schwitter MR, Burgr C, von Schulhess GK. PET-CT image co-registration in the thorax: influence of respiration. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2002;29:351–360.
Ketai L, Hartshorne M. Potential of computed tomography-SPECT and computed tomography: coincidence fusion images of the chest. Clin Nucl Med 2001;26:433–441.
Suga K, Yasuhiko K, Iwanaga H, Hayashi N, Yamashita T, Matsunaga N. Enhanced perfusion defect clarity and inhomogeneity in smoker’s lungs with deep-inspiratory breath-hold perfusion SPECT images. Nucl Med Commun 2005;26:801–807.
Suga K, Kawakami Y, Iwanaga H, Hayashi N, Seto A, Matsunaga N. Comprehensive assessment of lung CT attenuation alteration at perfusion defects of acute pulmonary thromboembolism with breath-hold SPECT-CT fusion images. J Comput Assist Tomogr 2006;30:83–91.
American Thoracic Society. Standards for the diagnosis and care of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1995;152:78–73.
Pauwels RA, Buist AS, Calverley PM, Jenkins CR, Hurd SS, GOLD Scientific Committee. Global strategy for the diagnosis, management, and prevention of chronic distructive pulmonary disease. NHLBI/WHO Global Initiative for Chronic Obctructive Lung Disease (GOLD) Workshop summary. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2001;163:1256–1276.
Sakai F, Gamsu G, Im J, Ray CS. Pulmonary function abnormalities in patients with CT-determined emphysema. J Comput Assist Tomogr 1987;11:963–968.
Lamers RJ, Thelissen GR, Kessels AG, Wouters EF, van Engelshoven JM. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: evaluation with spirometrically controlled CT lung densitometry. Radiology 1994;193:109–113.
Nishimura K, Urata K, Yamagishi M, Itoh H, Ikeda A, Tsukino M, et al. Comparison of different computed tomography scanning methods for quantifying emphysema. J Thorac Imaging 1998;13:193–198.
Park KJ, Bergin CJ, Clausen JL. Quantitative of emphysema with three-dimensional CT densitometry: comparison with two-dimensional analysis, visual emphysema scores, and pulmonary function test results. Radiology 1999;211:541–547.
Miller RP, Müller NL, Vedal S. Limitations of computed tomography in the assessment of emphysema. Am Rev Respir Dis 1989;139:980–983.
Müller NL, Coxson H. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: 4. Imaging the lungs in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Thorax 2005;57:982–985.
Sudoh M, Ueda K, Kaneda Y, Jinbo M, Li TS, Suga K, et al. Breath-hold single-photon emission tomography and computed tomography for predicting residual pulmonary function in patients with lung cancer. J Thoracic Cardiovasc Surg 2006;131:994–1001.
Ardekani BA, Braun M, Hutton BF, Kanno I, Iida H. A fully automatic multimodality image registration algorithm. J Comput Assist Tomogr 1995;19:615–623.
Alderson PO, Vieras F, Housholder DF, Mendenhall KG, Wagner HN Jr. Gated and cinematic perfusion lung imaging in dogs with experimental pulmonary embolism. J Nucl Med 1979;20:407–412.
Nakano Y, Muro S, Sakai H, Hirai T, Chin K, Tsukino M, et al. Computed tomographic measurements of airway dimensions and emphysema in smokers: correlation with lung function. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2000;162:1102–1108.
Madani A, Zanen J, de Maertelaer V, Gevenois PA. Pulmonary emphysema: objective quantification at multi-detector row CT: comparison with macroscopic and microscopic morphometry. Radiology 2006;238:1036–1043.
Kuwano K, Matsuba K, Ikeda T, Murakami J, Araki A, Nishitani H, et al. The diagnosis of mild emphysema: correlation of computed tomography and pathology scores. Am Rev Respir Dis 1990;141:169–178.
Gevenois PA, De Vuyst P, de Maertelaer V, Zanen J, Jacobovitz D, Cosio MG, et al. Comparison of computed density and microscopic morphometry in pulmonary emphysema. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1996;154:187–192.
Remy-Jardin M, Remy J, Gosselin B, Copin MC, Wurtz A, Duhamel A. Sliding thin slab, minimum intensity projection technique in the diagnosis of emphysema: histopathologic-CT correlation. Radiology 1996;200:665–671.
Cooper JD, Trulock EP, Triantafillou AN, Patterson GA, Pohl MS, Deloney PA, et al. Bilateral pneumonectomy (volume reduction) for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J Thoracic Cardiovasc Surg 1995;109:106–119.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Suga, K., Kawakami, Y., Iwanaga, H. et al. Assessment of anatomic relation between pulmonary perfusion and morphology in pulmonary emphysema with breath-hold SPECT-CT fusion images. Ann Nucl Med 22, 339–347 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12149-007-0137-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12149-007-0137-5