Abstract
Objective
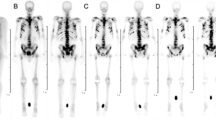
Bone scan is the accepted initial imaging modality for skeletal metastases. Cisplatin is a cell-cycle nonspecific antineoplastic agent used in some chemotherapy regimens. Knowing that platinum reacts with phosphate compounds such as methylenediphosphonic acid (MDP), decreases bone resorption and new bone formation, it can be proposed that cisplatin chemotherapy may decrease Tc-99m MDP bone uptake. We aimed to demonstrate, if present, the decrease in bone uptake and to determine the duration of this effect.
Methods
Thirty male Wistar rats were randomized into five groups, namely, placebo group (G1) and cisplatin groups (G2, G3, G4, G5). Pre-therapy bone scintigraphies were obtained in all the groups. Cisplatin chemotherapy was given as infusion. Post-therapy bone scintigraphies were obtained 10 min, 1 h, 24 h, and 72 h after chemotherapy in groups G2–G5, respectively. A placebo bone scintigraphy was obtained 10 min after infusion of serum physiologic in G1. Plasma samples for cisplatin plasma values were obtained. The graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrophotometry technique was used for cisplatin analysis. Quantitative analysis (bone uptake ratios) was performed by drawing regions of interest on the right femur, vertebral column, and adjacent soft tissues. The injection/examination time delay and the net injected MDP doses were also noted.
Results
There was no statistically significant difference in bone uptake values, injected MDP doses or injection/examination time delay in any group. Cisplatin plasma values were significantly different in G2, G3, G4, and G5 (P < 0.05) but not in G1.
Conclusions
Cisplatin chemotherapy seems to have no effect on the Tc-99m MDP uptake of normal bone.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Francis MD, Ferguson DL, Tofe AJ, Bevan JA, Michaels SE. Comparative evaluation of three diphosphonates: in vitro adsorption (C-14 labeled) and in vivo osteogenic uptake (Tc-99m complexed). J Nucl Med 1980;21:1185–1189.
Murphy KJ, Line BR, Malfetano J. Etidronate therapy decreases the sensitivity of bone scanning with methylene diphosphonate labeled with technetium-99m. Can Assoc Radiol J 1997;48:199–202.
Boulikas T, Vougiouka M. Recent clinical trials using cisplatin, carboplatin and their combination chemotherapy drugs (review). Oncol Rep 2004;11:559–595.
Lipp HP, Hartmann JT. Platinum compounds: metabolism, toxicity and supportive strategies. Schweiz Rundsch Med Prax 2005;94:187–198.
Slavin LL, Bose RN. Phosphonato complexes of platinium(II): kinetics of formation and phosphorus-31 NMR characterization studies. J Inorg Biochem 1990;40:339–347.
McAfee JG, Singh A, Roskopf M, Ritter C, Lyons B, Schoonmaker JE, et al. Experimental drug induced changes in renal function and biodistribution of 99mTc-MDP. Invest Radiol 1983;18:470–478.
Nakayama Y, Okuno S, Miki T, Nishizawa Y, Morii H. A case of esophageal carcinoma with hypercalcemia caused by PTH-rP: the effect of therapy on the bone and calcium metabolism. Nippon Naibunpi Gakkai Zasshi 1992;68:1294–1299.
Suliburk JW, Helmer KS, Gonzalez EA, Robinson EK, Mercer DW. Ketamine attenuates liver injury attributed to endotoxemia: role of cyclooxygenase-2. Surgery 2005;138:134–140.
Ozkan KU, Kucukaydin M, Muhtaroglu S, Kontas O. Evaluation of contralateral testicular damage after unilateral testicular torsion by serum inhibin B levels. J Pediatr Surg 2001;36:1050–1053.
Fonseca E, Grau JJ, Sastre J, García-Gómez JM, Rueda A, Pastor M, et al. Induction chemotherapy with cisplatin/docetaxel versus cisplatin/5-fluorouracil for locally advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck: a randomised phase II study. Eur J Cancer 2005;41:1254–1260.
Freireich EJ, Gehan EA, Rall DP, Schmidt LH, Skipper HE. Quantitative comparison of toxicity of anticancer agents in mouse, rat, hamster, dog, monkey, and man. Cancer Chemother Rep 1966;50:219–244.
Cornelison TL, Reed E. Nephrotoxicity and hydration management for cisplatin, carboplatin, and ormaplatin. Gynecol Oncol 1993;50:147–158.
Hopfer SM, Ziebka L, Sunderman FW Jr, Sporn JR, Greenberg BR. Direct analysis of platinum in plasma and urine by electrothermal atomic absorption spectrophotometry. Ann Clin Lab Sci 1989;19:389–396.
D’Addabbo A, Rubini G, Mele M, Lauriero F. A new method for assessing 99Tcm-MDP bone uptake from a bone scan image: quantitative measurement of radioactivity in global skeletal regions of interest. Nucl Med Commun 1992;13:55–60.
Raymakers JA, Savelkoul TJ, Hoekstra A, Visser WJ, van Rijk PP, Duursma SA. The value of local 99mTc(Sn)-MDP bone to soft tissue uptake ratio in osteoporosis, before and during fluoride therapy. Eur J Nucl Med 1990;16:157–160.
Chen YM, Yu CJ, Yang CH, Perng RP, Tsai CM, Shih JF, et al. A phase II study of oral vinorelbine in combination with cisplatin conducted in Taiwan in patients with unresectable localized or metastatic non-small cell lung carcinoma. Lung Cancer 2007;56:89–95.
Kausch I, Jiang H, Thode B, Doehn C, Kruger S, Jocham D. Inhibition of bcl-2 enhances the efficacy of chemotherapy in renal cell carcinoma. Eur Urol 2005;47:703–709.
Mastrangelo R, Tornesello A, Lasorella A, Iavarone A, Mastrangelo S, Riccardi R, et al. Optimal use of the 131-Imetaiodobenzylguanidine and cisplatin combination in advanced neuroblastoma. J Neurooncol 1997;31:153–158.
Sato T, Yoshioka S, Ogata Y, Abe Y, Takahashi J, Yamada K, et al. Analysis of contributing factors with high renal uptake of 99mTc-MDP after anti-cancer chemotherapy including cisplatin. Kaku Igaku 1996;33:1221–1226.
Igari H, Yamada K, Fuziwara T, Watai K, Kakei M, Matsui K, et al. Renal accumulation of technetium-99m-labeled bone imaging agents in patients treated with cisplatin (in Japanese). Nippon Igaku Hoshasen Gakkai Zasshi 1989;49:1017–1024.
Wilson MA. Musculoskeletal system. In: Wilson MA, editor. Textbook of nuclear medicine. Philadelphia: Lippincott-Raven; 1997. p. 13.
Fruhling J, Verbist A, Balikdjian D. Which diphosphonate for routine bone scintigraphy (MDP, HDP or DPD)? Nucl Med Commun 1986;7:415–425.
Esquis P, Consolo D, Magnin G, Pointaire P, Moretto P, Ynsa MD, et al. High intra-abdominal pressure enhances the penetration and antitumor effect of intraperitoneal cisplatin on experimental peritoneal carcinomatosis. Ann Surg 2006;244:106–112.
Thomas Dickey D, Muldoon LL, Kraemer DF, Neuwelt EA. Protection against cisplatin-induced ototoxicity by N-acetylcysteine in a rat model. Hear Res 2004;193:25–30.
Food and Drug Administration. Oncology Tools. Center of Drug Evaluation and Research. 2008-05-05. http://www.fda.gov/cder/cancer/aminalframe.htm. Accessed 5 May 2008.
Yonezawa A. Association between tubular toxicity of cisplatin and expression of organic cation transporter rOCT2 (Slc22a2) in the rat. Biochem Pharmacol 2005;70:1823–1831.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ozdogan, O., Ertay, T., Arslan, G. et al. Does cisplatin chemotherapy decrease the MDP uptake of normal bone? An experimental study. Ann Nucl Med 22, 357–362 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12149-007-0129-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12149-007-0129-5