Abstract
Objective
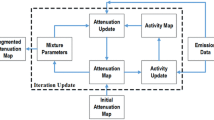
Recently, whole-body positron emission tomography (PET) examination has greatly developed. To reduce the overall examination time, the transmission scan has been increasingly shortened. Many noise-reduction processes have been developed for count-limited transmission data. Segmented attenuation correction (SAC) is one method by which the pixel values of transmission image are transformed into several groups. The median root prior-ordered subset convex (MRP-OSC) algorithm is another method that is applicable to control the noise level on the basis that the change of the pixel value is locally monotonous. This article presents an alternative approach on the basis of the Bayesian iterative reconstruction technique incorporating a median prior and an anatomical prior from the segmented μ-map for count-limited transmission data.
Methods
The proposed method is based on the Bayesian iterative reconstruction technique. The median prior and the anatomical prior are represented as two Gibbs distributions. The product of these distributions was used as a penalty function.
Results
In the thorax simulation study, the mean square error from the true transmission image of the presented method (5.74 × 10−5) was lower than MRP-OSC (6.72 × 10−5) and SAC (7.08 × 10−5). The results indicate that the noise of the image reconstructed from the proposed technique was decreased more than that of MRP-OSC without segmentation error such as that of an SAC image. In the thorax phantom study, the emission image that was corrected using the proposed technique displayed little noise and bias (27.42 ± 0.96 kBq/ml, calculated from a region of interest drawn on the liver of the phantom); it was very similar to the true value (28.0 kBq/ml).
Conclusions
The proposed method is effective for reducing propagation of noise from transmission data to emission data without loss of the quantitative accuracy of the PET image.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Xu EZ, Mullani NA, Gould KL, Anderson WL. A segmented attenuation correction for PET. J Nucl Med 1991;32:161–165.
Meikle SR, Dahlbom M, Cherry SR. Attenuation correction using count-limited transmission data in positron emission tomography. J Nucl Med 1993;34:143–150.
Xu M, Luk WK, Culter PD, Digby WM. Local threshold for segmented attenuation correction of PET imaging of the thorax. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci 1994;41:1532–1537.
Xu M, Cutler PD, Luk WK. Adaptive segmented attenuation correction for whole-body PET imaging. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci 1996;43:331–337.
Kitamura K, Iida H, Shidahara M, Miura S, Kanno I. Noise reduction in PET attenuation correction using non-linear Gaussian filters. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci 2000;47:994–999.
Zaidi H, Diaz-Gomez M, Boundraa A, Solosman DO. Fuzzy clustering-based segmented attenuation correction in whole-body PET imaging. Phys Med Biol 2002;47:1143–1160.
Lange K. Convergence of EM image reconstruction algorithms with Gibbs smoothing. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 1990;9:439–446.
Alenius S. On noise reduction in iterative reconstruction algorithm for positron emission tomography: median root prior. PhD thesis, Tampere University of Technology; 1999.
Alenius S, Ruotsalainen U, Astola J. Attenuation correction for PET using count-limited transmission images reconstructed with median root prior. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci 1999;46:646–651.
Lange K, Bahn M, Little R. A theoretical study of some maximum likelihood algorithms for emission and transmission tomography. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 1987;6:106–114.
Green PJ. Bayesian reconstructions from emission tomography data using a modified EM algorithm. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 1990;9:84–93.
Freedman NM, Bacharach SL, Carson RE, Price JC, Dilsizian V. Effect of smoothing during transmission processing on quantitative cardiac PET scans. J Nucl Med 1996;37:690–694.
Yavuz M, Fessler J. Penalized-likelihood estimators and noise analysis for random-precorrected PET transmission scans. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 1998;18:665–674.
Lipinski B, Herzog H, Kops ER, Oberschelp W, Mullergartner HW. Expectation maximization reconstruction of positron emission tomography images using anatomical magnetic resonance information. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 1997;16:129–136.
Alessio A, Kinahan P, Cheng P, Vesselle H, Karp J. PET/CT scanner instrumentation, challenges, and solutions. Radiol Clin North Am 2004;42:1017–1032.
Bettinardi V, Alenius S, Numminen P, Teras M, Gilardi MC, Fazio F, et al. Implementation and evaluation of an ordered subsets reconstruction algorithm for transmission PET studies using median root prior and inter-update median filtering. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2003;30:222–231.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sakaguchi, K., Shinohara, H., Hashimoto, T. et al. An iterative reconstruction using median root prior and anatomical prior from the segmented μ-map for count-limited transmission data in PET imaging. Ann Nucl Med 22, 269–279 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12149-007-0098-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12149-007-0098-8