Abstract
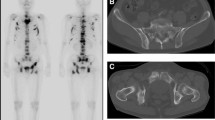
A 64-year-old woman presented with a painless breast mass. Tc-99m methoxyisobutylisonitrile scintigraphy of both breasts showed a local area of abnormal uptake in the left breast in 5 min and 2 h. A skeletal scan showed very intense concentration of activity in the primary breast tumor in the left breast. A left mastectomy and an axillary dissection were performed. The predominant histologic type of the mass was an osteosarcoma, and the diagnosis of a primary osteogenic sarcoma of the breast was made. Primary osteogenic sarcoma of the breast is rare and represents less than 1% of all primary breast malignancies.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Taillefer R, Robidoux A, Lambert R, Turpin S, Laperriere J. Technetium-99m-sestamibi prone scintimammography to detect primary breast cancer and axillary lymph node involvement. J Nucl Med 1995;36:1758–1765.
Maublant JC, Zhang Z, Rapp M, Ollier M, Michelot J, Veyre A. In vitro update of technetium-99m-teboroxime in carcinoma cell lines and normal cells: comparison with technetium-99m-sestamibi and thallium-201. J Nucl Med 1993;34:1949–1952.
Melloul M, Paz A, Ohana G, Laver O, Michalevich D, Koren R, et al. Double-phase 99m Tc-sestamibi scintimammography and trans-scan in diagnosing breast cancer. J Nucl Med 1999;40:376–380.
Maini L, de Notaristefani F, Tofani A, Lacopi F, Scjuto R, Semprebene A, et al. 99m Tc-MIBI scintimammography using a dedicated nuclear mammography. J Nucl Med 1999;40:46–51.
Thrall J, Ziessman H, editors. The requisites nuclear medicine. St. Louis: Mosby; 2001. p. 36–39.
Schwartz Z, Shanj J, Soskolne WA, Touma H, Amir D, Sela J. Uptake and biodistribution of technetium-99m-MDP during rat tibial bone repair. J Nucl Med 1993;34:104–108.
Zucker I, Charkes ND, Seidmon EJ, Maurer AH. Soft-tissue uptake of technetium-99m-MDP after prostate cryoablation. J Nucl Med 1997;38:525–528.
Ergun EL, Ceylan E. Soft tissue uptake observed on Tc-99m MDP bone scans: rare imaging patterns in two cases. Clin Nucl Med 2001;26:958–959.
Loutfi I, Collier BD, Mohammed AM. Nonosseous abnormalities on bone scans. J Nucl Med Technol 2003;31:149–153.
Papantoniou V, Sotiropoulou M, Stipsaneli E, Louvrou A, Feda H, Christodoulidou J, et al. Scintimammographic findings of in situ ductal breast carcinoma in a double-phase study with Tc-99m (V)DMSA and Tc-99m MIBI: value of Tc-99m (V)DMSA. Clin Nucl Med 2000;25:434–439.
Papantoniou V, Christodoulidou J, Papadaki E, Louvrou A, Feda H, Christodoulidou J, et al. 99mTc-(V)DMSA scintimammography in the assessment of breast lesions: comparative study with 99mTc-MIBI. Eur J Nucl Med 2001;28:923–928.
Palmedo H, Hensel J, Reinhardt M, Von Mallek D, Matthies A, Biersack HJ. Breast cancer imaging with PET and SPECT agents: an in vivo comparison. Nucl Med Biol 2002;29:809–815.
Ali I, Johns W, Gupta SM. Visualization of hepatic metastases of medullary thyroid carcinoma on Tc-99m MDP bone scintigraphy. Clin Nucl Med 2006;31:611–613.
Mariani G. Unexpected keys in cell biochemistry imaging: some lessons from technetium-99m-sestamibi. J Nucl Med 1996;37:536–538.
Taki J, Sumiya H, Asada N, Ueda Y, Tsuchiya H, Tonami N. Assessment of P-glycoprotein in patients with malignant bone and soft-tissue tumors using technetium-99m-MIBI scintigraphy. J Nucl Med 1998;39:1179–1184.
Schmidt E, Kett K, Anga B, Bodis J, Zambo K. Diagnostic value of 99mTc-methoxy-isobutyl-isonitril and 99mTc-methylene diphosphonate scintimammography in the preoperative evaluation of breast cancer. Orv Hetil 2003;144:787–792.
Ozcan Z, Burak Z, Erinc R, Dirlik A, Basdemir G, Sabah D, et al. Correlation of 99mTc-sestamibi uptake with blood-pool and osseous phase 99mTc-MDP uptake in malignant bone and soft-tissue tumours. Nucl Med Commun 2001;22:679–683.
Cancer B, Kitapcl M, Unlu M, Erbengi G, Calikoglu T, Gogus T, et al. Technetium-99m-MIBI uptake in benign and malignant bone lesions: a comparative study with technetium-99m-MDP. J Nucl Med 1992;33:319–324.
Alexandrakis MG, Kyriakou DS, Passam F, Koukouraki S, Karkavitsas N. Value of Tc-99m sestamibi scintigraphy in the detection of bone lesions in multiple myeloma: comparison with Tc-99m methylene diphosphonate. Ann Hematol 2001;80:349–353.
McPherson K, Steel CM, Dixon JM. ABC of breast diseases, breast cancer epidemiology, risk factors, and genetics. BMJ 2000;321:624–628.
Shimazu K, Funata N, Yamamoto Y, Mori T. Primary osteosarcoma arising in the colon: report of a case. Dis Colon Rectum 2001;44:1367–1370.
Minami H, Wakita N, Kawanishi Y, Kitano I, Sakata M, Shida T. Primary osteosarcoma of heart with severe congestive heart failure. Jpn J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2000;48:607–609.
Lee JS, Choi YD, Choi C. Primary testicular osteosarcoma with hydrocele. Virchows Arch 2004;445:210–213.
Olgyai G, Horvath V, Kocsis J, Buza N, Olah A. Extraskeletal osteosarcoma in the gallbladder. Magy Seb 2003;56:57–60.
Oluwasola AO, Adebamowo CA, Ezeome ER, Oduntan O, Akang EE. Osteogenic sarcoma of the breast: case report of a diagnostic dilemma. Afr J Med Med Sci 2000;30:129–131.
Hosoi H, Yoshioka M, Tanaka Y, Wada I, Nakao M, Maeda S, et al. Primary osteogenic sarcoma of the breast: report of a case. Nippon Geka Gakkai Zasshi 1989;90:1262–1265.
Roebuck DJ, Salo JK, Fahmy J. Breast metastases in osteosarcoma. Aust Radiol 1999;43:108–110.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, JG., Li, CL., Hao, RR. et al. Primary osteogenic sarcoma of breast detected on Tc-99m MIBI scintigraphy and Tc-99m MDP skeletal scintigraphy. Ann Nucl Med 22, 79–82 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12149-007-0074-3
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12149-007-0074-3