Abstract
Objectives
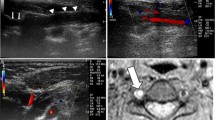
To explore the cerebral hemodynamics in subclavian steal syndrome, we examined the cerebral perfusion of seven patients with subclavian steal (one symptomatic and six asymptomatic) using single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) during resting, arm exercise, and acetazolamide-activated conditions.
Methods
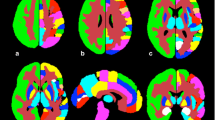
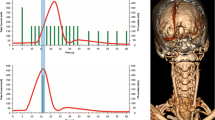
The regional CBF (rCBF) was measured with SPECT under all conditions, and region of interest (ROI) analysis was performed using a three-dimensional stereotaxic ROI template (3DSRT). We evaluated the relationship between arm exercise-induced rCBF change and (1) presence of subclavian artery stenosis, (2) vertebral reverse flow severity, (3) presence of vertebro-basilar insufficiency (VBI) symptoms, and (4) cerebrovascular reactivity (CVR) to acetazolamide.
Results
Overall, no arm exercise-induced rCBF reduction was observed on either the affected or the unaffected side, even in patients with severe vertebral reverse flow. One patient with VBI symptoms showed an arm exercise-induced global rCBF reduction in the cerebrum and cerebellum, whereas the other asymptomatic patients did not. The %rCBF changes in segments with severely impaired CVR (−8.6%± 10.7%, mean ± SD) were significantly lower than those in other segments with less impaired CVR (P < 0.01).
Conclusions
Our results suggest that subclavian steal is a benign condition in asymptomatic patients. On the other hand, arm exercise-induced rCBF reduction can occur in the cerebrum and cerebellum in patients with VBI symptoms possibly related to low CVR.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A Branchereau PE Magnen H Espinoza JM Bartoli (1991) ArticleTitleSubclavian artery stenosis: hemodynamic aspects and surgical outcome J Cardiovasc Surg 32 604–12 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK38%2Fkt1arug%3D%3D
M Hennerici C Klemm W Rautenberg (1996) ArticleTitleSubclavian steal phenomenon: a common vascular disorder with rare neurologic deficits Neurology 38 669–73
CF Lum PF Ilsen B Kawasaki (2004) ArticleTitleSubclavian steal syndrome Optometry 75 147–59 Occurrence Handle15058696
NM Bornstein A Krajewski JW Norris (1988) ArticleTitleBasilar artery blood flow in subclavian steal Can J Neurol Sci 15 417–9 Occurrence Handle3061632 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaL1M%2FovFChtw%3D%3D
MW Webster L Downs H Yonas MS Makaroun DL Steed (1994) ArticleTitleThe effect of arm exercise on regional cerebral blood flow in the subclavian steal syndrome Am J Surg 168 91–3 Occurrence Handle8053533 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0002-9610(94)80042-1 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK2czjtVGmtw%3D%3D
M Mase K Yamada T Matsumoto S Fujimoto A Iida (1999) ArticleTitleCerebral blood flow and metabolism of steal syndrome evaluated by PET Neurology 52 1515–6 Occurrence Handle10227652 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1M3kt1Wqsw%3D%3D
WJ Powers (1991) ArticleTitleCerebral hemodynamics in ischemic cerebrovascular disease Ann Neurol 29 231–40 Occurrence Handle2042939 Occurrence Handle10.1002/ana.410290302 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK3M3lsVSjsQ%3D%3D
S Vorstrup (1988) ArticleTitleTomographic cerebral blood flow measurements in patients with ischemic cerebrovascular disease and evaluation of the vasodilatory capacity by the acetazolamide test Acta Neurol Scand Suppl 114 1–48 Occurrence Handle3259361 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaL1c3hvF2ntw%3D%3D
H Yonas RR Pindzola (1994) ArticleTitlePhysiological determination of cerebral vascular reserves and its use in clinical management Cerebrovasc Brain Metab Rev 6 325–40 Occurrence Handle7880717 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK2M7os1emtA%3D%3D
CS Patlak RG Blasberg JD Fenstermacher (1983) ArticleTitleGraphical evaluation of blood-to-brain transfer constants from multiple-time uptake data J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 3 1–7 Occurrence Handle6822610 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaL3s7gvFegtA%3D%3D
CS Patlak R Blasberg (1985) ArticleTitleGraphical evaluation of blood-to-brain transfer constants from multiple-time uptake data Generalizations. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 5 584–90 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaL28%2FjsVahuw%3D%3D
NA Lassen AR Andersen L Friberg OB Paulson (1988) ArticleTitleThe retention of [99mTc]-d,l-HMPAO in the human brain bolus injection: a kinetic analysis J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 8 IssueIDsuppl 1 S13–22 Occurrence Handle3192638 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL1MXntF2ntw%3D%3D
R Takeuchi H Matsuda Y Yonekura H Sakahara J Konishi (1997) ArticleTitleNoninvasive quantitative measurements of regional cerebral blood flow using technetium-99m-L, L-ECD SPECT activated with acetazolamide: quantification analysis by equal-volume split 99mTc-ECD consecutive SPECT method J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 17 1020–32 Occurrence Handle9346426 Occurrence Handle10.1097/00004647-199710000-00003 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1c%2FgsVCisA%3D%3D
KJ Friston CD Frith PF Liddle RJ Dolan AA Lammertsma RS Frackowiak (1990) ArticleTitleThe relationship between global and local changes in PET scans J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 10 458–66 Occurrence Handle2347879 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK3c3ntVaquw%3D%3D
R Takeuchi H Matsuda K Yoshioka Y Yonekura (2004) ArticleTitleCerebral blood flow SPET in transient global amnesia with automated ROI analysis by 3D SRT Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 29 331–41 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s00259-001-0715-z Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XhvVCmsrc%3D
H Okazawa H Yamauchi K Sugimoto H Toyoda Y Kishibe M Takahashi (2001) ArticleTitleEffects of acetazolamide on cerebral blood flow, blood volume, and oxygen metabolism: a positron emission tomography study with healthy volunteers J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 21 1472–9 Occurrence Handle11740209 Occurrence Handle10.1097/00004647-200112000-00012 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XjvV2gsg%3D%3D
L Thomassen JA Aarli (1994) ArticleTitleSubclavian steal phenomenon: clinical and hemodynamic aspects Acta Neurol Scand 90 241–4 Occurrence Handle7839808 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK2M7ktFOltA%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1111/j.1600-0447.1994.tb01587.x
A Berni L Tromba S Cavaiola T Tombesi L Castellani (1997) ArticleTitleClassification of the subclavian steal syndrome with transcranial Doppler J Cardiovasc Surg 38 141–5 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK2szksVOmtQ%3D%3D
SS Kety CF Schmidt (1948) ArticleTitleThe effects of altered arterial tension of carbon dioxide and oxygen on the cerebral blood flow and carbon dioxide consumption of normal young men J Clin Invest 27 484–92 Occurrence Handle16695569 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaG3MXjvFGitg%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1172/JCI101995
H Ito I Kanno M Ibaraki J Hatazawa S Miura (2003) ArticleTitleChanges in human cerebral blood flow and cerebral blood volume during hypercapnia and hypocapnia measured by positron emission tomography J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 23 665–70 Occurrence Handle12796714 Occurrence Handle10.1097/01.WCB.0000067721.64998.F5
LL Levy JD Wallace JA Stolwijk ER Poindexter (1976) ArticleTitleCerebral blood flow regulation: vascular resistance adjustments in the circle of Willis Stroke 7 147–50 Occurrence Handle1265807 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaE287nvV2itQ%3D%3D
JF Jimenez-Bonilla R Quirce A Hernandez NK Vallina C Guede I Banzo et al. (2001) ArticleTitleAssessment of cerebral perfusion and cerebrovascular reserve in insulin-dependent diabetic patients without central neurological symptoms by means of 99mTc-HMPAO SPET with acetazolamide Euro J Nucl Med 28 1647–54 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s002590100595 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXnvFGhsbg%3D
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaneko, K., Fujimoto, S., Okada, Y. et al. SPECT evaluation of cerebral blood flow during arm exercise in patients with subclavian steal. Ann Nucl Med 21, 463–470 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12149-007-0054-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12149-007-0054-7