Abstract
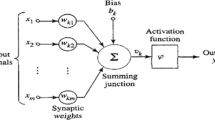
Precise weather forecasting is one of the most significant challenges in the modern world. The significant meteorological parameter, air temperature (TP), is often measured with limited spatial resolution, which necessitates the prediction of them at places far from monitoring stations and in the cases of accidentally missing data from the data loggers of monitoring stations. This study supports a non-location-specific model for air temperature prediction by combining a three-layer backpropagation artificial neural network (ANN) and meteorological data. The predictor identification method (PIM) & cross-validation method incorporated with the ANN model reveals density altitude (DA), heat index (HI), relative humidity (RH), and wet bulb temperature (WB) as potential input variables for the prediction of TP. DA and HI are strongly correlated to TP for the whole year for all types of land covers, whereas the dependency of TP on RH varies seasonally. RH is always a topping variable for air temperature prediction, which undoubtedly enhances the prediction accuracy. In pre-monsoon and monsoon, there are only three dominant input variables for predicting air temperature, i.e., DA, HI, and RH. In the post-monsoon, WB comes into the role of an additional predictor. The temperature prediction model shows a good agreement between ANN-estimated air temperature and measured air temperature, with the coefficient of determination value of 99.46%, 99.23%, 99.73%, and 99.18% for pre-monsoon, monsoon, post-monsoon, and winter season, respectively using the predictor set of potential input variables. Therefore, in this study, ANN modeling emerged as a reliable method for air temperature prediction.
















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors will certainly be available to answer readership eventual questions and enlarge the worldwide database of legal precedents.
References
Abdelkhalek HS, Medhat H, Ziedan I, Amal M (2019) Simulation and prediction for a satellite temperature sensors based on artificial neural network. J Aerospace Technol Manag 11. https://doi.org/10.5028/jatm.v11.1055
Ajina A, Jaya Christiyan KG, Bhat DN, Saxena K (2023) Prediction of weather forecasting using artificial neural networks. J Appl Res Technol 21(2):205–211. https://doi.org/10.22201/icat.24486736e.2023.21.2.1698
Baboo SS, Shereef IK (2010) An efficient weather forecasting system using artificial neural network. Int J Environ Sci Dev 1(4):321. https://doi.org/10.7763/IJESD.2010.V1.63
Bowden GJ, Dandy GC, Maier HR (2005) Input determination for neural network models in water resources applications. Part 1—background and methodology. J Hydrol 301(41–4):75–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2004.06.021
Bradley JB (1995) Neural networks: A comprehensive foundation: S. HAYKIN. New York: Macmillan College (IEEE Press Book) (1994). v+ 696 pp. ISBN 0–02–352761–7
Brahme A (2014) Comprehensive biomedical physics. Newnes. https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/veterinary-science-and-veterinary-medicine/artificial-neural-network. Accessed 22 June 2022
Census of India (2011) Provisional Population Totals. Office of the Registrar General and Census Commissioner, New Delhi. https://censusindia.gov.in/nada/index.php/catalog/1428. Accessed 18 Feb 2023
Chai H, Cheng W, Zhou C, Chen X, Ma X, Zhao S (2011) Analysis and comparison of spatial interpolation methods for temperature data in Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China. Nat Sci 3(12):999. https://doi.org/10.4236/ns.2011.312125
Cifuentes J, Marulanda G, Bello A, Reneses J (2020) Air temperature forecasting using machine learning techniques: a review. Energies 13(16):4215. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13164215
Devi CJ, Reddy BSP, Kumar KV, Reddy BM, Nayak NR (2012) ANN approach for weather prediction using back propagation. Int J Eng Trends Technol 3(1):19–23. http://www.ijettjournal.org/volume-3/issue-1/IJETT-V3I1P204.pdf. Accessed 06 Jan 2023
Dombayci ÖA, Gölcü M (2009) Daily means ambient temperature prediction using artificial neural network method: A case study of Turkey. Renew Energy 34(4):1158–1161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2008.07.007
Fahimi Nezhad E, Fallah Ghalhari G, Bayatani F (2019) Forecasting maximum seasonal temperature using artificial neural networks “Tehran case study.” Asia-Pac J Atmos Sci 55:145–153. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13143-018-0051-x
Green MA (2003) General temperature dependence of solar cell performance and implications for device modelling. Prog Photovoltaics Res Appl 11(5):333–340. https://doi.org/10.1002/pip.496
Johnstone C, Sulungu ED (2021) Application of neural network in prediction of temperature: a review. Neural Comput Appl 33(18):11487–11498. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-020-05582-3
Jovic S, Nedeljkovic B, Golubovic Z, Kostic N (2018) Evolutionary algorithm for reference evapotranspiration analysis. Comput Electron Agric 150:1–4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compag.2018.04.003
Jung SK, McDonald K (2011) Visual gene developer: a fully programmable bioinformatics software for synthetic gene optimization. BMC Bioinform 12:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-12-340
Kumar A, Elumalai SP (2015) Impacts of Urbanization on Urban Heat Island. July 28–29, 2015. Climate Change Combating Through Science and Technology. Indian Institute of Forest Management, Bhopal, p 301–310. ISBN: 978–81–211–0949–9
Kumar A, Mishra JR, Elumalai SP (2023) Importance of measuring the temperature of paved surfaces to study the changes in the microclimate of an urban area. J Build Perform Simul. https://doi.org/10.1080/19401493.2023.2232336
Kumar P, Kashyap PS (2013) Temperature forecasting using artificial neural networks (ANN). J Hill Agric 4(2):110–112. https://www.indianjournals.com/ijor.aspx?target=ijor:jha&volume=4&issue=2&article=011. Accessed 06 Jan 2023
Litta AJ, Idicula, MS, Mohanty UC (2013) Artificial neural network model in prediction of meteorological parameters during premonsoon thunderstorms. Int J Atmos Sci 2013. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/525383
Madni HA, Anwar Z, Shah MA (2017) Data mining techniques and applications—A decade review. In 2017 23rd international conference on automation and computing (ICAC). IEEE. IEEE, p 1–7. https://doi.org/10.23919/IConAC.2017.8082090
Marzo A, Trigo-Gonzalez M, Alonso-Montesinos J, Martínez-Durbán M, López G, Ferrada P, ... Batlles FJ (2017) Daily global solar radiation estimation in desert areas using daily extreme temperatures and extraterrestrial radiation. Renew Energy 113:303–311. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2017.01.061
Mba L, Meukam P, Kemajou A (2016) Application of artificial neural network for predicting hourly indoor air temperature and relative humidity in modern building in humid region. Energy Build 121:32–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enbuild.2016.03.046
McCulloch WS, Pitts W (1943) A logical calculus of the ideas immanent in nervous activity. Bull Math Biophys 5:115–133. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02478259
Mohamed ZE (2019) Using the artificial neural networks for prediction and validating solar radiation. J Egyptian Math Soc 27:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1186/s42787-019-0043-8
Nayak PC, Sudheer KP, Rangan DM, Ramasastri KS (2004) A neuro-fuzzy computing technique for modeling hydrological time series. J Hydrol 291(1–2):52–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2003.12.010
Nayak PC, Sudheer KP, Rangan DM, Ramasastri KS (2005) Short‐term flood forecasting with a neurofuzzy model. Water Resour Res 41(4). https://doi.org/10.1029/2004WR003562
Ozturk M, Salman O, Koc M (2011) Artificial neural network model for estimating the soil temperature. Can J Soil Sci 91(4):551–562. https://doi.org/10.4141/cjss10073
Pachauri RK, Allen MR, Barros VR, Broome J, Cramer W, Christ ., ... van Ypserle JP (2014) Climate change 2014: synthesis report. Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the fifth assessment report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (p. 151). Ipcc. https://www.ipcc.ch/site/assets/uploads/2018/05/SYR_AR5_FINAL_full_wcover.pdf. Accessed 05 Jan 2023
Price DT, McKenney DW, Nalder IA, Hutchinson MF, Kesteven JL (2000) A comparison of two statistical methods for spatial interpolation of Canadian monthly mean climate data. Agric for Meteorol 101(2–3):81–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-1923(99)00169-0
Sardans J, Peñuelas J, Estiarte M (2006) Warming and drought alter soil phosphatase activity and soil P availability in a Mediterranean shrubland. Plant Soil 289:227–238. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-006-9131-2
Schulte PA, Bhattacharya A, Butler CR, Chun HK, Jacklitsch B, Jacobs T, ... Wagner GR (2016) Advancing the framework for considering the effects of climate change on worker safety and health. J Occup Environ Hyg 13(11):847–865. https://doi.org/10.1080/15459624.2016.1179388
Sharma A (2000) Seasonal to interannual rainfall probabilistic forecasts for improved water supply management: Part 1—A strategy for system predictor identification. J Hydrol 239(1–4):232–239. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-1694(00)00346-2
Shrivastava VK, Shrivastava A, Sharma N, Mohanty SN, Pattanaik CR (2023) Deep learning model for temperature prediction: A case study in New Delhi. J Forecast. https://doi.org/10.1002/for.2966
Singh S, Elumalai SP, Pal AK (2016) Rain pH estimation based on the particulate matter pollutants and wet deposition study. Sci Total Environ 563:293–301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.04.066
Smith DM, Cusack S, Colman AW, Folland CK, Harris GR, Murphy JM (2007) Improved surface temperature prediction for the coming decade from a global climate model. Science 317(5839):796–799. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1139540
Tadeusiewicz R (1995) Neural networks: A comprehensive foundation: by Simon HAYKIN; Macmillan College Publishing, New York, USA; IEEE Press, New York, USA; IEEE Computer Society Press, Los Alamitos, CA, USA; 1994; 696 pp.; $69–95; ISBN: 0–02–352761–7
Tang C, Crosby BT, Wheaton JM, Piechota TC (2012) Assessing streamflow sensitivity to temperature increases in the Salmon River Basin, Idaho. Global Planet Change 88:32–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloplacha.2012.03.002
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the Department of Environmental Science and Engineering at the Indian Institute of Technology (Indian School of Mines), Dhanbad, for logistical support. We pay our sincere thanks to Dr. Ravi Sahu (Ph.D., IIT-ISM Dhanbad), Dr. Anil Kumar (Ph.D., IIT-ISM Dhanbad), Dr. Sandeep Kumar Chaudhary (Ph.D., IIT-ISM Dhanbad) & Mr. Ambasht Kumar (Research Scholar, IIT-ISM Dhanbad) for their help in conducting field studies. We also want to thank Dr. Megha Tyagi (Jr. Scientist, CSE New Delhi) and Ms. Nidhi (Research Scholar, IIT-ISM Dhanbad) for their helpful feedback and support. We express our sincere thanks to the reviewers for helping to bring this manuscript to the present level.
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Kumar A. conceived of the presented idea, developed the theory and performed the measurements and analysis. Elumalai S. P. supervised and encouraged the findings of this work. All authors discussed the results and contributed to the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Communicated by: Hassan Babaie
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, A., Elumalai, S.P. Application of artificial neural network to screen out the dominant meteorological parameters for prediction of air temperature. Earth Sci Inform 16, 3697–3716 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-023-01107-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-023-01107-3