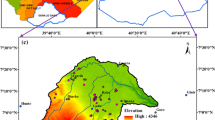
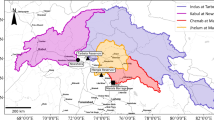
Abstract
River-aquifer interaction is a key component of the hydrological cycle that affects water resources and quality. Recently, the application of integrated models to assess interaction has been increasing. However, calibration and uncertainty analysis of coupled models has been a challenge, especially for large-scale applications. In this study, we used PESTPP-IES, an implementation of the Gauss-Levenberg–Marquardt iterative ensemble smoother, to calibrate and quantify the uncertainty of an integrated SWAT-MODFLOW model for watershed-scale river aquifer interaction assessment. SWAT-MODFLOW combines the Soil and Water Assessment Tool (SWAT), a widely used watershed model, with a three-dimensional groundwater flow model (MODFLOW). The calibration performance of the model was evaluated, and the uncertainty in the parameters and observed ensemble, including the uncertainty in forecasting groundwater levels, was assessed. The results showed that the technique could enhance the model performance and reduce uncertainty. However, the results also revealed some limitations and biases, such as overestimating the groundwater levels in most monitoring wells. These biases were attributed to the limited availability of groundwater level in the first year of the calibration and the uncertainty in groundwater flow model parameters. The river-aquifer interactions analysis shows that water exchange occurs in almost all cells along the river, with most of the high-elevation areas receiving groundwater and flatter regions discharging water to the aquifer. The study showed that PESTPP-IES is a robust technique for watershed-scale river-aquifer modeling that can ensure model calibration and parameter uncertainty analysis. The findings of this study can be used to improve water resources management in watersheds and help decision-makers in making informed decisions.













Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
AceroTriana JS, Chu ML, Guzman JA et al (2019) Beyond model metrics: The perils of calibrating hydrologic models. J Hydrol 578:124032. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JHYDROL.2019.124032
Aliyari F, Bailey RT, Tasdighi A et al (2019) Coupled SWAT-MODFLOW model for large-scale mixed agro-urban river basins. Environ Model Softw 115:200–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsoft.2019.02.014
Anderson MP, Woessner WW, Hunt RJ (2015) Applied groundwater modeling simulation of flow and advective transport, 2nd ed. Academic Press, Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1016/C2009-0-21563-7
Aouissi J, Benabdallah S, Lili Chabaâne Z, Cudennec C (2016) Evaluation of potential evapotranspiration assessment methods for hydrological modelling with SWAT—Application in data-scarce rural Tunisia. Agric Water Manag 174:39–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2016.03.004
Arnold JG, Allen PM, Bernhardt G (1993) A comprehensive surface-groundwater flow model. J Hydrol 142:47–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-1694(93)90004-S
Arnold JG, Srinivasan R, Muttiah RS, Williams JR (1998) Large area hydrologic modeling and assessment part I: model development. J Am Water Resour Assoc 34:73–89. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1752-1688.1998.tb05961.x
Arnold JG, Moriasi DN, Gassman PW et al (2012) SWAT: Model use, calibration, and validation. Trans ASABE 55:1491–1508
Bailey RT, Wible TC, Arabi M et al (2016) Assessing regional-scale spatio-temporal patterns of groundwater-surface water interactions using a coupled SWAT-MODFLOW model. Hydrol Process 143:103662. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.10933
Baratelli F, Flipo N, Moatar F (2016) Estimation of stream-aquifer exchanges at regional scale using a distributed model: Sensitivity to in-stream water level fluctuations, riverbed elevation and roughness. J Hydrol 542:686–703. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2016.09.041
Barthel R, Banzhaf S (2016) Groundwater and Surface Water Interaction at the Regional-scale – A Review with Focus on Regional Integrated Models. Water Resour Manag 30:1–32
Bauwe A, Kahle P, Lennartz B (2016) Hydrologic evaluation of the curve number and Green and Ampt infiltration methods by applying Hooghoudt and Kirkham tile drain equations using SWAT. J Hydrol 537:311–321. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2016.03.054
Beven K (2007) Environmental modelling: an uncertain future?, 1st edn. CRC Press, London. https://doi.org/10.1201/9781482288575
Bocquet M, Sakov P (2013) Joint state and parameter estimation with an iterative ensemble Kalman smoother. Nonlinear Process Geophys 20:803–818. https://doi.org/10.5194/npg-20-803-2013
Bocquet M, Sakov P (2014) An iterative ensemble Kalman smoother. Q J R Meteorol Soc 140:1521–1535. https://doi.org/10.1002/qj.2236
Brunner P, Simmons CT (2012) HydroGeoSphere: A Fully Integrated, Physically Based Hydrological Model. Ground Water 50:170–176. https://doi.org/10.1111/J.1745-6584.2011.00882.X
Chen Y, Oliver DS (2013) Levenberg–Marquardt forms of the iterative ensemble smoother for efficient history matching and uncertainty quantification. Comput Geosci 17:689–703. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10596-013-9351-5
Chen Y, Oliver DS (2017) Localization and regularization for iterative ensemble smoothers. Comput Geosci 21:13–30. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10596-016-9599-7
Cheng Q-B, Reinhardt-Imjela C, Chen X et al (2016) Improvement and comparison of the rainfall–runoff methods in SWAT at the monsoonal watershed of Baocun, Eastern China. Hydrol Sci J 61:1460–1476. https://doi.org/10.1080/02626667.2015.1051485
Chung I-M, Lee J, Kim NW et al (2014) Estimating exploitable amount of groundwater abstraction using an integrated surface water-groundwater model: Mihocheon watershed. South Korea Hydrol Sci J 60:141217125340005. https://doi.org/10.1080/02626667.2014.980261
Chunn D, Faramarzi M, Smerdon B, Alessi D (2019) Application of an Integrated SWAT–MODFLOW Model to Evaluate Potential Impacts of Climate Change and Water Withdrawals on Groundwater-Surface Water Interactions in West-Central Alberta. Water 11:110. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11010110
Crestani E, Camporese M, Baú D, Salandin P (2013) Ensemble Kalman filter versus ensemble smoother for assessing hydraulic conductivity via tracer test data assimilation. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 17:1517–1531. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-17-1517-2013
Doherty J (2004) PEST model-independent parameter estimation user manual. Watermark Numer Comput Brisbane, Aust 3338:3349
Emerick AA, Reynolds AC (2012) History matching time-lapse seismic data using the ensemble Kalman filter with multiple data assimilations. Comput Geosci 16:639–659. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10596-012-9275-5
Emerick AA, Reynolds AC (2013) Ensemble smoother with multiple data assimilation. Comput Geosci 55:3–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cageo.2012.03.011
Evensen G (1994) Sequential data assimilation with a nonlinear quasi-geostrophic model using Monte Carlo methods to forecast error statistics. J Geophys Res 99:10143. https://doi.org/10.1029/94JC00572
Evensen G (2003) The Ensemble Kalman Filter: theoretical formulation and practical implementation. Ocean Dyn 53:343–367. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10236-003-0036-9
Ficklin DL, Zhang M (2013) A Comparison of the Curve Number and Green-Ampt Models in an Agricultural Watershed. Trans ASABE 56:61–69. https://doi.org/10.13031/2013.42590
Fleckenstein JH, Krause S, Hannah DM, Boano F (2010) Groundwater-surface water interactions: New methods and models to improve understanding of processes and dynamics. Adv Water Resour 33:1291–1295. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advwatres.2010.09.011
Flipo N, Mouhri A, Labarthe B et al (2014) Continental hydrosystem modelling: the concept of nested stream-aquifer interfaces. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 18:3121–3149. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-18-3121-2014
Freeze RA (1972) Role of subsurface flow in generating surface runoff: 1. Base flow contributions to channel flow. Water Resour Res 8:609–623. https://doi.org/10.1029/WR008i003p00609
Furman A (2008) Modeling Coupled Surface-Subsurface Flow Processes: A Review. Vadose Zo J 7:741–756. https://doi.org/10.2136/vzj2007.0065
Gao F, Feng G, Han M et al (2019) Assessment of Surface Water Resources in the Big Sunflower River Watershed Using Coupled SWAT–MODFLOW Model. Water 11:528. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11030528
Green H, Ampt GA (1912) Studies on Soil Physics: Part II — The Permeability of an Ideal Soil to Air and Water. J Agric Sci 5:1–26. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0021859600001751
Gupta HV, Sorooshian S, Yapo PO (1999) Status of Automatic Calibration for Hydrologic Models: Comparison with Multilevel Expert Calibration. J Hydrol Eng 4:135–143. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)1084-0699(1999)4:2(135)
Guzman JA, Moriasi DN, Gowda PH et al (2015) A model integration framework for linking SWAT and MODFLOW. Environ Model Softw 73:103–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsoft.2015.08.011
Hanke M (1997) A regularizing Levenberg - Marquardt scheme, with applications to inverse groundwater filtration problems. Inverse Probl 13:79–95. https://doi.org/10.1088/0266-5611/13/1/007
Harbaugh AW (2005) MODFLOW-2005, The U.S. Geological Survey modular ground-water model — the ground-water flow process. US Department of the Interior, US Geological Survey, Reston, Virginia
Hargreaves George H, Samani Zohrab A (1985) Reference Crop Evapotranspiration from Temperature. Appl Eng Agric 1:96–99. https://doi.org/10.13031/2013.26773
Hassan AE, Bekhit HM, Chapman JB (2008) Uncertainty assessment of a stochastic groundwater flow model using GLUE analysis. J Hydrol 362:89–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JHYDROL.2008.08.017
Her Y, Frankenberger J, Chaubey I, Srinivasan R (2015) Threshold effects in HRU definition of the soil and water assessment tool. Trans ASABE 58:367–378. https://doi.org/10.13031/trans.58.10805
Herrera PA, Marazuela MA, Hofmann T (2022) Parameter estimation and uncertainty analysis in hydrological modeling. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Water 9:1–23. https://doi.org/10.1002/wat2.1569
Jobson HE, Harbaugh AW (1999) Modifications to the diffusion analogy surface water flow model (DAFLOW) for coupling to the modular finite-difference groundwater flow model (MODFLOW). US Geol Surv Open-File Rep 99–217:99–218
Jobson HE (1989) Users manual for an open-channel streamflow model based on the diffusion analogy. Water-Resources Investigations. Rep. 89–4133, U.S. Geological Survey
Jung C-G, Lee D-R, Moon J-W (2016) Comparison of the Penman-Monteith method and regional calibration of the Hargreaves equation for actual evapotranspiration using SWAT-simulated results in the Seolma-cheon basin, South Korea. Hydrol Sci J 61:793–800. https://doi.org/10.1080/02626667.2014.943231
Kim NW, Chung IM, Won YS, Arnold JG (2008) Development and application of the integrated SWAT–MODFLOW model. J Hydrol 356:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2008.02.024
King KW, Arnold JG, Bingner RL (1999) Comparison of Green-Ampt and Curve Number Methods on Goodwin Creek Watershed using SWAT. Trans ASAE 42:919–926. https://doi.org/10.13031/2013.13272
KMA (2022) Korea Meteorological Administration. In: Korea Meteorol. Adm. http://www.kma.go.kr/eng/biz/observation_01.jsp. Accessed 30 Nov 2022
Kolditz O, Bauer S, Bilke L et al (2012) OpenGeoSys: an open-source initiative for numerical simulation of thermo-hydro-mechanical/chemical (THM/C) processes in porous media. Environ Earth Sci 67:589–599. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-012-1546-x
Kollet SJ, Maxwell RM (2006) Integrated surface–groundwater flow modeling: A free-surface overland flow boundary condition in a parallel groundwater flow model. Adv Water Resour 29:945–958. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advwatres.2005.08.006
Kumar N, Singh SK, Srivastava PK, Narsimlu B (2017) SWAT Model calibration and uncertainty analysis for streamflow prediction of the Tons River Basin, India, using Sequential Uncertainty Fitting (SUFI-2) algorithm. Model Earth Syst Environ 3:30. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-017-0306-z
Laurent F, Ruelland D (2011) Assessing impacts of alternative land use and agricultural practices on nitrate pollution at the catchment scale. J Hydrol 409:440–450. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JHYDROL.2011.08.041
Leavesley GH, Lichty RW, Troutman BM, Saindon LG (1983) Precipitation-Runoff Modeling System: User’s Manual
Li L, Puzel R, Davis A (2018) Data assimilation in groundwater modelling: ensemble Kalman filter versus ensemble smoothers. Hydrol Process 32:2020–2029. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.13127
Liu W, Bailey RT, Andersen HE et al (2020) Assessing the impacts of groundwater abstractions on flow regime and stream biota: Combining SWAT-MODFLOW with flow-biota empirical models. Sci Total Environ 706:135702. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135702
Liu W, Park S, Bailey RT et al (2020b) Quantifying the streamflow response to groundwater abstractions for irrigation or drinking water at catchment scale using SWAT and SWAT–MODFLOW. Environ Sci Eur 32:1–25. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12302-020-00395-6
Markstrom SL, Niswonger RG, Regan RS, et al (2008) GSFLOW—Coupled Ground-Water and Surface-Water Flow Model Based on the Integration of the Precipitation-Runoff Modeling System (PRMS) and the Modular Ground-Water Flow Model (MODFLOW-2005)
MOE (2018) Basin groundwater investigation at Uiwang, Gwacheon, and Seongnam region. https://policy.nl.go.kr/search/searchDetail.do?rec_key=UH1_00000127563316. Accessed 24 May 2022
Moges E, Demissie Y, Larsen L, Yassin F (2020a) Review: Sources of Hydrological Model Uncertainties and Advances in Their Analysis. Water 13:28. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13010028
Moges E, Demissie Y, Li H (2020) Uncertainty propagation in coupled hydrological models using winding stairs and null-space Monte Carlo methods. J Hydrol 589:125341. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.125341
Molina-Navarro E, Bailey RT, Andersen HE et al (2019) Comparison of abstraction scenarios simulated by SWAT and SWAT-MODFLOW. Hydrol Sci J 64:434–454. https://doi.org/10.1080/02626667.2019.1590583
Monteith JL (1965). Evaporation and environment. In Symposia of the society for experimental biology, vol. 19. Cambridge University Press (CUP) Cambridge, pp 205–234
Moriasi DN, Arnold JG, Van Liew MW et al (2007) Model evaluation guidelines for systematic quantification of accuracy in watershed simulations. Trans ASABE 50:885–900. https://doi.org/10.13031/2013.23153
Nash JEE, Sutcliffe JVV (1970) River flow forecasting through conceptual models part I — A discussion of principles. J Hydrol 10:282–290. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-1694(70)90255-6
NGII (2022) National Geographic Information Institute. https://www.ngii.go.kr/eng/main.do. Accessed 24 May 2022
NIAS (2022) National Institute of Agricultural Sciences. http://www.naas.go.kr/english/. Accessed 5 Dec 2022
Niswonger RG, Panday S, Motomu I (2011) MODFLOW-NWT, A Newton Formulation for MODFLOW-2005. USA, U.S, Geological Survey, Reston, Virginia
Ntona MM, Busico G, Mastrocicco M, Kazakis N (2022) Modeling groundwater and surface water interaction: An overview of current status and future challenges. Sci Total Environ 846:157355. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.157355
Pasetto D, Camporese M, Putti M (2012) Ensemble Kalman filter versus particle filter for a physically-based coupled surface–subsurface model. Adv Water Resour 47:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advwatres.2012.06.009
Priestley CHB, Taylor RJ (1972) On the Assessment of Surface Heat Flux and Evaporation Using Large-Scale Parameters. Mon Weather Rev 100:81–92. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0493(1972)100%3c0081:OTAOSH%3e2.3.CO;2
Renard B, Kavetski D, Kuczera G et al (2010) Understanding predictive uncertainty in hydrologic modeling: The challenge of identifying input and structural errors. Water Resour Res 46:1–22. https://doi.org/10.1029/2009WR008328
Schaffranek RW, Baltzer RA, Goldberg DE (1981) A model for simulation of flow in singular and interconnected channels. US Department of the Interior, Geological Survey
SCS (1972) National engineering handbook, Supplement A, Section 4, Chapter 10, Soil Conservation Service, USDA, Washington, DC
Sorooshian S, Duan Q, Gupta VK (1993) Calibration of rainfall-runoff models: Application of global optimization to the Sacramento Soil Moisture Accounting Model. Water Resour Res 29:1185–1194. https://doi.org/10.1029/92WR02617
Surfleet CG, Tullos D (2013) Uncertainty in hydrologic modelling for estimating hydrologic response due to climate change (Santiam River, Oregon). Hydrol Process 27:3560–3576. https://doi.org/10.1002/HYP.9485
Swain ED, Wexler EJ (1993) A coupled surface-water and ground-water flow model for simulation of stream-aquifer interaction. US Geological Survey; Books and Open-File Reports Section [distributor] 92-138
Taie Semiromi M, Koch M (2019) Analysis of spatio-temporal variability of surface–groundwater interactions in the Gharehsoo river basin, Iran, using a coupled SWAT-MODFLOW model. Environ Earth Sci 78:201. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-019-8206-3
Tian Y, Zheng Y, Wu B et al (2015) Modeling surface water-groundwater interaction in arid and semi-arid regions with intensive agriculture. Environ Model Softw 63:170–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENVSOFT.2014.10.011
van Leeuwen PJ, Evensen G (1996) Data Assimilation and Inverse Methods in Terms of a Probabilistic Formulation. Mon Weather Rev 124:2898–2913. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0493(1996)124%3c2898:DAAIMI%3e2.0.CO;2
WAMIS (2022) Water Resources Management Information System (WAMIS). http://www.wamis.go.kr/ . Accessed 5 Dec 2022
Wang Y, Chen N (2021) Recent progress in coupled surface–ground water models and their potential in watershed hydro-biogeochemical studies: A review. Watershed Ecol Environ 3:17–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wsee.2021.04.001
Wei X, Bailey RT, Records RM et al (2019) Comprehensive simulation of nitrate transport in coupled surface-subsurface hydrologic systems using the linked SWAT-MODFLOW-RT3D model. Environ Model Softw 122:104242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsoft.2018.06.012
White JT (2018) A model-independent iterative ensemble smoother for efficient history-matching and uncertainty quantification in very high dimensions. Environ Model Softw 109:191–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsoft.2018.06.009
White JT, Fienen MN, Doherty JE (2016) A python framework for environmental model uncertainty analysis. Environ Model Softw 85:217–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsoft.2016.08.017
White JT, Hunt RJ, Fienen MN et al (2020) Approaches to highly parameterized inversion: PEST++ Version 5, a software suite for parameter estimation, uncertainty analysis, management optimization and sensitivity analysis. US Geological Survey 7-C26
Wu B, Zheng Y, Tian Y et al (2014) Systematic assessment of the uncertainty in integrated surface water-groundwater modeling based on the probabilistic collocation method. Water Resour Res 50:5848–5865. https://doi.org/10.1002/2014WR015366
Yifru BA, Chung I-M, Kim M-G, Chang SW (2020) Assessment of Groundwater Recharge in Agro-Urban Watersheds Using Integrated SWAT-MODFLOW Model. Sustainability 12:6593. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12166593
Yifru BA, Chung I-M, Kim M-G, Chang SW (2022) Assessing the effect of urbanization on regional-scale surface water-groundwater interaction and nitrate transport. Sci Rep 12:12520. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-16134-1
Zamani M, Shrestha NK, Akhtar T et al (2021) Advancing model calibration and uncertainty analysis of SWAT models using cloud computing infrastructure: LCC-SWAT. J Hydroinformatics 23:1–15. https://doi.org/10.2166/hydro.2020.066
Funding
This work was supported by Korea Environment Industry & Technology Institute (KEITI) through Aquatic Ecosystem Conservation Research Program, funded by Korea Ministry of Environment (MOE) (2020003030004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Bisrat Ayalew Yifru authored the majority of the manuscript, while Seoro Lee developed the evaluation experiments. Kyoung Jae Lim provided revisions and enhancements to the discussion section of the paper. All authors contributed to the review of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Communicated by H. Babaie.
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yifru, B.A., Lee, S. & Lim, K.J. Calibration and uncertainty analysis of integrated SWAT-MODFLOW model based on iterative ensemble smoother method for watershed scale river-aquifer interactions assessment. Earth Sci Inform 16, 3545–3561 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-023-01071-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-023-01071-y