Abstract
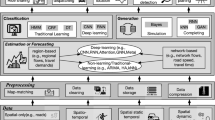
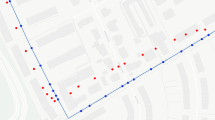
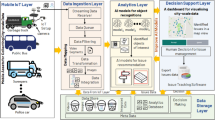
The data mining on GNSS network RTK trajectories could be used to reveal the user behavior pattern, assess the local economy development and even improve the work plan. While the identification of the survey points by stationary and moving states information, is one of the most critical step of data preparation. The performance of traditional DBSCAN approach is not desired since it only supports the horizontal geographic distance information. In this paper an improved DBSCAN clustering is proposed. A novel set of parameters as the change of heights, number of satellites, fixing statues, are taken into consideration as well as the traditional ones as time interval, horizontal distance and minimal neighbors. After the clustering, the centroid analysis is applied to determine the survey points from each cluster. Both the simulated and real data experiments from HNCORS GNSS network RTK services are carried out to test the performance. The results show that the identification rate could reach 86.3%, which is increased by 15.2% compared to the traditional approach. Meanwhile, the best identification recall rate 90.6% occurs for road style surveying activities. Moreover, this approach could also be able to find the invalid or abnormal surveys.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Some or all data and materials that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Ao M, Dong M, Chu B, Zeng X, Li C (2019) Revealing the user behavior pattern using HNCORS RTK location big data. IEEE Access 7:30302–30312. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2902577
Aslam NS, Cheng T, Cheshire J (2019) A high-precision heuristic model to detect home and work locations from smart card data. Geo Spat Inf Sci 22(1):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1080/10095020.2018.1545884
Bermingham L, Lee I (2018) A probabilistic stop and move classifier for noisy GPS trajectories. Data Min Knowl Disc 32(6):1634–1662. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10618-018-0568-8
Bhattacharya T, Kulik L, Bailey J (2015) Automatically recognizing places of interest from unreliable GPS data using spatio-temporal density estimation and line intersections. Pervasive Mob Comput 19:86–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmcj.2014.08.003
Boonchoo T, Ao X, Liu Y, Zhao Z, Zhuang F, He Q (2019) Grid-based DBSCAN: Indexing and inference. Pattern Recogn 90:271–284. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2019.01.034
Chen R, Zhao S, Liang M (2021) A Fast Multiscale Clustering Approach Based on DBSCAN. Wirel Commun Mob Com. 2021: ID4071177. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/4071177.
Cheng D, Yue G, Pei T, Wu M (2021) Clustering indoor positioning data using E-DBSCAN. ISPRS Int J Geo-Inf 10(10):669. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi10100669
Dong M, Hua L, Yin H, Liu Z, Chen C, Ao M, Li C, Chu B, Zeng X (2019) Specification for realtime kinematic surveys using Hunan global navigation satellite reference stations network. Administration of Market Regulation of Hunan Province, Changsha, China
Feng Z, Zhu Y (2016) A survey on trajectory data mining: Techniques and applications. IEEE Access 4:2056–2067. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2016.2553681
Gholizadeh N, Saadatfar H, Hanafi N (2021) K-DBSCAN: An improved DBSCAN algorithm for big data. J Super Comput 77:6214–6235. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-020-03524-3
Grinberger AY, Shoval N (2015) A temporal-contextual analysis of urban dynamics using location-based data. Int J Geogr Inf Sci 29(11):1969–1987. https://doi.org/10.1080/13658816.2015.1049951
Gülal E, Erdoğan H, Tiryakioğlu I (2013) Research on the stability analysis of GNSS reference stations network by time series analysis. Digit Signal Process 23(6):1945–1957. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dsp.2013.06.014
Huang G, He J, Zhou W, Huang G, Guo L, Zhou Z, Tang F (2016) Discovery of stop regions for understanding repeat travel behaviors of moving objects. J Comput Syst Sci 82(4):582–593. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcss.2015.10.006
Huang Y, Xiao Z, Wang D, Jiang H, Wu D (2020) Exploring individual travel patterns across private car trajectory data. IEEE Trans Intell Transp Syst 21(12):5036–5050. https://doi.org/10.1109/tits.2019.2948188
Keller A, Krisp JM, Ding L (2020) Extracting commuter-specific destination hot spots from trip destination data - comparing the boro taxi service with Citi bike in NYC. Geo Spat Inf Sci 23(2):141–152. https://doi.org/10.1080/10095020.2019.1621008
Khan KA, Akhter G, Ahmad Z (2011) An activex control for embedding GPS capability in custom applications. GPS Solut 15:433–439. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-011-0236-6
Kim J, Mahmassani MS (2015) Spatial and temporal characterization of travel patterns in a traffic network using vehicle trajectories. Transp Res Part C Emerg Technol 59:375–390. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trc.2015.07.010
Kranzinger S, Rehrl K, Grőchenig S (2020) Why did a vehicle stop? a methodology for detection and classification of stops in vehicle trajectories. Int J Geogr Inf Sci 34(10):1953–1979. https://doi.org/10.1080/13658816.2020.1740999
Kumar D, Wu H, Rajasegarar S, Leckie C, Krishnaswamy S, Palaniswami M (2018) Fast and scalable big data trajectory clustering for understanding urban mobility. IEEE Trans Intell Transp Syst 19(11):3709–3722. https://doi.org/10.1109/TITS.2018.2854775
Latifi-Pakdehi A, Daneshpour N (2021) DBHC: A DBSCAN-based hierarchical clustering algorithm. Data Knowl Eng 135:101922. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.datak.2021.101922
Lee HT, Lee JS, Yang H, Cho IS (2021) An AIS data-driven approach to analyze the pattern of ship trajectories in ports using the DBSCAN algorithm. Appl Sci 11(2):799. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11020799
Li X, Ceikute V, Jensen CS, Tan and K L, (2013) Effective online group discovery in trajectory databases. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 25(12):2752–2766. https://doi.org/10.1109/TKDE.2012.193
Li H, Liu J, Wu K, Yang Z, Liu RW, Xiong N (2018) Spatio-temporal vessel trajectory clustering based on data mapping and density. IEEE Access 6:58939–58954. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2018.2866364
Li C, Zhang Y, Ao M, Liu Q, Tang C (2017) Integrated services management and statistic system for HNCORS. IEEE 2nd International Conference on Cloud Computing and Big Data Analysis (ICCCBDA), China, Chengdu, 473–477. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCCBDA.2017.7951960
Luo T, Zheng X, Xu G, Fu K, Ren W (2017) An improved DBSCAN algorithm to detect stops in individual trajectories. ISPRS Int J GeoInf 6(3):63. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi6030063
Ma X, Wu YJ, Wang Y, Chen F, Liu J (2013) Mining smart card data for transit riders’ travel patterns. Transp Res Part C Emerg Technol 36:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trc.2013.07.010
Manzano-Agugliaro F, Castro-Garcia M, Pèrez-Romero AM, Garcìa-Cruz A, Novas N, Salmeròn-Manzano E (2016) Alternative methods for teaching cadastre and remote sensing. Surv Rev 48(351):450–459. https://doi.org/10.1179/1752270615y.0000000046
Mao Y, Zhong H, Qi H, Ping P, Li X (2017) An adaptive trajectory clustering method based on grid and density in mobile pattern analysis. Sensors 17(9):2013. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17092013
Minatel D, Ferreira V, Lopes AA (2021) Local-entity resolution for building location-based social networks by using stay points. Theor Comput Sci 851:62–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tcs.2020.10.013
Mousavi S, Harwood A, Karunasekera S, Maghrebi M (2017) Geometry of interest (GOI): spatio-temporal destination extraction and partitioning in GPS trajectory data. J Ambient Intell Human Comput 8(3):419–434. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-016-0400-5
Parent C, Spaccapietra S, Renso C, Andrienko G, Andrienko N, Bogorny V, Damiani ML, Gkoulalas A, Macedo J, Pelekis N, Theodoridis Y, Yan and Z, (2013) Semantic trajectories modeling and analysis. ACM Comput Surv 45(4):1–32. https://doi.org/10.1145/2501654.2501656
Park B, Kee C (2010) The compact network rtk method: An effective solution to reduce GNSS temporal and spatial decorrelation error. J Navig 63(2):343–362. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0373463309990440
Pérez-Torres R, Torres-Huitzil C, Galeana-Zapién H (2016) Full on device stay points detection in smartphones for location-based mobile applications. Sensors 16(10):1693. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16101693
Pérez-Torres R, Torres-Huitzil C, Galeana-Zapién H (2019) A cognitive inspired event-based control for power-aware human mobility analysis in iot devices. Sensors 19(4):832. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19040832
Ros F, Guillaume S, Riad R, Hajji ME (2022) Detection of natural clusters via S-DBSCAN a Self-tuning version of DBSCAN. Knowl Based Syst. 241:108288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2022.108288
Schubert E, Sander J, Ester M, Kriegel HP, Xu X (2017) DBSCAN revisited, revisited: Why and how you should (still) use DBSCAN. ACM Trans on Database Systems 42(3):1–21. https://doi.org/10.1145/3068335
Servizi V, Petersen NC, Pereira FC, Nielsen OA (2020) Stop detection for smartphone-based travel surveys using geo-spatial context and artificial neural networks. Transp Res Part C Emerg Technol 121:102834. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trc.2020.102834
Shi K, Xu M, Jin H, Qiao T, Yang X, Zheng N, Xu J, Choo RK (2020) A novel file carving algorithm for National Marine Electronics Association (NMEA) logs in GPS forensics. Digit Investig 23:11–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diin.2017.08.004
Sun D, Leurent F, Xie X (2021a) Mining vehicle trajectories to discover individual significant places: Case study using floating car data in the Paris region. Transp Res Rec 2675(8):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1177/0361198121995500
Sun H, Dong M, Chu B, Ao M, Chen C, Gu S (2021b) Multi-level high precision LBS architecture based on GNSS CORS network, a case study of HNCORS. IEEE Access 7:185042–185054. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2019.2960598
Suo Y, Chen W, Claramunt C, Yang S (2020) A ship trajectory prediction framework based on a recurrent neural network. Sensors 20(18):5133. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20185133
Tang J, Liu F, Wang Y, Wang H (2015) Uncovering urban human mobility from large scale taxi GPS data. Phys A Stat Mech Appl 438:140–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physa.2015.06.032
Ugwoke PO, Bakpo FS, Udanor CN, Okoronkwo MC (2022) A framework for monitoring movements of pandemic disease patients based on GPS trajectory datasets. Wireless Netw 28:1–28. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-021-02819-4
Wang C, Zourlidou S, Golze J, Sester M (2021) Trajectory analysis at intersections for traffic rule identification. Geo Spat Inf Sci 24(1):75–84. https://doi.org/10.1080/10095020.2020.1843374
Wei L, Chen G, Sun W, Li G (2021) Recognition of operating characteristics of heavy trucks based on the identification of GPS trajectory stay points. Security and Communication Networks. 2021: ID9998405. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/9998405
Xu Z, Cui G, Zhong M, Wang X, Maghrebi M (2019) Anomalous urban mobility pattern detection based on GPS trajectories and POI data. ISPRS Int J Geo-Inf 8(7):308. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi8070308
Yin B, Leurent F (2021) Exploring individual activity-travel patterns based on geolocation data from mobile phones. Transp Res Rec 2675(12):771–783. https://doi.org/10.1177/03611981211031234
Zhang S, Shi G, Liu Z, Zhao Z, Wu Z (2018) Data-driven based automatic maritime routing from massive AIS trajectories in the face of disparity. Ocean Eng 155:240–250. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oceaneng.2018.02.060
Zhang B, Wang Q, Li J, Zhou Y (2021) Spatial-temporal grid clustering method based on frequent stay point recognition. Neural Comput Applic 34:9247–9255. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-021-06274-2
Zhao L, Shi G (2019) A trajectory clustering method based on Douglas-Peucker compression and density for marine traffic pattern recognition. Ocean Eng 172:456–467. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oceaneng.2018.12.019
Zheng Y (2015) Trajectory data mining: An overview. ACM Trans Intell Syst Technol 6(3):1–41. https://doi.org/10.1145/2743025
Zheng Y, Chen Y, Li Q, Xie X, Ma W (2010) Understanding transportation modes based on GPS data for web applications. ACM Trans Web 4(1):1–36. https://doi.org/10.1145/1658373.1658374
Funding
This work was supported by the [National Natural Science Foundation] under Grant [No. 42074016], the [Science and Technology Platform and Talent Program of Hunan Science and Technology Administration] under Grant [No. 2018TP2040], the [Changsha City Natural Science Foundation] under Grant [No. kq2014161] and the [Science and Technology Research Program of Hunan Provincial Natural Resources Department] under [No. 2021–08].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Program were realized by M. Ao, X. Zeng, B. Chu and C. Zhou. Data collection and analysis were performed by X. Zeng, C. Chen, B. Chu and Y. Zhang. The first draft was written by M. Ao. All authors reviewed the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declared that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by: H. Babaie
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ao, M., Zeng, X., Chen, C. et al. Identification of The Survey Points from Network RTK Trajectory with Improved DBSCAN Clustering, Case Study on HNCORS. Earth Sci Inform 16, 1835–1847 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-023-00959-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-023-00959-z