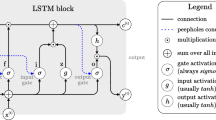
Abstract
Rainfall forecasting is a challenging task due to the time-dependencies of the variables and the stochastic behavior of the process. The difficulty increases when the zone of interest is characterized by a large spatio-temporal variability of its meteorological variables, causing large variations of rainfall even within a small zone such as the Tropical Andes. To address this problem, we propose a methodology for building a group of models based on Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) neural networks using Bayesian optimization. We optimize the model hyperparameters using accumulated experience to reduce the hyperparameter search space over successive iterations. The result is a large reduction in modeling time that allows the building of specialized LSTM models for each zone and forecasting time. We evaluated the method by forecasting rain events in the urban zone of Cuenca City in Ecuador, a city with large spatio-temporal variability. The results show that our proposed model offers better performance over the trivial forecaster for up to 9 hours of future forecasts with an accuracy of up to 84.4%. The model was compared to its equivalent LSTM model without optimization.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data used in this work is available in ETAPA EP.
References
Abbot J, Marohasy J (2014) Input selection and optimisation for monthly rainfall forecasting in queensland, australia, using artificial neural networks. Atmos Res 138:166–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2013.11.002
Aswin S, Geetha P, Vinayakumar R (2018) Deep Learning Models for the Prediction of Rainfall. In: International Conference on Communication and Signal Processing. IEEE, India, pp 657–661, https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCSP.2018.8523829
Barrera-Animas AY, Oyedele LO, Bilal M, et al (2022) Rainfall prediction: A comparative analysis of modern machine learning algorithms for time-series forecasting. Mach Learn Appl 7(November 2021):100,204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mlwa.2021.100204
Battersby S (2013) Beyond the butterfly effect: How life shapes the weather. New Scientist 218 (2923):32–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0262-4079(13)61624-3
Bendix A, Bendix J (2006) Heavy rainfall episodes in Ecuador during El Niño events and associated regional atmospheric circulation and SST patterns. Adv Geosci 6:43–49
Bendix J, Rollenbeck R, Reudenbach C (2006) Diurnal patterns of rainfall in a tropical Andean valley of southern Ecuador as seen by a vertically pointing K-band Doppler radar. Int J Climatol 26(6):829–846. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.1267
Bendix J, Fries A, Zárate J, et al (2017) RadarNet-Sur first weather radar network in tropical high mountains. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 98(6):1235–1254. https://doi.org/10.1175/BAMS-D-15-00178.1
Benevides P, Catalao J, Nico G (2019) Neural Network Approach to Forecast Hourly Intense Rainfall Using GNSS Precipitable Water Vapor and Meteorological Sensors. Remote Sens 11(8):966. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11080966
Bengio Y, Simard P, Frasconi P (1994) Learning long-term dependencies with gradient descent is difficult. Trans Neural Netw 5(2):157–166. https://doi.org/10.1109/72.279181
Bergstra J, Bengio Y (2012) Random search for hyper-parameter optimization. J Mach Learn Res 13:281–305
Bergstra J, Bardenet R, Bengio Y, et al (2011) Algorithms for Hyper-parameter Optimization. In: Proceedings of the 24th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Curran Associates Inc., USA, NIPS’11, pp 2546–2554, http://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=2986459.2986743
Bergstra J, Yamins D, Cox D (2013) Making a Science of Model Search: Hyperparameter Optimization in Hundreds of Dimensions for Vision Architectures. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, pp 407–424
Cabrera D, Sancho F, Li C, et al (2017) Automatic feature extraction of time-series applied to fault severity assessment of helical gearbox in stationary and non-stationary speed operation. Appl Soft Comput J 58:53–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2017.04.016
Cabrera D, Sancho F, Cerrada M, et al (2018) Echo state network and variational autoencoder for efficient one-class learning on dynamical systems. J Intell Fuzzy Syst 34(6):3799–3809. https://doi.org/10.3233/JIFS-169552
Campozano L, Célleri R, Trachte K, et al (2016) Rainfall and cloud dynamics in the Andes: A southern Ecuador case study. Advances in Meteorology. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/3192765
Campozano L, Trachte K, Célleri R, et al (2018) Climatology and Teleconnections of Mesoscale Convective Systems in an Andean Basin in Southern Ecuador: The Case of the Paute Basin. Adv Meteorol
Celleri R, Willems P, Buytaert W, et al (2007) Space-time rainfall variability in the Paute basin, Ecuadorian Andes. Hydrol Proc Int J 21(24):3316–3327
Chao Z, Pu F, Yin Y, et al (2018) Research on real-time local rainfall prediction based on MEMS sensors. Journal of Sensors 2018. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/6184713
Dabhi VK, Chaudhary S (2014) Hybrid Wavelet-Postfix-GP Model for Rainfall Prediction of Anand Region of India. Adv Artif Intell 2014:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/717803
French MN, Krajewski WF, Cuykendall RR (1992) Rainfall forecasting in space and time using a neural network. J Hydrol 137(1-4):1–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-1694(92)90046-X
Hochreiter S, Schmidhuber J (1997) Long Short-Term Memory. Neural Comput 9(8):1735–1780. https://doi.org/10.1162/neco.1997.9.8.1735
Hong W C (2008) Rainfall forecasting by technological machine learning models. Appl Math Comput 200(1):41–57
Hossain I, Rasel H, Imteaz M (2020) Long-term seasonal rainfall forecasting using linear and non-linear modelling approaches: a case study for western australia. Meteorog Atmos Phys 132:131–141
Huang M, Lin R, Huang S, et al (2017) A novel approach for precipitation forecast via improved K-nearest neighbor algorithm. Adv Eng Inform 33:89–95
Insel N, Poulsen C, Ehlers T (2010) Influence of the andes mountains on south american moisture transport, convection, and precipitation. Clim Dyn 35
Jones DR (2001) A Taxonomy of Global Optimization Methods Based on Response Surfaces. J Glob Optim 21:345–383
Kang J, Wang H, Yuan F, et al (2020) Prediction of precipitation based on recurrent neural networks in Jingdezhen, Jiangxi Province, China. Atmosphere 11(3):246
Khairudin N, Mustapha NB, Aris T, et al (2020) Comparison of machine learning models for rainfall forecasting. In: 2020 International Conference on Computer Science and Its Application in Agriculture (ICOSICA)
Kiefer J, Wolfowitz J (1952) Stochastic Estimation of the Maximum of a Regression Function. Ann Math Stat 23(3):462–466. https://doi.org/10.1214/aoms/1177729392
Kingma DP, Ba J (2014) Adam: A Method for Stochastic Optimization. arXiv:14126980 [csLG]. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1412.6980
Kotsiantis S, Kanellopoulos D, Pintelas P (2006) Handling imbalanced datasets: A review. GESTS International Transactions on Computer Science and Engineering 30
Kumar D, Singh A, Samui P, et al (2019) Forecasting monthly precipitation using sequential modelling. Hydrol Sci J 64(6):690–700. https://doi.org/10.1080/02626667.2019.1595624
Lepioufle JM, Leblois E, Creutin JD (2012) Variography of rainfall accumulation in presence of advection. J Hydrol 464:494– 504
Li C, de Oliveira JLV, Lozada MC, et al (2018a) A systematic review of fuzzy formalisms for bearing fault diagnosis. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems p 1. https://doi.org/10.1109/tfuzz.2018.2878200
Li C, Tao Y, Ao W, et al (2018b) Improving forecasting accuracy of daily enterprise electricity consumption using a random forest based on ensemble empirical mode decomposition. Energy 165:1220–1227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2018.10.113
Maqsood I, Abraham A (2007) Weather analysis using ensemble of connectionist learning paradigms. Appl Soft Comput 7(3):995–1004. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2006.06.005
Marzban C, Stumpf GJ (1998) A neural network for damaging wind prediction. Weather Forecast 13(1):151–163. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0434(1998)013〈0151:ANNFDW〉2.0.CO;2
Matovelle C, Andreo B, Mudarra M (2021) Análisis de la influencia de la altitud en los eventos de máxima precipitación en una cuenca del pacífico: tendencias y variabilidad. Información Tecnológica 32(6). https://doi.org/10.4067/S0718-07642021000600003
Moya-Álvarez A, Gálvez J, Holguin A, et al (2018) Extreme Rainfall Forecast with the WRF-ARW Model in the Central Andes of Peru. Atmosphere 9(9):362
Narasimha P, Prudhvi K, Naidu M (2013) An approach to prediction of precipitation using gini index in sliq decision tree. 4th International Conference on Intelligent Systems, Modelling and Simulation
Nastos PT, Moustris KP, Larissi IK, et al (2013) Rain intensity forecast using Artificial Neural Networks in Athens, Greece. Atmos Res 119:153–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2011.07.020
Navone HD, Ceccatto HA (1994) Predicting Indian monsoon rainfall: a neural network approach. Clim Dyn 10(6-7):305–312
Ni L, Wang D, Singh VP, et al (2020) Streamflow and rainfall forecasting by two long short-term memory-based models. J Hydrol 583:124,296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.124296
Oñate-Valdivieso F, Fries A, Mendoza K, et al (2018) Temporal and spatial analysis of precipitation patterns in an Andean region of southern Ecuador using LAWR weather radar. Meteorog Atmos Phys 130(4):473–484
Orellana-Alvear J, Célleri R, Rollenbeck R, et al (2017) Analysis of Rain Types and Their Z–R Relationships at Different Locations in the High Andes of Southern Ecuador. J Appl Meteorol Climatol 56(11):3065–3080
Padrón RS, Wilcox BP, Crespo P, et al (2015) Rainfall in the Andean Páramo: new insights from high-resolution monitoring in Southern Ecuador. J Hydrometeorol 16(3):985–996
Rahma A, Abbas S, Gollapalli M, et al (2022) Rainfall prediction system using machine learning fusion for smart cities. Sensors 22(9):3504
Ramirez MCV, Velho de Campos, HF Ferreira NJ (2005) Artificial neural network technique for rainfall forecasting applied to the Sao Paulo region. J Hydrol 301(1–4):146–162
Ridwan WM, Sapitang M, Aziz A, et al (2021) Rainfall forecasting model using machine learning methods: Case study Terengganu, Malaysia. Ain Shams Eng J 12(2):1651–1663. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asej.2020.09.011
Robert C, Casella G (2011) A Short History of Markov Chain Monte Carlo: Subjective Recollections from Incomplete Data. Stat Sci 26(1):102–115. https://doi.org/10.1214/10-sts351
Schultz M, Betancourt C, Gong B, et al (2021) Can deep learning beat numerical weather prediction? The Royal Society Publishing, London
Segura H, Junquas C, Espinoza J, et al (2019) New insights into the rainfall variability in the tropical andes on seasonal and interannual time scales. Clim Dyn 53:405–426
Smith LN (2017) Cyclical Learning Rates for Training Neural Networks. In: 2017 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV)
Sucozhañay A, Célleri R (2018) Impact of Rain Gauges Distribution on the Runoff Simulation of a Small Mountain Catchment in Southern Ecuador. Water 10(9):1169
Sulaiman J, Wahab SH (2018) Heavy rainfall forecasting model using artificial neural network for flood prone area. Converg Sec 2017(1):68–76. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-6451-7_97_9
Velasco LCP, Serquiña RP, Abdul Zamad MSA, et al (2019) Week-ahead rainfall forecasting using multilayer perceptron neural network. Procedia Comput Sci 161:386–397. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2019.11.137
Venkata R, Krishna B, Kumar SR, et al (2013) Monthly Rainfall Prediction Using Wavelet Neural Network Analysis. Water Resour Manag 27(10):3697–3711. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-013-0374-4
Vuille M, Bradley R, Keimig F (1999) Climate variability in the andes of Ecuador and its relation to tropical pacific and atlantic sea surface temperature anomalies. J Clim 13
Werbos PJ (1990) Backpropagation through time: what it does and how to do it. Proc IEEE 78 (10):1550–1560. https://doi.org/10.1109/5.58337
Wu CL, Chau KW (2013) Prediction of rainfall time series using modular soft computingmethods. Eng Appl Artif Intell 26(3):997–1007. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engappai.2012.05.023
Yáñez-Morroni G, Gironás J, Caneo M, et al (2018) Using the weather research and forecasting (WRF) model for precipitation forecasting in an Andean region with complex topography. Atmosphere 9(8):304
Yaseen ZM, Ghareb MI, Ebtehaj I, et al (2018) Rainfall Pattern Forecasting Using Novel Hybrid Intelligent Model Based ANFIS-FFA. Water Resour Manag 32(1):105–122. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-017-1797-0
Acknowledgements
The work was sponsored in part by the GIDTEC project (No. 003-002-2016-03-03). The signal acquisition work was developed by the hydrometeorological network of the Empresa Pública Municipal de Telecomunicaciones, Agua Potable, Alcantarillado y Saneamiento de Cuenca ETAPA EP. The computational work was developed at the GIDTEC Research Group Lab of the Universidad Politécnica Salesiana de Cuenca, Ecuador.
Funding
The authors did not receive support from any organization for the submitted work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization- Diego Cabrera, Vinicio Sánchez, Mariela Cerrada, Chuan Li. Data collection- Mario Guallpa. Model creation- Diego Cabrera, María Quinteros. Writing original draft- Diego Cabrera, María Quinteros. Writing-Review and Editing- Fernando Sancho, Mariela Cerrada.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interests
The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Additional information
Communicated by: H. Babaie
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Cabrera, D., Quinteros, M., Cerrada, M. et al. Rainfall Forecasting using a Bayesian framework and Long Short-Term Memory Multi-model Estimation based on an hourly meteorological monitoring network. Case of study: Andean Ecuadorian Tropical City. Earth Sci Inform 16, 1373–1388 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-023-00958-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-023-00958-0