Abstract
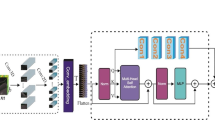
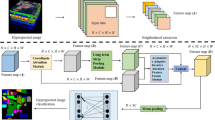
Deep learning, especially 3D convolutional neural networks (CNNs), has been proved to be an excellent feature extractor in the hyperspectral image (HSI) classification. However, simply accumulating conventional 3D convolution units and blindly increasing the depth of the network does not improve the model performance effectively. Besides, most deep learning models tend to struggle due to the serious overfitting problem under the condition of small sample, this seriously restricts the accuracy of model classification. To solve the abovementioned problems, we proposed a multiscale 3D convolution with context attention network for HSI classification. Specifically, we introduce a multiscale 3D convolution composed of convolution kernels of different sizes to replace the conventional 3D convolution to enlarge the receptive field and adaptively detect the HSI features in different scales. Then, based on multiscale 3D convolution, we build two subnetworks to efficiently exploit hierarchical spectral and spatial features respectively, and enhance the transmission of features. Finally, to explore the discriminative features further, we design two types of attention mechanisms (AM) to build compact relationships between each position\channel and aggregation center instead of model any position\channel and position\channel relationships. After each 3D convolution layer, a compact AM is adopted to refine extracted hierarchical spectral and spatial features respectively, and boost the performance of the model. Experiments were conducted on four benchmark HSI datasets, the results demonstrate that the proposed method outperforms state-of-the-art models with the overall accuracy of 96.39%, 97.83%, 98.58%, and 97.98% over Indian Pines, Salinas Valley, Pavia University and Botswana dataset, respectively.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdolrasol MGM, Hussain SMS, Ustun TS, Sarker MR, Hannan MA, Mohamed R, Ali JA, Mekhilef S, Milad A (2021) Artificial neural networks based optimization techniques: A review. Electronics 10(21). https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10212689
Akar O, Tunc Gormus E (2021) Land use/land cover mapping from airborne hyperspectral images with machine learning algorithms and contextual information. Geocarto Int :1–28. https://doi.org/10.1080/10106049.2021.1945149
Bellman RE (2015) Adaptive control processes: a guided tour. Princeton University Press, Princeton
Camps-Valls G, Bruzzone L (2005) Kernel-based methods for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sensing 43(6):1351–1362. https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2005.846154
Cavallaro G, Mura MD, Benediktsson JA, Bruzzone L (2015) Extended self-dual attribute profiles for the classification of hyperspectral images. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens Lett 12(8):1690–1694. https://doi.org/10.1109/LGRS.2015.2419629
Chen Y, Jiang H, Li C, Jia X, Ghamisi P (2016) Deep feature extraction and classification of hyperspectral images based on convolutional neural networks. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sensing 54(10):6232–6251. https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2016.2584107
Chen Y, Zhu L, Ghamisi P, Jia X, Li G, Tang L (2017) Hyperspectral images classification with gabor filtering and convolutional neural network. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens Lett 14(12):2355–2359. https://doi.org/10.1109/LGRS.2017.2764915
Ding C, Li Y, Xia Y, Wei W, Zhang L, Zhang Y (2017) Convolutional neural networks based hyperspectral image classification method with adaptive kernels. Remote Sens 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9060618
Dossa RFJ, Huang S, Ontañón S, Matsubara T (2021) An empirical investigation of early stopping optimizations in proximal policy optimization. IEEE Access 9:117981–117992. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3106662
Fang L, Wang C, Li S, Benediktsson JA (2017) Hyperspectral image classification via multiple-feature-based adaptive sparse representation. IEEE Trans Instrum Meas 66(7):1646–1657. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIM.2017.2664480
Fu J, Liu J, Tian H, Li Y, Bao Y, Fang Z, Lu H (2019) Dual attention network for scene segmentation. 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2019.00326
Gao H, Yang Y, Li C, Zhou H, Qu X (2018) Joint alternate small convolution and feature reuse for hyperspectral image classification. ISPRS Int J Geo-Inf 7(9). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi7090349
Ghamisi P, Maggiori E, Li S, Souza R, Tarablaka Y, Moser G, Giorgi AD, Fang L, Chen Y, Chi M, Serpico SB, Benediktsson JA (2018) New frontiers in spectral-spatial hyperspectral image classification: The latest advances based on mathematical morphology, markov random fields, segmentation, sparse representation, and deep learning. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens Mag 6(3):10–43. https://doi.org/10.1109/MGRS.2018.2854840
Guo M-H, Xu T-X, Liu J-J, Liu Z-N, Jiang P-T, Mu T-J, Zhang S-H, Martin RR, Cheng M-M, Hu S-M (2022) Attention mechanisms in computer vision: A survey. Comput vis Media 8(3):331–368. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41095-022-0271-y
Ham J, Yangchi C, Crawford MM, Ghosh J (2005) Investigation of the random forest framework for classification of hyperspectral data. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sensing 43(3):492–501. https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2004.842481
Haut JM, Paoletti ME, Plaza J, Plaza A, Li J (2019) Hyperspectral image classification using random occlusion data augmentation. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens Lett 16(11):1751–1755. https://doi.org/10.1109/LGRS.2019.2909495
He L, Li J, Liu C, Li S (2018) Recent advances on spectral-spatial hyperspectral image classification: An overview and new guidelines. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sensing 56(3):1579–1597. https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2017.2765364
Huang G, Liu Z, Maaten LVD, Weinberger KQ (2017) Densely connected convolutional networks. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2017.243
Hughes G (1968) On the mean accuracy of statistical pattern recognizers. IEEE Trans Inf Theory 14(1):55–63. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIT.1968.1054102
Jiang X, Pang Y, Li X, Pan J, Xie Y (2018) Deep neural networks with Elastic Rectified Linear Units for object recognition. Neurocomputing 275:1132–1139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2017.09.056
Li G, Zhang M, Li J, Lv F, Tong G (2021a) Efficient densely connected convolutional neural networks. Pattern Recognit 109:107610. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2020.107610
Li Z, Cui X, Wang L, Zhang H, Zhu X, Zhang Y (2021b) Spectral and spatial global context attention for hyperspectral image classification. Remote Sens 13(4). https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13040771
Li J, Zhao X, Li Y, Du Q, Xi B, Hu J (2018a) Classification of hyperspectral imagery using a new fully convolutional neural network. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens Lett 15(2):292–296. https://doi.org/10.1109/LGRS.2017.2786272
Li Y, Wang N, Shi J, Hou X, Liu J (2018b) Adaptive Batch Normalization for practical domain adaptation. Pattern Recognit 80:109–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2018.03.005
Li R, Zheng S, Duan C, Yang Y, Wang X (2020) Classification of hyperspectral image based on double-branch dual-attention mechanism network. Remote Sens 12(3). https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12030582
Liao J, Wang L, Hao S (2018) Hyperspectral image classification based on adaptive optimisation of morphological profile and spatial correlation information. Int J Remote Sens 39(23):9159–9180. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431161.2018.1508913
Liu T, Gu Y, Chanussot J, Mura MD (2017) Multimorphological superpixel model for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 55(12):6950–6963. https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2017.2737037
Liu Y, Yu J, Han Y (2018) Understanding the effective receptive field in semantic image segmentation. Multimed Tools Appl 77(17):22159–22171. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-018-5704-3
Loncomilla P, Ruiz-del-Solar J, Martínez L (2016) Object recognition using local invariant features for robotic applications: A survey. Pattern Recognit 60:499–514. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2016.05.021
Ma W, Yang Q, Wu Y, Zhao W, Zhang X (2019) Double-branch multi-attention mechanism network for hyperspectral image classification. Remote Sens 11(11):1307. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11111307
Navin MS, Agilandeeswari L (2020) Multispectral and hyperspectral images based land use / land cover change prediction analysis: an extensive review. Multimed Tools Appl 79(39):29751–29774. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-020-09531-z
Niu Z, Zhong G, Yu H (2021) A review on the attention mechanism of deep learning. Neurocomputing 452:48–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2021.03.091
Rehman Au, Qureshi SA (2021) A review of the medical hyperspectral imaging systems and unmixing algorithms’ in biological tissues. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther 33:102165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pdpdt.2020.102165
Rosas-Arias L, Benitez-Garcia G, Portillo-Portillo J, Sánchez-Pérez G, Yanai K (2021) Fast and accurate real-time semantic segmentation with dilated asymmetric convolutions. 2020 25th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICPR48806.2021.9413176
Shi C, Liao D, Zhang T, Wang L (2022) Hyperspectral image classification based on 3D coordination attention mechanism network. Remote Sens 14(3). https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14030608
Stuart MB, Davies M, Hobbs MJ, Pering TD, McGonigle AJS, Willmott JR (2022) High-resolution hyperspectral imaging using low-cost components: Application within environmental monitoring scenarios. Sensors 22(12). https://doi.org/10.3390/s22124652
Wang W, Dou S, Jiang Z, Sun L (2018) A fast dense spectral–spatial convolution network framework for hyperspectral images classification. Remote Sens 10(7). https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10071068
Xing F, Yao H, Liu Y, Dai X, Brown RL, Bhatnagar D (2019) Recent developments and applications of hyperspectral imaging for rapid detection of mycotoxins and mycotoxigenic fungi in food products. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 59(1):173–180. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2017.1363709
Xu Y, Du B, Zhang F, Zhang L (2018) Hyperspectral image classification via a random patches network. ISPRS-J Photogramm Remote Sens 142:344–357. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2018.05.014
Xue J, Zheng T, Han J (2021) Exploring attention mechanisms based on summary information for end-to-end automatic speech recognition. Neurocomputing 465:514–524. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2021.09.017
Yan H, Wang J, Tang L, Zhang E, Yan K, Yu K, Peng J (2021) A 3D cascaded spectral–spatial element attention network for hyperspectral image classification. Remote Sens 13(13). https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13132451
Zeng Y, Dai T, Chen B, Xia S-T, Lu J (2021) Correlation-based structural dropout for convolutional neural networks. Pattern Recognit 120:108117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2021.108117
Zhao J, Hu L, Dong Y, Huang L, Weng S, Zhang D (2021) A combination method of stacked autoencoder and 3D deep residual network for hyperspectral image classification. Int J Appl Earth Obs Geoinf 102:102459. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jag.2021.102459
Zhong Z, Li J, Luo Z, Chapman M (2018) Spectral-spatial residual network for hyperspectral image classification: A 3-D deep learning framework. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 56(2):847–858. https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2017.2755542
Zhu J, Fang L, Ghamisi P (2018) Deformable convolutional neural networks for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens Lett 15(8):1254–1258. https://doi.org/10.1109/LGRS.2018.2830403
Funding
This work was supported in part by the Research Foundation of Education Department of Sichuan Province under grant no. 14ZB0282, and in part by the Research Foundation of Yibin University under grant no. 2019PY37.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by H. Babaie.
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, L., Wang, H. & Zhang, T. A multiscale 3D convolution with context attention network for hyperspectral image classification. Earth Sci Inform 15, 2553–2569 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-022-00858-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-022-00858-9