Abstract
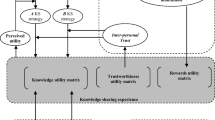
Under the background of knowledge economy, knowledge exchange and sharing among team members is extremely important for team development and organizational innovation. However, previous studies have neglected the root dilemma of individual sharing behavior. Based on costly signaling theory and social hierarchy theory, this study discusses the influence of individual power-status inconsistency on knowledge sharing. Study 1 issued 629 questionnaires to team members of high-tech industries. The results shows that power-status inconsistency has a positive impact on knowledge sharing, and the knowledge sharing level of those with high power and low status is higher than that of those with low power and high status. In study 2, the psychological mechanism of two types of individuals with inconsistent power and status was deeply explored through experiments, which affected individual knowledge sharing by positive cognitive self-efficacy and negative emotion. This paper is helpful to broaden the social hierarchy theory and provide suggestions for knowledge management within the team.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The current study has been validated through an empirical study. The data support the fndings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Ahmad, N., Ullah, Z., Ryu, H. B., Ariza-Montes, A., & Han, H. (2023). From corporate social responsibility to employee well-being: Navigating the pathway to sustainable healthcare. Psychology Research and Behavior Management, 16, 1079–1095. https://doi.org/10.2147/PRBM.S398586
Anderson, C., & Brown, C. E. (2010). The functions and dysfunctions of hierarchy. Research in Organizational Behavior, 30, 55–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.riob.2010.08.002
Anderson, C., Hildreth, J. A. D., & Howland, L. (2015). Is the desire for status a fundamental human motive? A review of the empirical literature. Psychological Bulletin, 141(3), 574–601. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0038781
Anicich, E. M., Fast, N. J., Halevy, N., & Galinsky, A. D. (2016). When the bases of social hierarchy collide: Power without status drives interpersonal conflict. Organization Science, 27(1), 123–140. https://doi.org/10.1287/orsc.2015.1019
Arain, G., Bhatti, Z. A., Ashraf, N., & Yuhui, F. (2020). Top-down knowledge hiding in organizations:An empirical study of the consequences of supervisor knowledge hiding among local and foreign workers in the Middle East. Journal of Business Ethics,164(3), 611–625. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10551-018-4056-2
Bandura, A. (1977). Self-efficacy: Toward a unifying theory of behavioral change. Psychological Review, 84(2), 191–215. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-295X.84.2.191
Barnes, L. Y., Lacerenza, C. N., & Volpone, S. (2023). Becoming a right-hand partner: How lower-power employees heedfully challenge organizational leaders. Academy of Management Journal. https://doi.org/10.5465/amj.2021.1390
Bian, F., & Wu, D. (2021). The impact of family socioeconomic status on prosocial behavior: A survey of college students in China. Current Psychology, 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-021-02611-9
Blader, S. L., & Chen, Y.-R. (2012). Differentiating the effects of status and power: A justice perspective. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 102(5), 994–1014. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0026651
Blader, S. L., Shirako, A., & Chen, Y. R. (2016). Looking out from the top: Differential effects of status and power on perspective taking. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin, 42(6), 723–737. https://doi.org/10.1177/0146167216636628
Bliege Bird, R., Smith, E., & Bird, D. W. (2001). The hunting handicap: Costly signaling in human foraging strategies. Behavioral Ecology and Sociobiology, 50, 9–19. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002650100375
Bol, J. C., & Leiby, J. (2022). Status motives and agent-to-agent information sharing. Review of Accounting Studies, 27(1), 122–147. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11142-021-09598-5
Bunderson, J. S., & Reagans, R. E. (2011). Power, status, and learning in organizations. Organization Science, 22(5), 1182–1194. https://doi.org/10.1287/orsc.1100.0590
Burić, I., & Macuka, I. (2018). Self-efficacy, emotions and work engagement among teachers: A two wave cross-lagged analysis. Journal of Happiness Studies, 19(7), 1917–1933. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10902-017-9903-9
Cheng, J. T., Tracy, J. L., Foulsham, T., Kingstone, A., & Henrich, J. (2013). Two ways to the top: Evidence that dominance and prestige are distinct yet viable avenues to social rank and influence. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 104(1), 103–125. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0030398
Chen, M., Zada, M., Khan, J., & Saba, N. U. (2022). How does servant leadership influences creativity? Enhancing employee creativity via creative process engagement and knowledge sharing. Frontiers in Psychology. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2022.947092. 13https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/
Colombo, O. (2021). The use of signals in new-venture financing: A review and research agenda. Journal of Management, 47(1), 237–259. https://doi.org/10.1177/0149206320911090
Connelly, B. L., Certo, S. T., Ireland, R. D., & Reutzel, C. R. (2011). Signaling theory: A review and assessment. Journal of Management, 37(1), 39–67. https://doi.org/10.1177/0149206310388419
David, T., & Shih, H. A. (2023). Evolutionary motives in employees’ knowledge behavior when being envied at work. Journal of Knowledge Management, ahead-of-print(ahead-of-print). https://doi.org/10.1108/JKM-12-2022-1004
Fast, N. J., & Chen, S. (2009). When the boss feels inadequate: Power, incompetence, and aggression. Psychological Science, 20(11), 1406–1413. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-9280.2009.02452.x
Fast, N. J., Halevy, N., & Galinsky, A. D. (2012). The destructive nature of power without status. Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, 48(1), 391–394. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jesp.2011.07.013
Feng, J., & Wang, C. (2019). Does abusive supervision always promote employees to hide knowledge? From both reactance and COR perspectives. Journal of Knowledge Management, 23(7), 1455–1474. https://doi.org/10.1108/JKM-12-2018-0737
Forgas, J. P. (2002). Feeling and doing: Affective influences on interpersonal behavior. Psychological Inquiry, 13(1), 1–28. https://doi.org/10.1207/S15327965PLI1301_01
Gintis, H., Smith, E. A., & Bowles, S. (2001). Costly signaling and cooperation. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 213(1), 103–119. https://doi.org/10.1006/jtbi.2001.2406
Gray, S. M., Bunderson, J. S., Van der Vegt, G. S., Rink, F., & Gedik, Y. (2023). Leveraging knowledge diversity in hierarchically differentiated teams: The critical role of hierarchy stability. Academy of Management Journal, 66(2), 462–488. https://doi.org/10.5465/amj.2020.1136
Greer, L. L., de Jong, B. A., Schouten, M. E., & Dannals, J. E. (2018). Why and when hierarchy impacts team effectiveness: A meta-analytic integration. Journal of Applied Psychology, 103(6), 591–613. https://doi.org/10.1037/apl0000409
Haesebrouck, K., Cools, M., & Van den Abbeele, A. (2018). Status differences and knowledge transfer: The effect of incentives. The Accounting Review, 93(1), 213–234. https://doi.org/10.1037/apl0000409
Han, J-H., & Pollock, T. G. (2021). The two towers (or somewhere on between), the behavioral consequences of positional inconsistency across status hierarchies. Academy of Management Journal, 64(1), 86–113. https://doi.org/10.5465/amj.2018.1091
Hays, N. A., & Bendersky, C. (2015). Not all inequality is created equal: Effects of status versus power hierarchies on competition for upward mobility. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 108(6), 867–882. https://doi.org/10.1037/pspi0000017
Hays, N. A., Li, H., Yang, X., Oh, J. K., Yu, A., Chen, Y. R.,... Jamieson, B. B. (2022). A tale of two hierarchies: Interactive effects of power differentiation and status differentiation on team performance. Organization Science, 33(6), 2085–2105. https://doi.org/10.1287/orsc.2021.1540
Hekkala, R., & Newman, M. (2013). Power and status theory as a lens to view knowledge sharing and knowledge building issues in an IOIS project. In 2013 46th Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences (pp. 4354–4363). IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/HICSS.2013.452
Henrich, J., & Gil-White, F. J. (2001). The evolution of prestige: Freely conferred deference as a mechanism for enhancing the benefits of cultural transmission. Evolution and Human Behavior, 22(3), 165–196. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1090-5138(00)00071-4
Hu, Q., & Xie, X. (2015). Group members’ status and knowledge sharing behavior: A motivational perspective. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 47(4), 545–554. https://doi.org/10.3724/SP.J.1041.2015.00545
Inesi, M. E., & Rios, K. (2023). How prosocial actors use power hierarchies to build moral reputation. Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, 106, 104441. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jesp.2022.104441
Kakkar, H., Sivanathan, N., & Gobel, M. S. (2020). Fall from grace: The role of dominance and prestige in the punishment of high-status actors. Academy of Management Journal, 63(2), 530–553. https://doi.org/10.5465/amj.2017.0729
Keltner, D., Gruenfeld, D. H., & Anderson, C. (2003). Power, approach, and inhibition. Psychological Review, 110(2), 265–284. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-295X.110.2.265
Khan, J., Saeed, I., Zada, M., Nisar, H. G., Ali, A., & Zada, S. (2022). The positive side of overqualification: Examining perceived overqualification linkage with knowledge sharing and career planning. Journal of Knowledge Management, 27(4), 993–1015. https://doi.org/10.1108/JKM-02-2022-0111
Lee, J. N. (2001). The impact of knowledge sharing, organizational capability and partnership quality on IS outsourcing success. Information and Management, 38(5), 323–335. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-7206(00)00074-4
Li, H., Wang, X., Williams, M., Chen, Y. R., & Brockner, J. (2023). My boss is younger, less educated, and shorter tenured: When and why status (in)congruence influences promotion system justification. Journal of Applied Psychology, 108(9), 1445–1460. https://doi.org/10.1037/apl0001086
Liu, Y., Zhu, J. N. Y., & Lam, L. W. (2020). Obligations and feeling envied: A study of workplace status and knowledge hiding. Journal of Managerial Psychology, 35(5), 347–359. https://doi.org/10.1108/JMP-05-2019-0276
Li, W., Lu, Y., Makino, S., & Lau, C. M. (2017). National power distance, status incongruence, and CEO dismissal. Journal of World Business, 52(6), 809–818. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwb.2017.08.001
Magee, J. C., & Galinsky, A. D. (2008). Social hierarchy: The self-reinforcing nature of power and status. Academy of Management Annals, 2(1), 351–398. https://doi.org/10.1080/19416520802211628
Mahadevan, N., Gregg, A. P., & Sedikides, C. (2023). How does social status relate to self-esteem and emotion? An integrative test of hierometer theory and social rank theory. Journal of Experimental Psychology, 152(3), 632–656. https://doi.org/10.1037/xge0001286
Martos, T., Jagodics, B., Kőrössy, J., & Szabó, É. (2023). Psychological resources, dropout risk and academic performance in university students–pattern-oriented analysis and prospective study of Hungarian freshmen. Current Psychology, 42(10), 8051–8065. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-021-02073-z
Matta, F. K., Erol-Korkmaz, H. T., Johnson, R. E., & Biçaksiz, P. (2014). Significant work events and counterproductive work behavior: The role of fairness, emotions, and emotion regulation. Journal of Organizational Behavior, 35(7), 920–944. https://doi.org/10.1002/job.1934
Millet, K., & Dewitte, S. (2007). Altruistic behavior as a costly signal of general intelligence. Journal of Research in Personality, 41(2), 316–326. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrp.2006.04.002
Mitchell, R., Schuster, L., & Jin, H. S. (2020). Gamification and the impact of extrinsic motivation on needs satisfaction: Making work fun? Journal of Business Research, 106, 323–330. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2018.11.022
Ndofor, H. A., & Levitas, E. (2004). Signaling the strategic value of knowledge. Journal of Management, 30(5), 685–702. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jm.2004.04.002
Neeley, T., & Reiche, B. S. (2022). How global leaders gain power through downward deference and reduction of social distance. Academy of Management Journal, 65(1), 11–34. https://doi.org/10.5465/amj.2019.0531
Park, J., Chae, H., & Choi, J. N. (2018). The need for status as a hidden motive of knowledge-sharing behavior: An application of costly signaling theory. Human Performance, 31(1), 76–76. https://doi.org/10.1080/08959285.2016.1263636
Preacher, K. J., & Selig, J. P. (2012). Advantages of Monte Carlo confidence intervals for indirect effects. Communication Methods and Measures, 6(2), 77–98. https://doi.org/10.1080/19312458.2012.679848
Prentice, C., Zeidan, S., & Nguyen, M. (2023). Want to feel better, share what you know. Knowledge Management Research & Practice, 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1080/14778238.2023.2169203
Saeed, I., Khan, J., Zada, M., Zada, S., Vega-Muñoz, A., & Contreras-Barraza, N. (2022). Linking ethical leadership to followers’ knowledge sharing: Mediating role of psychological ownership and moderating role of professional commitment. Frontiers in Psychology, 13, 841590. https://www.frontiersin.org/articleshttps://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2022.841590
Santhose, S. S., & Lawrence, L. N. (2023). Understanding the implementations and limitations in knowledge management and knowledge sharing using a systematic literature review. Current Psychology, 1–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-022-04115-6
Scott, B. A., & Judge, T. A. (2009). The popularity contest at work: Who wins, why, and what do they receive? Journal of Applied Psychology, 94(1), 20–33. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0012951
Spreitzer, G. (1995). Psychological empowerment in the workplace: Dimensions, measurement, and validation. Academy of Management Journal, 38(5), 1442–1465. https://doi.org/10.2307/256865
Steckler, C. M., & Tracy, J. L. (2014). The emotional underpinnings of social status. The Psychology of Social Status, 201–224. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-0867-7_10
Van Dijk, H., Shantz, A., & Alfes, K. (2020). Welcome to the bright side: Why, how, and when overqualification enhances performance. Human Resource Management Review, 30(2), 100688. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hrmr.2019.04.004
Vuori, T. O., & Huy, Q. N. (2016). Distributed attention and shared emotions in the innovation process: How Nokia lost the smartphone battle. Administrative Science Quarterly, 61(1), 9–51. https://doi.org/10.1177/0001839215606951
Watson, D., Anna, L., & Tellegen, A. (1988). Development and validation of brief measures of positive and negative affect: The PANAS scales. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 54(6), 1063–1070. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.54.6.1063
Witkower, Z., Mercadante, E. J., & Tracy, J. L. (2020). How affect shapes status: Distinct emotional experiences and expressions facilitate social hierarchy navigation. Current Opinion in Psychology, 33, 18–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copsyc.2019.06.006
Yang, W., & Li, C. (2021). The relationship between perceived over-qualification and individual performance and mediating mechanisms: A meta-analytic review and examination of emotional and cognitive processing systems and cultural contexts. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 53(5), 527–554. https://doi.org/10.3724/SP.J.1041.2021.00527
Yu, A., Hays, N. A., & Zhao, E. Y. (2019). Development of a bipartite measure of social hierarchy: The perceived power and perceived status scales. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes, 152, 84–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.obhdp.2019.03.011
Zada, M., Zada, S., Khan, J., Saeed, I., Zhang, Y. J., Vega-Muñoz, A., & Salazar-Sepúlveda, G. (2022). Does servant leadership control psychological distress in crisis? Moderation and mediation mechanism. Psychology Research and Behavior Management, 15, 607–622. https://doi.org/10.2147/PRBM.S354093
Zada, S., Khan, J., Zada, M., Saeed, I., & Jun, Z. Y. (2023). Does servant leadership enhance employee creativity and performance? Mediating role of knowledge sharing and moderating the role of self-efficacy. Journal of Organizational and End User Computing, 35(1), 1–24. https://doi.org/10.4018/JOEUC.321656
Zahavi, A. (1995). Altruism as a handicap: The limitations of kin selection and reciprocity. Journal of Avian Biology, 26(1), 1–3. https://doi.org/10.2307/3677205
Zhao, L., & Detlor, B. (2021). Towards a contingency model of knowledge sharing: Interaction between social capital and social exchange theories. Knowledge Management Research and Practice, 21(1), 197–209. https://doi.org/10.1080/14778238.2020.1866444
Zhong, Y., & Li, H. (2023). Do lower-power individuals really compete less? An investigation of covert competition. Organization Science. https://doi.org/10.1287/orsc.2023.1684
Zhu, G., Ma, X., & Liu, B. (2019). Research on the mechanism of knowledge and intelligence sharing in enterprises under big data: From the perspective of status-striving motivation and opinion dynamics. Expert Systems, 36(5), 2881–2888. https://doi.org/10.1111/exsy.12313
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the editors and reviewers for their valuable contributions to the improvement of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China Project(72072086) and Postgraduate Research Innovation Program of Jiangsu Province (KYCX23_0064; KYCX23_0066).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The authors confirm contribution to the paper as follows: study conception and design: Liu Ruhong; data collection: Long Jing; analysis and interpretation of results: Liu Longjun; draft manuscript preparation: Liu Ruhong, Liu Longjun. All authors reviewed the results and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Consent to participate
Since data is collected from the employee of businesses and MBA students, verbal consent was taken from all respondents to participate in this research.
Conflict of interest
The authors claim that there is not any potential conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, R., Long, J. & Liu, L. Power-status inconsistency and knowledge sharing behavior: the mediating role of self-efficacy and negative emotion. Curr Psychol (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-024-06125-y
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-024-06125-y