Abstract
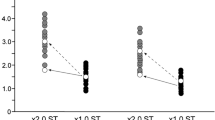
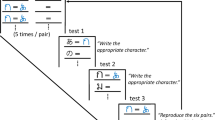
Grapheme-color synesthesia (GC-S) is a neurological condition in which the perception of a grapheme elicits the experience of color or even the visual representation of that grapheme as colored. Previous research using transcranial magnetic stimulation on GC-synesthetes demonstrated enhanced excitability of the visual cortex. Consequently, we hypothesized that using anodal "offline" transcranial direct current stimulation on the visual cortex in area V4 followed by visual training could boost cortical excitability in the target areas and thus produce effects similar to GC-S in non-synesthetes. We discovered that after anodal stimulation, participants had a considerably smaller mean change in reaction time on white symbols than after sham and cathodal stimulation. Our findings indirectly support the cross-activation hypothesis.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allison, T., McCarthy, G., Nobre, A., Puce, A., & Belger, A. (1994). Human extrastriate visual cortex and the perception of faces, words, numbers, and colors. Cerebral Cortex, 4(5), 544?554.
Amsel, B. D., Kutas, M., & Coulson, S. (2017). Projectors, associators, visual imagery, and the time course of visual processing in grapheme-color synesthesia. Cognitive Neuroscience, 8(4), 206?223.
Barbieri, M., Negrini, M., Nitsche, M. A., & Rivolta, D. (2016). Anodal-tDCS over the human right occipital cortex enhances the perception and memory of both faces and objects. Neuropsychologia, 81, 238?244.
Bargary, G., & Mitchell, K. J. (2008). Synaesthesia and cortical connectivity. Trends in Neurosciences, 31(7), 335?342.
Baron-Cohen, S., Harrison, J., Goldstein, L. H., & Wyke, M. (1993). Coloured speech perception: Is synaesthesia what happens when modularity breaks down? Perception, 22(4), 419?426.
Brang, D., & Ramachandran, V. S. (2008). Psychopharmacology of synesthesia; the role of serotonin S2a receptor activation. Medical Hypotheses, 70(4), 903?904.
Brang, D., Hubbard, E. M., Coulson, S., Huang, M., & Ramachandran, V. S. (2010). Magnetoencephalography reveals early activation of V4 in grapheme-color synesthesia. Neuroimage, 53(1), 268?274.
Brang D, Ramachandran V. S (2008) Psychopharmacology of synesthesia; the role of serotonin S2a receptor activation. Med Hypotheses 70(4): 903?904.
Cohen Kadosh, R., Henik, A., Catena, A., Walsh, V., & Fuentes, L. J. (2009). Induced cross-modal synaesthetic experience without abnormal neuronal connections. Psychological Science, 20(2), 258?265.
Cytowic, R. E. (2003). The Man Who Tasted Shapes, rev. ed.
Cytowic, R. E., & Eagleman, D. M. (2009). Wednesday is indigo blue: Discovering the brain of synesthesia. Boston Review.
Eagleman, D. M., Kagan, A. D., Nelson, S. S., Sagaram, D., & Sarma, A. K. (2007). A standardized test battery for the study of synesthesia. Journal of Neuroscience Methods, 159(1), 139?145.
Hadjikhani, N., Liu, A. K., Dale, A. M., Cavanagh, P., & Tootell, R. B. (1998). Retinotopy and color sensitivity in human visual cortical area V8. Nature Neuroscience, 1(3), 235?241.
Hamada, D., Yamamoto, H., & Saiki, J. (2017). Multilevel analysis of individual differences in regularities of grapheme?color associations in synesthesia. Consciousness and Cognition, 53, 122?135.
Jacome, D. E., & Gumnit, R. J. (1979). Audioalgesic and audiovisuoaglesic synesthesias: Epileptic manifestation. Neurology, 29(7), 1050?1050.
Lueck, C. J., Zeki, S., Friston, K. J., Deiber, M. P., Cope, P., Cunningham, V. J., & Frackowiak, R. S. J. (1989). The colour centre in the cerebral cortex of man. Nature, 340(6232), 386?389.
Nair, A., & Brang, D. (2019). Inducing synesthesia in non-synesthetes: Short-term visual deprivation facilitates auditory-evoked visual percepts. Consciousness and Cognition, 70, 70?79.
Ramachandran, V., & Hubbard, E. (2001). Synaesthesia -- a window into perception, thought and language. Journal of Consciousness Studies, 8(12), 3?34.
Reif, J. H., & Alhalabi, W. (2018). Advancing Attention Control Using VR-Induced Multimodal Artificial Synesthesia.. https://doi.org/10.20944/preprints201808.0134.v1
Rouw, R., & Scholte, H. S. (2007). Increased structural connectivity in grapheme-color synesthesia. Nature Neuroscience, 10(6), 792?797.
Terhune, D. B., Tai, S., Cowey, A., Popescu, T., & Kadosh, R. C. (2011). Enhanced cortical excitability in grapheme-color synesthesia and its modulation. Current Biology, 21(23), 2006?2009.
Thielscher, A., Antunes, A., & Saturnino, G. B. (2015, August). Field modeling for transcranial magnetic stimulation: a useful tool to understand the physiological effects of TMS? In 2015 37th annual international conference of the IEEE engineering in medicine and biology society (EMBC) (pp. 222?225). IEEE.
van Leeuwen, T. M., den Ouden, H. E., & Hagoort, P. (2011). Effective connectivity determines the nature of subjective experience in grapheme-color synesthesia. The Journal of Neuroscience: The Official Journal of the Society for Neuroscience,31(27), 9879?9884. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0569-11.2011
Zeki, S., & Marini, L. (1998). Three cortical stages of colour processing in the human brain. Brain: A Journal of Neurology, 121(9), 1669?1685.
Acknowledgements
This article is an output of a research project implemented as part of the Basic Research Program at the National Research University Higher School of Economics (HSE University) which was carried out using HSE Automated system of non-invasive brain stimulation with the possibility of synchronous registration of brain activity and registration of eye movements.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
A.S., M.V. and G.A. conceived the design. A.S., M.V. acquired the data. A.S., M.V. analyzed the data. A.S., M.V. prepared the figures. A.S., M.V., Z.O. and G.A. contributed to the interpretation of the results. A.S., M.V., Z.O. drafted the manuscript. All authors revised critically the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher?s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Andreev, S., Moskvoretskiy, V., Gorin, A. et al. Grapheme-color synesthesia induction with V4 transcranial direct current stimulation. Curr Psychol (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-024-06068-4
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-024-06068-4