Abstract
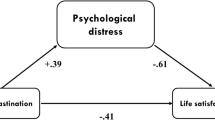
Human temperament, in terms of sensitivity to punishment and rewards, immensely impacts emotions, behaviours, and psychological well-being. Punishment sensitivity is a significant predictor of depression, but, only a few studies have explored the mediating mechanisms between them. The current study attempts to test the causal effect between punishment sensitivity and depression among students, and the chain mediating effects of procrastination (active and traditional) and academic satisfaction. For this purpose, self-report surveys were conducted on a sample of 295 engineering undergraduates in India. The data has been analyzed using structural equation modelling, where hypothesized models that connect punishment sensitivity, procrastination (active procrastination and traditional procrastination), academic satisfaction, and depression, were tested. The result revealed that punishment sensitivity positively predicts depression, and this relationship is serially mediated by procrastination (active and traditional) and academic satisfaction, respectively. Active procrastination negatively and traditional procrastination positively predict depression. Based on the study findings, future interventions against procrastination must consider punishment sensitivity as an important variable. The implications of the research are discussed.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data and material will be available from the corresponding author on reasonable requests.
References
Balkis, M. (2013). Academic procrastination, academic life satisfaction and academic achievement: the mediation role of rational beliefs about studying. Journal of Cognitive & Behavioral Psychotherapies, 13(1).
Balkis, M., & Duru, E. (2015). Procrastination, self-regulation failure, academic life satisfaction, and affective well-being: Underregulation or misregulation form. European Journal of Psychology of Education, 31(3), 439–459.
Barrós-Loscertales, A., Meseguer, V., Sanjuán, A., Belloch, V., Parcet, M. A., Torrubia, R., & Ávila, C. (2006). Behavioral Inhibition System activity is associated with increased amygdala and hippocampal gray matter volume: A voxel-based morphometry study. NeuroImage, 33(3), 1011–1015.
Beck, A. T. (Ed.). (1979). Cognitive therapy of depression. Guilford press.
Bennett, C., & Bacon, A. M. (2019). At long last – A reinforcement sensitivity theory explanation of procrastination. Journal of Individual Differences, 40(4), 234–241.
Bowins, B. (2014). Depression: Discrete or continuous? Psychopathology, 48(2), 69–78.
Brockner, J., & Higgins, E. T. (2001). Regulatory focus theory: Implications for the study of emotions at work. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes, 86(1), 35–66.
Carlson, M. D., & Morrison, R. S. (2009). Study design, precision, and validity in observational studies. Journal of palliative medicine, 12(1), 77–82.
Chibnall, J. T., & Tait, R. C. (1994). The short form of the Beck Depression Inventory: Validity issues with chronic pain patients. The Clinical Journal of Pain, 10(4), 261–266.
Choi, J. N., & Moran, S. V. (2009). Why not procrastinate? Development and validation of a new active procrastination scale. The Journal of Social Psychology, 149(2), 195–212.
Chowdhury, S. F., & Pychyl, T. A. (2018). A critique of the construct validity of active procrastination. Personality and Individual Differences, 120, 7–12.
Chun Chu, A. H., & Choi, J. N. (2005). Rethinking procrastination: Positive effects of “active” procrastination behavior on attitudes and performance. The Journal of Social Psychology, 145(3), 245–264.
Clark, R. (2015). Neuroticism and its associations with higher cognitive functions (Doctoral dissertation, University of Minnesota).
Cohen, J. (1992). Quantitative methods in psychology: A power primer. Psychological Bulletin, 112, 1155–1159.
Constantin, K., English, M. M., & Mazmanian, D. (2018). Anxiety, depression, and procrastination among students: Rumination plays a larger mediating role than worry. Journal of Rational-Emotive & Cognitive-Behavior Therapy, 36, 15–27.
Corr, P. J. (2004). Reinforcement sensitivity theory and personality. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 28(3), 317–332.
Davis, C., Levitan, R. D., Kaplan, A. S., Carter, J., Reid, C., Curtis, C., Patte, K., Hwang, R., & Kennedy, J. L. (2008). Reward sensitivity and the D2 dopamine receptor gene: A case-control study of binge eating disorder. Progress in Neuro-Psychopharmacology and Biological Psychiatry, 32(3), 620–628.
Duffy, R. D., Allan, B. A., & Dik, B. J. (2011). The presence of a calling and academic satisfaction: Examining potential mediators. Journal of Vocational Behavior, 79(1), 74–80.
Dong, W., Luo, J., Huo, H., Seger, C. A., & Chen, Q. (2022). Frontostriatal functional connectivity underlies the association between punishment sensitivity and procrastination. Brain Sciences, 12(9), 1163.
Ellis, A., & Knaus, W. J. (1977). Overcoming procrastination: Or how to think and act rationally in spite of life’s inevitable hassles (p. 400). Signet Book.
Faeq, D. (2016). Depression among students: Critical review. Retrieved June, 12, 2019.
Faul, F., Erdfelder, E., Lang, A. G., & Buchner, A. (2007). G* Power 3: A flexible statistical power analysis program for the social, behavioral, and biomedical sciences. Behavior Research Methods, 39(2), 175–191.
Figuera Gazo, P., Llanes Ordóñez, J., Torrado Fonseca, M., Valls Figuera, R. G., & Buxarrais Estrada, M. R. (2022). Reasons for course selection and academic satisfaction among Master’s degree students. Journal of Hispanic Higher Education, 21(3), 261–281.
Flett, A. L., Haghbin, M., & Pychyl, T. A. (2016). Procrastination and depression from a cognitive perspective: An exploration of the associations among procrastinatory automatic thoughts, rumination, and mindfulness. Journal of Rational-Emotive & Cognitive-Behavior Therapy, 34(3), 169–186.
Gray, J. A. (1991). The neuropsychology of temperament. Explorations in temperament (pp. 105–128). Springer, US.
Grunschel, C., Patrzek, J., & Fries, S. (2012). Exploring reasons and consequences of academic procrastination: An interview study. European Journal of Psychology of Education, 28(3), 841–861.
Hayes, A. F. (2017). Introduction to mediation, moderation, and conditional process analysis: A regression-based approach. Guilford publications.
Heubeck, B. G., Wilkinson, R. B., & Cologon, J. (1998). A second look at Carver and White’s (1994) BIS/BAS scales. Personality and Individual Differences, 25(4), 785–800.
Hevey, D., Thomas, K., Laureano-Schelten, S., Looney, K., & Booth, R. (2017). Clinical depression and punishment sensitivity on the BART. Frontiers in Psychology, 8, 670.
Hewitt, P. L., & Flett, G. L. (1991). Perfectionism in the self and social contexts: Conceptualization, assessment, and association with psychopathology. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 60(3), 456–470.
Higgins, E. T. (1998). Promotion and prevention: Regulatory focus as A motivational principle. Advances in Experimental Social Psychology (pp. 1–46). Elsevier.
Jensen, K. J., & Cross, K. J. (2021). Engineering stress culture: Relationships among mental health, engineering identity, and sense of inclusion. Journal of Engineering Education, 110(2), 371–392.
Judge, T. A., & Larsen, R. J. (2001). Dispositional affect and job satisfaction: A review and theoretical extension. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes, 86(1), 67–98.
Kasch, K. L., Rottenberg, J., Arnow, B. A., & Gotlib, I. H. (2002). Behavioural activation and inhibition systems and the severity and course of depression. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 111(4), 589–597.
Katz, B. A., & Yovel, I. (2022). Reinforcement sensitivity predicts affective psychopathology via emotion regulation: Cross-sectional, longitudinal and quasi-experimental evidence. Journal of Affective Disorders, 301, 117–129.
Kim, K. R., & Seo, E. H. (2015). The relationship between procrastination and academic performance: A meta-analysis. Personality and Individual Differences, 82, 26–33.
Kline, R. (2005). Principles and practices of structural equation modeling (2nd Ed.). New York: Guilford Press
Kroese, F. M., Nauts, S., Kamphorst, B. A., Anderson, J. H., & de Ridder, D. T. D. (2016). In Health Procrastination (Ed.), and Well-Being (pp. 93–119). Elsevier.
Krupić, D., & Corr, P. J. (2014). Individual differences in emotion elicitation in university examinations: A quasi-experimental study. Personality and Individual Differences, 71, 176–180.
Kumar, P. K., & Dileep, P. K. (2006). Academic life satisfaction scale (ALSS) and its effectiveness in predicting academic success (pp. 1–15).
Lejuez, C. W., Read, J. P., Kahler, C. W., Richards, J. B., Ramsey, S. E., Stuart, G. L., Strong, D. R., & Brown, R. A. (2002). Evaluation of a behavioral measure of risk taking: The Balloon Analogue Risk Task (BART). Journal of Experimental Psychology: Applied, 8(2), 75–84.
Lent, R. W., Brown, S. D., & Hackett, G. (1994). Toward a unifying social cognitive theory of career and academic interest, choice, and performance. Journal of Vocational Behavior, 45(1), 79–122.
Levita, L., Bois, C., Healey, A., Smyllie, E., Papakonstantinou, E., Hartley, T., & Lever, C. (2014). The Behavioural Inhibition System, anxiety and hippocampal volume in a non-clinical population. Biology of Mood & Anxiety Disorders, 4(1), 4.
Li, Z., Li, Y., Chen, L., Chen, P., & Hu, Y. (2015). Prevalence of depression in patients with hypertension. Medicine, 94(31), e1317.
Markarian, S. A., Pickett, S. M., Deveson, D. F., & Kanona, B. B. (2013). A model of BIS/BAS sensitivity, emotion regulation difficulties, and depression, anxiety, and stress symptoms in relation to sleep quality. Psychiatry Research, 210(1), 281–286.
Mellick, W., Sharp, C., & Alfano, C. (2014). The role of BIS/BAS in the vulnerability for depression in adolescent girls. Personality and Individual Differences, 69, 17–21.
Miles, D. A. (2017, August). A taxonomy of research gaps: Identifying and defining the seven research gaps. In Doctoral student workshop: finding research gaps-research methods and strategies, Dallas, Texas (pp. 1–15).
Miles, G. J., Smyrnios, K. X., Jackson, M., & Francis, A. J. P. (2019). Reward-punishment sensitivity bias predicts narcissism subtypes: Implications for the etiology of narcissistic personalities. Personality and Individual Differences, 141, 143–151.
Müller-Bloch, C., & Kranz, J. (2015). A framework for rigorously identifying research gaps in qualitative literature reviews. In T. Carte, A. Heinzl, & C. Urquhart (Eds.), Proceedings of the international conference on information systems. Fort Worth, TX.
Nolen-Hoeksema, S., Wisco, B. E., & Lyubomirsky, S. (2008). Rethinking rumination. Perspectives on Psychological Science, 3(5), 400–424.
Pychyl, T. A., & Flett, G. L. (2012). Procrastination and self-regulatory failure: An introduction to the special issue. Journal of Rational-Emotive & Cognitive-Behavior Therapy, 30(4), 203–212.
Raman. (2023). Conduct mental health survey as promised, say IIT-Madras students, Times of India, https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/city/chennai/conduct-mental-health-survey-as-promised-say-iit-madras-students/articleshow/99179894.cms Accessed 26 Sept 2023
Rawlings, A. M., Tapola, A., & Niemivirta, M. (2017). Predictive effects of temperament on motivation. International Journal of Educational Psychology, 6(2), 148.
Rozental, A., & Carlbring, P. (2014). Understanding and treating procrastination: A review of a common self-regulatory failure. Psychology, 05(13), 1488–1502.
Saxena, S. K., Mani, R. N., Dwivedi, A. K., Ryali, V. S. S. R., & Timothy, A. (2019). Association of educational stress with depression, anxiety, and substance use among medical and engineering undergraduates in India. Industrial Psychiatry Journal, 28(2), 160.
Schödl, M. M., Raz, A., & Kluger, A. N. (2018). On the positive side of avoidance motivation: An increase in avoidance motivation reduces procrastination among students. Applied Psychology, 67(4), 655–685.
Shaked, L., & Altarac, H. (2022). Exploring academic procrastination: Perceptions, self-regulation, and consequences. Journal of University Teaching and Learning Practice, 19(3), 15
Siaputra, I. B. (2010). Temporal motivation theory: Best theory (yet) to explain procrastination. Anima Indonesian Psychological Journal, 25(3), 206–214.
Sirois, F. M., Yang, S., & van Eerde, W. (2019). Development and validation of the general procrastination scale (GPS-9): A short and reliable measure of trait procrastination. Personality and Individual Differences, 146, 26–33.
Slessareva, E., & Muraven, M. (2004). Sensitivity to punishment and self-control: The mediating role of emotion. Personality and Individual Differences, 36(2), 307–319.
Smillie, L. D., & Jackson, C. J. (2006). Functional impulsivity and reinforcement sensitivity theory. Journal of Personality, 74(1), 47–84.
Steel, P. (2007). The nature of procrastination: A meta-analytic and theoretical review of quintessential self-regulatory failure. Psychological Bulletin, 133(1), 65–94.
Steel, P., & König, C. J. (2006). Integrating theories of motivation. Academy of Management Review, 31(4), 889–913.
Tomer, R., Slagter, H. A., Christian, B. T., Fox, A. S., King, C. R., Murali, D., Gluck, M. A., & Davidson, R. J. (2014). Love to win or hate to lose? Asymmetry of dopamine D2 receptor binding predicts sensitivity to reward versus punishment. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 26(5), 1039–1048.
Turner, L. A., & Turner, P. E. (2011). The relation of behavioral inhibition and perceived parenting to maladaptive perfectionism in college students. Personality and Individual Differences, 50(6), 840–844.
Uzun Ozer, B., Demir, A., & Ferrari, J. R. (2013). Reducing academic procrastination through a group treatment program: A pilot study. Journal of Rational-Emotive & Cognitive-Behavior Therapy, 31, 127–135.
van der Linden, D., Beckers, D. G. J., & Taris, T. W. (2007). Reinforcement sensitivity theory at work: Punishment sensitivity as a dispositional source of job-related stress. European Journal of Personality, 21(7), 889–909.
van Eerde, W., & Klingsieck, K. B. (2018). Overcoming procrastination? A meta-analysis of intervention studies. Educational Research Review, 25, 73–85.
Wang, Y., Gao, H., Sun, C., Liu, J., & Fan, X. (2021). Academic procrastination in college students: The role of self-leadership. Personality and Individual Differences, 178, 110866.
Zhao, J., Meng, G., Sun, Y., Xu, Y., Geng, J., & Han, L. (2019). The relationship between self-control and procrastination based on the self-regulation theory perspective: The moderated mediation model. Current Psychology, 40(10), 5076–5086.
Zhou, M. (2019). The role of personality traits and need for cognition in active procrastination. Acta Psychologica, 199, 102883.
Funding
This research received no specific funding from any agency in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
The data and material will be available from the corresponding author on reasonable requests.
Conflicts of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Additional information
The corresponding author accepts responsibility for releasing this material on behalf of any and all co-authors.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Maji, S., Sinha, S., Chaturmohta, A. et al. Punishment sensitivity and depression: the serially mediating role of procrastination and academic satisfaction. Curr Psychol 43, 18552–18560 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-024-05660-y
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-024-05660-y