Abstract
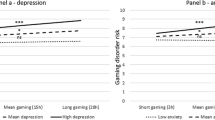
Biological and psychological factors influence the multifaceted addictive behavior of excessive gaming. While studies have reported the association of individual monoamine genes and depression or anxiety with excessive gaming, no study has explored the interplay between the biological and psychological factors underlying excessive gaming. Thus, this study examines whether the effects of depression or anxiety on excessive gaming differ as a function of cumulative genetic score (CGS) of seven monoamine genes. We conducted cross-sectional and longitudinal analyses over a year with 117 college students (63.2% male; mean age = 21.87). The cross-sectional analyses showed significant interactions between CGS and depression/anxiety on concurrent excessive gaming at an initial and later time point (i.e., Time 1 and Time 2). Higher levels of depression or anxiety led to higher levels of excessive gaming among individuals with higher CGS even after controlling the effect of anxiety or changes in behavior between Time 1 (T1) and Time 2 (T2). These findings suggest that the effects of psychological distress on excessive gaming may differ as a function of the collective effects of seven monoamine genes. This study also suggests that identifying individuals genetically prone to excessive gaming is crucial-treating their depression or anxiety may be effective in curbing the inclination towards excessive gaming.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Alhamoud, M. A., Alkhalifah, A. A., Althunyan, A. K., Mustafa, T., Alqahtani, H. A., & Al Awad, F. A. (2022). Internet gaming disorder: Its prevalence and associated gaming behavior, anxiety, and depression among high school male students, Dammam, Saudi Arabia. Journal of Family & Community Medicine, 29(2), 93. https://doi.org/10.4103/jfcm.jfcm_48_22
American Psychiatric Association. (2022). Other conditions that may be a focuse of clinical attention in diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders(5th ed., text rev.). https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.books.9780890425787.Other_Conditions_Z_codes
Audrain-McGovern, J., Lerman, C., Wileyto, P., Rodriguez, D., & Shields, P. G. (2004). Interacting effects of genetic predisposition and depression on adolescent smoking progression. American Journal of Psychiatry, 161(7), 1224–1230. https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.ajp.161.7.1224
Baysak, E., Yertutanol, F. D. K., Dalgar, I., & Candansayar, S. (2018). How game addiction rates and related psychosocial risk factors change within 2-years: A follow-up study. Psychiatry investigation, 15(10), 984. https://doi.org/10.30773/pi.2018.08.16
Belsky, D. W., Moffitt, T. E., Baker, T. B., Biddle, A. K., Evans, J. P., Harrington, H., Houts, R., Meier, M., Sugden, K., Williams, B., Poulton, R., & Caspi, A. (2013). Polygenic risk and the developmental progression to heavy, persistent smoking and nicotine dependence: Evidence from a 4-decade longitudinal study. JAMA Psychiatry, 70(5), 534–542. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2013.736
Berardelli, I., Serafini, G., Cortese, N., Fiaschè, F., O’Connor, R. C., & Pompili, M. (2020). The involvement of hypothalamus–pituitary–adrenal (HPA) axis in suicide risk. Brain Sciences, 10(9), 653. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10090653
Blum, K., Baron, D., Lott, L., Ponce, J. V., Siwicki, D., Boyett, B., Steinberg, B., Modestino, E. J., Fried, L., Hauser, M., Simpatico, T., Downs, B. W., McLaughlin, T., Hajela, R., & Badgaiyan, R. D. (2020). In search of Reward Deficiency Syndrome (RDS)-Free Controls: The “Holy Grail” in genetic addiction risk testing. Current Psychopharmacology, 9(1), 7–21. https://doi.org/10.2174/2211556008666191111103152
Blum, K., Chen, T. J., Meshkin, B., Downs, B. W., Gordon, C. A., Blum, S., ... & Martinez-Pons, M. (2007). Genotrim™, a DNA-customized nutrigenomic product, targets genetic factors of obesity: Hypothesizing a dopamine–glucose correlation demonstrating reward deficiency syndrome (RDS). Medical Hypotheses, 68(4), 844–852. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mehy.2006.08.0411
Bonnaire, C., & Baptista, D. (2019). Internet gaming disorder in male and female young adults: The role of alexithymia, depression, anxiety and gaming type. Psychiatry Research, 272, 521–530. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psychres.2018.12.158
Brand, M., Young, K. S., Laier, C., Wölfling, K., & Potenza, M. N. (2016). Integrating psychological and neurobiological considerations regarding the development and maintenance of specific Internet-use disorders: An Interaction of Person-Affect-Cognition-Execution (I-PACE) model. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 71, 252–266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2016.08.033
Brand, M., Wegmann, E., Stark, R., Müller, A., Wölfling, K., Robbins, T. W., & Potenza, M. N. (2019). The Interaction of Person-Affect-Cognition-Execution (I-PACE) model for addictive behaviors: Update, generalization to addictive behaviors beyond internet-use disorders, and specification of the process character of addictive behaviors. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 104, 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2019.06.032
Brilliant, T. D., Nouchi, R., & Kawashima, R. (2019). Does video gaming have impacts on the brain: Evidence from a systematic review. Brain sciences, 9(10), 251. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci9100251
Cerniglia, L., Cimino, S., Marzilli, E., Pascale, E., & Tambelli, R. (2020). Associations among Internet addiction, genetic polymorphisms, family functioning, and psychopathological Risk: Cross-sectional exploratory study. JMIR Mental Health, 7(12), e17341. https://doi.org/10.2196/17341
Chang, S. M., & Lin, S. S. (2019). Online gaming motive profiles in late adolescence and the related longitudinal development of stress, depression, and problematic internet use. Computers & Education, 135, 123–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2019.02.003
Chen, J., Lipska, B. K., Halim, N., Ma, Q. D., Matsumoto, M., Melhem, S., Kolachana, B. S., Hyde, T. M., Herman, M. M., Apud, J., Egan, M. F., Kleinman, J. E., & Weinberger, D. R. (2004). Functional analysis of genetic variation in catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT): Effects on mRNA, protein, and enzyme activity in postmortem human brain. The American Journal of Human Genetics, 75(5), 807–821. https://doi.org/10.1086/425589
Chen, C., Chen, C., Moyzis, R., Stern, H., He, Q., Li, H., ... & Dong, Q. (2011). Contributions of dopamine-related genes and environmental factors to highly sensitive personality: A multi-step neuronal system-level approach. Plos one, 6(7), e21636. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0021636
Cho, S. H., & Kwon, J. H. (2017). A validation of the Korean version of the Internet Gaming Disorder Scale (K-IGDS): Findings from a community sample of adults. Korean Journal of Clinical Psychology, 36(1), 104–117. https://doi.org/10.15842/kjcp.2017.36.1.010
Comings, D. E., Gade-Andavolu, R., Gonzalez, N., Wu, S., Muhleman, D., Chen, C., Koh, P., Farwell, K., Blake, H., Dietz, G., MacMurray, J. P., Lesieur, H. R., Rugle, L. J., & Rosenthal, R. J. (2001). The additive effect of neurotransmitter genes in pathological gambling. Clinical Genetics, 60(2), 107–116. https://doi.org/10.1034/j.1399-0004.2001.600204.x
Cote, A. C. (2017). “I can defend myself” women’s strategies for coping with harassment while gaming online. Games and Culture, 12(2), 136–155. https://doi.org/10.1177/1555412015587603
Dick, D. M., Cho, S. B., Latendresse, S. J., Aliev, F., Nurnberger Jr, J. I., Edenberg, H. J., ... & Kuperman, S. (2014). Genetic influences on alcohol use across stages of development: GABRA2 and longitudinal trajectories of drunkenness from adolescence to young adulthood. Addiction Biology, 19(6), 1055–1064. https://doi.org/10.1111/adb.12066
Duan, J., Wainwright, M. S., Comeron, J. M., Saitou, N., Sanders, A. R., Gelernter, J., & Gejman, P. V. (2003). Synonymous mutations in the human dopamine receptor D2 (DRD2) affect mRNA stability and synthesis of the receptor. Human Molecular Genetics, 12(3), 205–216. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddg055
Dullur, P., & Starcevic, V. (2018). Internet gaming disorder does not qualify as a mental disorder. Australian and New Zealand Journal of Psychiatry, 52(2), 110–111. https://doi.org/10.1177/0004867417741554
Duncan, L. E., & Keller, M. C. (2011). A critical review of the first 10 years of candidate gene-by-environment interaction research in psychiatry. American Journal of Psychiatry, 168(10), 1041–1049. https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.ajp.2011.11020191
Evren, C., Evren, B., Dalbudak, E., Topçu, M., Kutlu, N., & Elhai, J. D. (2020). Relationship between internet gaming disorder symptoms with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder and alexithymia symptoms among university students. Addicta: the Turkish Journal on Addictions, 7(1), 1–9. https://doi.org/10.5152/addicta.2020.19076
Faravelli, C., Lo Sauro, C., Lelli, L., Pietrini, F., Lazzeretti, L., Godini, L., ... & Ricca, V. (2012). The role of life events and HPA axis in anxiety disorders: A review. Current Pharmaceutical Design, 18(35), 5663–5674. https://doi.org/10.2174/138161212803530907
Felger, J. C. (2018). Imaging the role of inflammation in mood and anxiety-related disorders. Current Neuropharmacology, 16(5), 533–558. https://doi.org/10.2174/1570159X15666171123201142
Forrest, C. J., King, D. L., & Delfabbro, P. H. (2017). Maladaptive cognitions predict changes in problematic gaming in highly-engaged adults: A 12-month longitudinal study. Addictive Behaviors, 65, 125–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addbeh.2016.10.013
Garg, S., Kharb, A., Verma, D., Antil, R., Khanna, B., Sihag, R., & Lamba, D. (2023). The mediating role of sleep quality on the relationship between internet gaming disorder and perceived stress and suicidal behaviour among Indian medical students. Clinical Psychology Review, 36(3), e100997. https://doi.org/10.1136/gpsych-2022-100997
González-Bueso, V., Santamaría, J. J., Fernández, D., Merino, L., Montero, E., & Ribas, J. (2018). Association between internet gaming disorder or pathological video-game use and comorbid psychopathology: A comprehensive review. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 15(4), 668. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15040668
Graham, J. W., Cumsille, P. E., & Elek-Fisk, E. (2003). Methods for Handling Missing Data. Handbook of Psychology, 87–114. https://doi.org/10.1002/0471264385.wei0204
Griffiths, M. D., Kuss, D. J., & Pontes, H. M. (2016). A brief overview of Internet gaming disorder and its treatment. Australian Clinical Psychologist, 2(1), 20108.
Guo, G., Ou, X. M., Roettger, M., & Shih, J. C. (2008). The VNTR 2 repeat in MAOA and delinquent behavior in adolescence and young adulthood: Associations and MAOA promoter activity. European Journal of Human Genetics, 16(5), 626–634. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejhg.5201999
Hamlen, K. R. (2014). Video game strategies as predictors of academic achievement. Journal of Educational Computing Research, 50(2), 271–284. https://doi.org/10.2190/EC.50.2.g
Han, D. H., Lee, Y. S., Yang, K. C., Kim, E. Y., Lyoo, I. K., & Renshaw, P. F. (2007). Dopamine genes and reward dependence in adolescents with excessive Internet video game play. Journal of Addiction Medicine, 1(3), 133–138. https://doi.org/10.1097/ADM.0b013e31811f465f
Holstein, B., Pedersen, T., Bendtsen, P., Madsen, K. R., Meilstrup, C. R., Nielsen, L., & Rasmussen, M. (2014). Perceived problems with computer gaming and internet use among adolescents: measurement tool for non-clinical survey studies. BMC Public Health, 14(1), 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2458-14-361
Hong, H. S., Jeong, J. E., Cho, H., Choi, M. R., Choi, J. S., Choi, S. W., Kwak, S. M., & Kim, D. J. (2018). Effect of stress and Serotonin-Transporter-Linked Polymorphic Region variants on Internet Gaming Disorder in Korean adults. Journal of the Korean Society of Biological Psychiatry, 25(3), 9. https://doi.org/10.22857/kjbp.2018.25.3.005
Hu, S., Brody, C., Fisher, C., Gunzerath, L., Nelson, M., Sabol, S., Sirota, L., Marcus, S., Greenberg, B., Murphy, D., & Hamer, D. (2000). Interaction between the serotonin transporter gene and neuroticism in cigarette smoking behavior. Molecular Psychiatry, 5(2), 181–188. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.mp.4000690
Kaess, M., Parzer, P., Mehl, L., Weil, L., Strittmatter, E., Resch, F., & Koenig, J. (2017). Stress vulnerability in male youth with Internet gaming disorder. Psychoneuroendocrinology, 77, 244–251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psyneuen.2017.01.008
Kaye, L. K., Pennington, C. R., & McCann, J. J. (2018). Do casual gaming environments evoke stereotype threat? Examining the effects of explicit priming and avatar gender. Computers in Human Behavior, 78, 142–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2017.09.031
Kim, E. H., & Kim, N. H. (2013). Comparison of stress level and HPA axis activity of internet game addiction vs. non-addiction in adolescents. Journal of Korean Biological Nursing Science, 15(4), 173–183. https://doi.org/10.7586/jkbns.2013.15.4.173
Kim, E. Y., Lee, Y. S., Han, D. H., Suh, D. S., & Kee, B. S. (2006). Temperament and genetic polymorphism in Korean male adolescents with internet addiction tendency. Journal of Korean Neuropsychiatric Association, 54(4), 468–475. https://doi.org/10.4306/jknpa.2015.54.4.468
Kim, J., Marciano, M. A., Ninham, S., Zaso, M. J., & Park, A. (2019). Interaction effects between the cumulative genetic score and psychosocial stressor on self-reported drinking urge and implicit attentional bias for alcohol: A human laboratory study. Alcohol and Alcoholism, 54(1), 30–37. https://doi.org/10.1093/alcalc/agy065
Kim, E., Lee, D., Do, K., & Kim, J. (2022a). Interaction effects of DRD2 genetic polymorphism and interpersonal stress on problematic gaming in college students. Genes, 13(3). https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13030449
Kim, H. S., Son, G. E., Roh, E. B., Ahn, W. Y., Kim, J., Shin, S. H., Chey, J. Y., & Choi, K. H. (2022b). Prevalence of gaming disorder: A meta-analysis. Addictive Behaviors, 126, 107183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addbeh.2021.107183
King, D. L., Delfabbro, P. H., & Griffiths, M. D. (2013). Trajectories of problem video gaming among adult regular gamers: An 18-month longitudinal study. Cyberpsychology, Behavior, and Social Networking, 16(1), 72–76. https://doi.org/10.1089/cyber.2012.0062
King, D. L., Chamberlain, S. R., Carragher, N., Billieux, J., Stein, D., Mueller, K., ... & Delfabbro, P. H. (2020). Screening and assessment tools for gaming disorder: A comprehensive systematic review. Clinical Psychology Review, 77, 101831. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cpr.2020.101831
Kline, R. B. (2015). Principles and Practice of Structural Equation Modeling. Guilford publications.
Krossbakken, E., Pallesen, S., Mentzoni, R. A., King, D. L., Molde, H., Finserås, T. R., & Torsheim, T. (2018). A cross-lagged study of developmental trajectories of video game engagement, addiction, and mental health. Frontiers in Psychology, 9, 2239. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2018.02239
Lemmens, J. S., Valkenburg, P. M., & Gentile, D. A. (2015). The internet gaming disorder scale. Psychological Assessment, 27(2), 567.
Lerman, C., Caporaso, N. E., Audrain, J., Main, D., Boyd, N. R., & Shields, P. G. (2000). Interacting effects of the serotonin transporter gene and neuroticism in smoking practices and nicotine dependence. Molecular Psychiatry, 5(2), 189–192. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.mp.4000672
Lesch, K. P., Bengel, D., Heils, A., Sabol, S. Z., Greenberg, B. D., Petri, S., Benjamin, J., Muller, C. R., Hamer, D. H., & Murphy, D. L. (1996). Association of anxiety related traits with a polymorphism in the serotonin transporter gene regulatory region. Science, 274(5292), 1527–1531. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.274.5292.1527
Levis, B., Sun, Y., He, C., Wu, Y., Krishnan, A., Bhandari, P. M., Neupane, D., Imran, M., Brehaut, E., Negeri, Z., Fischer, F. H., Benedetti, A., & Thombs, B. D. (2020). Accuracy of the PHQ-2 alone and in combination with the PHQ-9 for screening to detect major depression: Systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA, 323(22), 2290–2300. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2020.6504
Li, H., Zou, Y., Wang, J., & Yang, X. (2016). Role of stressful life events, avoidant coping styles, and neuroticism in online game addiction among college students: A moderated mediation model. Frontiers in Psychology, 7, 1794. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2016.01794
Lin, P. Y., Lin, H. C., Lin, P. C., Yen, J. Y., & Ko, C. H. (2020). The association between emotional regulation and internet gaming disorder. Psychiatry Research, 289, 113060. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psychres.2020.113060
Madigan, M. A., Gupta, A., Bowirrat, A., Baron, D., Badgaiyan, R. D., Elman, I., ... & Blum, K. (2022). Precision behavioral management (PBM) and cognitive control as a potential therapeutic and prophylactic modality for reward deficiency syndrome (RDS): Is there enough evidence? International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(11), 6395. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19116395
McClelland, G. H., & Judd, C. M. (1993). Statistical difficulties of detecting interactions and moderator effects. Psychological Bulletin, 114, 376–390. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-2909.114.2.376
McGeary, J. E., Knopik, V. S., Hayes, J. E., Palmer, R. H., Monti, P. M., & Kalman, D. (2012). Predictors of relapse in a bupropion trial for smoking cessation in recently-abstinent alcoholics: Preliminary results using an aggregate genetic risk score. Substance Abuse: Research and Treatment, 6, 107–114. https://doi.org/10.4137/SART.S8866
Miezah, D., Batchelor, J., Megreya, A. M., Richard, Y., & Moustafa, A. A. (2020). Video/computer game addiction among university students in ghana: Prevalence, correlates and effects of some demographic factors. Psychiatry and Clinical Psychopharmacology, 30(1), 17–23. https://doi.org/10.5455/PCP.20200320092210
Ostinelli, E. G., Zangani, C., Giordano, B., Maestri, D., Gambini, O., D’Agostino, A., Furukawa, T. A., & Purgato, M. (2021). Depressive symptoms and depression in individuals with internet gaming disorder: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of Affective Disorders, 284, 136–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2021.02.014
Park, S. J., Choi, H. R., Choi, J. H., Kim, K. W., & Hong, J. P. (2010). Reliability and validity of the Korean Version of the Patient Health Questionnaire-9 (PHQ-9). Anxiety and Mood, 6(2), 119–124.
Piasecki, T. M., Gizer, I. R., & Slutske, W. S. (2019). Polygenic risk scores for psychiatric disorders reveal novel clues about the genetics of disordered gambling. Twin Research and Human Genetics, 22(5), 283–289. https://doi.org/10.1017/thg.2019.90
Plummer, F., Manea, L., Trepel, D., & McMillan, D. (2016). Screening for anxiety disorders with the GAD-7 and GAD-2: A systematic review and diagnostic metaanalysis. General Hospital Psychiatry, 39, 24–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.genhosppsych.2015.11.005
Richard, J., Temcheff, C. E., & Derevensky, J. L. (2020). Gaming disorder across the lifespan: A scoping review of longitudinal studies. Current Addiction Reports, 7, 561–587. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40429-020-00339-3
Scharkow, M., Festl, R., & Quandt, T. (2014). Longitudinal patterns of problematic computer game use among adolescents and adults—A 2-year panel study. Addiction, 109(11), 1910–1917. https://doi.org/10.1111/add.12662
Schoots, O., & Van Tol, H. H. (2003). The human dopamine D4 receptor repeat sequences modulate expression. The Pharmacogenomics Journal, 3(6), 343–348. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.tpj.6500208
Si, S., Su, Y., Zhang, S., & Zhang, J. (2020). Genetic susceptibility to parenting style: DRD2 and COMT influence creativity. NeuroImage, 213, 116681. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2020.116681
Spitzer, R. L., Kroenke, K., Williams, J. B. W., & Lowe, B. (2006). A Brief measure for assessing Generalized Anxiety Disorder. Archives of Internal Medicine, 166(10), 1092–1097. https://doi.org/10.1001/archinte.166.10.1092
Stetina, B. U., Kothgassner, O. D., Lehenbauer, M., & Kryspin-Exner, I. (2011). Beyond the fascination of online-games: Probing addictive behavior and depression in the world of online-gaming. Computers in Human Behavior, 27(1), 473–479. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2010.09.015
Stevens, M. W., King, D. L., Dorstyn, D., & Delfabbro, P. H. (2019). Cognitive–behavioral therapy for Internet gaming disorder: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clinical Psychology & Psychotherapy, 26(2), 191–203. https://doi.org/10.1002/cpp.2341
Stevens, C., Zhang, E., Cherkerzian, S., Chen, J. A., & Liu, C. H. (2020). Problematic internet use/computer gaming among US college students: Prevalence and correlates with mental health symptoms. Depression and Anxiety, 37(11), 1127–1136. https://doi.org/10.1002/da.23094
Sun, Y., Fang, J., Wan, Y., Hu, J., Xu, Y., & Tao, F. (2018). Polygenic differential susceptibility to cumulative stress exposure and childhood obesity. International Journal of Obesity, 42(6), 1177–1184. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41366-018-0116-z
Van Rooij, A. J., Schoenmakers, T. M., Van de Eijnden, R. J., & Van de Mheen, D. (2010). Compulsive internet use: The role of online gaming and other internet applications. Journal of Adolescent Health, 47(1), 51–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jadohealth.2009.12.021
Van Rooij, A. J., Ferguson, C. J., Colder Carras, M., Kardefelt-Winther, D., Shi, J., Aarseth, E., ... & Przybylski, A. K. (2018). A weak scientific basis for gaming disorder: Let us err on the side of caution. Journal of Behavioral Addictions, 7(1), 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1556/2006.7.2018.19
VanNess, S. H., Owens, M. J., & Kilts, C. D. (2005). The variable number of tandem repeats element in DAT1 regulates in vitro dopamine transporter density. BMC Genetics, 6, 55. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2156-6-55
Vink, J. M., Hottenga, J. J., de Geus, E. J., Willemsen, G., Neale, M. C., Furberg, H., & Boomsma, D. I. (2014). Polygenic risk scores for smoking: Predictors for alcohol and cannabis use? Addiction, 109(7), 1141–1151. https://doi.org/10.1111/add.12491
Vreeburg, S. A., Hoogendijk, W. J., van Pelt, J., DeRijk, R. H., Verhagen, J. C., van Dyck, R., ... & Penninx, B. W. (2009). Major depressive disorder and hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis activity: results from a large cohort study. Archives of General Psychiatry, 66(6), 617–626. https://doi.org/10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2009.50
Wakil, K., Omer, S., & Omer, B. (2017). Impact of computer games on students GPA. European Journal of Education Studies., 8(3), 262–272. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.827400
Wang, H. Y., & Cheng, C. (2021). New perspectives on the prevalence and associated factors of gaming disorder in Hong Kong community adults: A generational approach. Computers in Human Behavior, 114, 106574. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2020.106574
Wang, C. Y., Wu, Y. C., Su, C. H., Lin, P. C., Ko, C. H., & Yen, J. Y. (2017). Association between Internet gaming disorder and generalized anxiety disorder. Journal of Behavioral Addictions, 6(4), 564–571. https://doi.org/10.1556/2006.6.2017.088
Wartberg, L., Kriston, L., Zieglmeier, M., Lincoln, T., & Kammerl, R. (2019). A longitudinal study on psychosocial causes and consequences of Internet gaming disorder in adolescence. Psychological Medicine, 49(2), 287–294. https://doi.org/10.1017/S003329171800082X
World Health Organization. (2018). International classification of diseases (ICD). ICD-11 for Mortality and Morbidity Statistics. Retrieved December 1, 2018, from https://icd.who.int/browse11/l-m/en#/http://id.who.int/icd/entity/1448597234
Xiang, G. X., Gan, X., Jin, X., Zhang, Y. H., & Zhu, C. S. (2022). Developmental assets, self-control and internet gaming disorder in adolescence: Testing a moderated mediation model in a longitudinal study. Frontiers in Public Health, 10, 808264. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2022.808264
Yen, J. Y., Yeh, Y. C., Wang, P. W., Liu, T. L., Chen, Y. Y., & Ko, C. H. (2018). Emotional regulation in young adults with internet gaming disorder. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 15(1), 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15010030
Yen, J. Y., Lin, P. C., Lin, H. C., Lin, P. Y., Chou, W. P., & Ko, C. H. (2022). Association of Internet gaming disorder with catechol-O-methyltransferase: Role of impulsivity and fun-seeking. The Kaohsiung Journal of Medical Sciences, 38(1), 70–76. https://doi.org/10.1002/kjm2.12454
Yen, J. Y., Chou, W. P., Lin, H. C., Wu, H. C., Tsai, W. X., & Ko, C. H. (2021). Roles of hostility and depression in the association between the MAOA gene polymorphism and internet gaming disorder. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(13), 6910. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18136910
Zajac, K., Ginley, M. K., & Chang, R. (2020). Treatments of internet gaming disorder: A systematic review of the evidence. Expert Review of Neurotherapeutics, 20(1), 85–93. https://doi.org/10.1080/14737175.2020.1671824
Zelinski, E. M., & Reyes, R. (2009). Cognitive benefits of computer games for older adults. Gerontechnology: International Journal on The Fundamental Aspects of Technology to Serve the Ageing Society, 8(4), 220. https://doi.org/10.4017/gt.2009.08.04.004.00
Zurita, F., Chacón, R., Castro, M., Martínez, A., Espejo, T., Knox, E., & JoaquínMuros, J. (2018). Problematic consumption of substances and video game use in Spanish university students depending on sex and place of residence. Health & Addictions/Salud y Drogas, 18(1), 89–96. https://doi.org/10.21134/haaj.v18i1.350
Funding
This study was funded by National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) [grant number: 2020R1G1A100828312]. NRF had no role in the study design, collection, analysis or interpretation of the data, writing the manuscript, or the decision to submit the paper for publication.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Dojin Lee and Seunghee Lee analyzed the data and wrote the draft of the manuscript. Jueun Kim conceived the original idea and reviewed the manuscript. All authors contributed to the manuscript writing and approved the submitted version.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
This study was performed in line with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. Approval was granted by the Institutional Review Board of the Chungnam National University (24 September 2021, protocol code 202003-SB-026–01).
Consent to participate
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Competing interests
The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Dojin Lee and Seunghee Lee contributed equally and should be considered as co-first authors.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, D., Lee, S. & Kim, J. Interaction effects of cumulative genetic score and psychological distress on excessive gaming: A 2-year longitudinal study. Curr Psychol 43, 16170–16182 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-023-05553-6
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-023-05553-6