Abstract
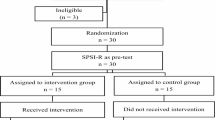
This study aimed to explore the effect of cognitive remediation on cognitive and behavioral emotion regulation of female deaf and hard-of-hearing (DHH) students. Thirty female DHH students, ages 14–16 years, were randomly selected and assigned to the treatment (n = 15) and control (n = 15) groups. The treatment group participated in ten sessions on cognitive remediation (lasts for five weeks), while the control group participated in three general placebo sessions. The participants were assessed before and after the intervention using the Cognitive Emotion Regulation Questionnaire (CERQ-short) and Behavioral Emotion Regulation Questionnaire (BERQ). The differences in cognitive and behavioral emotion regulation between the treatment and control groups were examined using a multivariate analysis of covariance. The results indicated that cognitive remediation training improved cognitive and behavioral emotion regulation in the treatment group. The cognitive remediation training was feasible and acceptable to DHH students.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Ashori, M., & Rashidi, A. (2020). Effectiveness of cognitive emotion regulation on emotional intelligence in students with hearing impairment. Iranian Rehabilitation Journal, 18(3), 239–248. https://doi.org/10.32598/irj.18.3.188.6.
Ashori, M., Yazdanipour, M., & Pahlavani, M. (2019). The effectiveness of cognitive rehabilitation program on auditory perception and verbal intelligibility of deaf children. American Journal of Otolaryngology–Head and Neck Medicine and Surgery, 40(5), 724–728. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjoto.2019.06.011.
Bamonti, P., Conti, E., Cavanagh, C., Gerolimatos, L., Gregg, J., Goulet, C., Pifer, M., & Edelstein, B. (2019). Coping, cognitive emotion regulation, and burnout in long-term care nursing staff: A preliminary study. Journal of Applied Gerontology, 38(1), 92–111. https://doi.org/10.1177/0733464817716970.
Bonanno, G. A., & Burton, C. L. (2013). Regulatory flexibility: An individual differences perspective on coping and emotion regulation. Perspectives on psychological science: A journal of the Association for Psychological Science, 8(6), 591–612. https://doi.org/10.1177/1745691613504116.
Broekhof, E., Bos, M. G. N., Camodeca, M., & Rieffe, C. (2018). Longitudinal associations between bullying and emotions in deaf and hard of hearing adolescents. Journal of Deaf Studies and Deaf Education, 23(1), 17–27. https://doi.org/10.1093/deafed/enx036.
Bucich, M., & MacCann, C. (2019). Emotional intelligence and day-to-day emotion regulation processes: Examining motives for social sharing. Personality and Individual Differences, 137, 22–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2018.08.002.
Chatzidamianos, G., McCarthy, R. A., Du Feu, M., Rosselló, J., & McKenna, P. J. (2018). Language abnormality in deaf people with schizophrenia: A problem with classifiers. Cognitive Neuropsychiatry, 23(4), 229–241. https://doi.org/10.1080/13546805.2018.1476227.
Cicerone, K. D., Goldin, Y., Ganci, K., Rosenbaum, A., Wethe, J. V., Langenbahn, D. M., Malec, J. F., Bergquist, T. F., Kingsley, K., Nagele, D., Trexler, L., Fraas, M., Bogdanova, Y., & Harley, J. P. (2019). Evidence-based cognitive rehabilitation: Systematic review of the literature from 2009 through 2014. Archives of physical medicine and rehabilitation, 100(8), 1515–1533. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apmr.2019.02.011.
Cohen, L., Manion, L., & Morrison, K. (2011). Research Methods in Education (7th ed.). Routledge. https://doi.org/10.4324/9780203720967.
Coll, K. M., Cutler, M. M., Thobro, P., Haas, R., & Powell, S. (2009). An exploratory study of psychosocial risk behaviors of adolescents who are deaf or hard of hearing: Comparisons and recommendations. American Annals of the Deaf, 154(1), 30–35. https://doi.org/10.1353/aad.0.0074.
Crowe, T. V. (2021). Factors associated with help-seeking and self-efficacy among a sample of deaf adults. Journal of Developmental and Physical Disabilities, 33(1), 51–63. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10882-020-09739-9.
Crowe, K., & Dammeyer, J. (2021). A review of the conversational pragmatic skills of children with cochlear implants. Journal of Deaf Studies and Deaf Education, 26(2), 171–186. https://doi.org/10.1093/deafed/enab001.
Fan, Q., Liao, L., & Pan, G. (2017). The application of cognitive remediation therapy in the treatment of mental disorders. Shanghai Archives of Psychiatry, 29(6), 373–375. https://doi.org/10.11919/j.issn.1002-0829.217079.
Finley, J. C., & Parente, F. (2019). A 30-year retrospective case analysis in the Delphi of cognitive rehabilitation therapy. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 138, 254–260. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2018.09.022.
Galletly, C., & Rigby, A. (2013). An overview of cognitive remediation therapy for people with severe mental illness. ISRN Rehabilitation, 984932, 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/984932.
Garnefski, N., & Kraaij, V. (2006). Cognitive emotion regulation questionnaire development of a short 18-item version (CERQ-short). Personality and Individual Differences, 41, 1045–1053. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2006.04.010.
Goubet, K. E., & Chrysikou, E. G. (2019). Emotion regulation flexibility: Gender differences in context sensitivity and repertoire. Frontiers in psychology, 10, 935. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2019.00935.
Gross, J. J. (2015). Emotion regulation: Current status and future prospects. Psychological Inquiry, 26(1), 1–26. https://doi.org/10.1080/1047840x.2014.940781.
Gunnesch-Luca, G., & Iliescu, D. (2020). Time and generational changes in cognitive performance in Romania. Intelligence, 79, 101430. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intell.2020.101430.
Hallahan, D. P., Pullen, P. C., & Kauffman, J. M. (2023). Exceptional learners: An introduction to special education (15th Ed.). Pearson Education, Inc. https://www.amazon.com/Exceptional-Learners-Introduction-Special-Education-ebook/dp/B09STKPCL3.
Hintermair, M. (2013). Executive functions and behavioral problems in Deaf and Hard-of-hearing students at General and Special Schools. Journal of Deaf Studies and Deaf Education, 18(3), 344–359. https://doi.org/10.1093/deafed/ent003.
Hosie, J. A., Gray, C. D., Russell, P. A., Scott, C., & Hunter, N. (1998). The matching of facial expressions by deaf and hearing children and their production and comprehension of emotion labels. Motivation and Emotion, 22(4), 293–313. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021352323157.
Joormann, J., & Stanton, C. H. (2016). Examining emotion regulation in depression: A review and future directions. Behavior Research and Therapy, 86, 35–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brat.2016.07.007.
Kato, T. (2015). Frequently used coping scales: A meta-analysis. Stress Health, 31, 315–323. https://doi.org/10.1002/smi.2557.
Kazempour, V., Ebrahimi, H., Asghari Jafarabadi, M., Nourazar, S. G., & Zamani, H. (2018). The effect of group cognitive behavioral therapy on cognitive emotion regulation strategies of adolescents with bipolar disorder during their euthymic phase: A single-blind, randomized controlled trial. Iranian Red Crescent Medical Journal, 20(S1), e61555. https://doi.org/10.5812/ircmj.61555.
Kraaij, V., & Garnefski, N. (2019). The behavioral emotion regulation questionnaire: Development, psychometric properties and relationships with emotional problems and the cognitive emotion regulation questionnaire. Personality and Individual Differences, 137, 56–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2018.07.036.
Livingston, E. M., Siegel, L. S., & Ribary, U. (2018). Developmental dyslexia: Emotional impact and consequences. Australian Journal of Learning Difficulties, 23(2), 1–29. https://doi.org/10.1080/19404158.2018.1479975.
Lubbadeh, T. (2020). Emotional intelligence and leadership- the dark and bright sides. Modern Management Review, 27(1), 39–50. https://doi.org/10.7862/rz.2020.mmr.5.
Marschark, M. (2007). Raising and educating a deaf child: A comprehensive guide to choices, controversies, and decisions faced by parents and educators (2nd ed.). Oxford University Press, Inc.
Mattingly, V., & Kraiger, K. (2019). Can emotional intelligence be trained? A meta-analytical investigation. Human Resource Management Review, 29(2), 140–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hrmr.2018.03.002.
Medalia, A., & Choi, J. (2009). Cognitive remediation in schizophrenia. Neuropsychology Review, 19(3), 353–364. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11065-009-9097-y.
Mellon, N. K., Ouellette, M., Greer, T., & Gates-Ulanet, P. (2009). Achieving developmental synchrony in young children with hearing loss. Trends in amplification, 13(4), 223–240. https://doi.org/10.1177/1084713809356701.
Mothersill, D., Dillon, R., Hargreaves, A., Castorina, M., Furey, E., Fagan, A. J., & Donohoe, G. (2018). Computerised working memory-based cognitive remediation therapy does not affect reading the mind in the eyes test performance or neural activity during a facial emotion recognition test in psychosis. European Journal of Neuroscience, 48(1), 1691–1705. https://doi.org/10.1111/ejn.13976.
Pichon, M., Howard-Merrill, L., Wamoyi, J., Buller, A. M., & Kyegombe, N. (2022). Aqualitative study exploring parent–daughter approaches for communicating about sex and transactional sex in Central Uganda: Implications for comprehensive sexuality education interventions. Journal of Adolescence, 94(5), 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1002/jad.1207112.
Rajeswaran, J., & Bennett, C. N. (2018). Cognitive rehabilitation in addictive disorders. Indian journal of psychiatry, 60(l 4), S490–s493. https://doi.org/10.4103/psychiatry.IndianJPsychiatry_17_18.
Rieffe, C. (2012). Awareness and regulation of emotions in deaf children. British Journal of Developmental Psychology, 30(4), 477–492. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.2044-02057.x.
Rudner, M., Seeto, M., Keidser, G., Johnson, B., & Rönnberga, J. (2019). Poorer speech reception threshold in noise is associated with lower brain volume in auditory and cognitive processing regions. Journal of Speech Language and Hearing Research, 62, 1117–1130. https://doi.org/10.1044/2018_JSLHR-H-ASCC7-18-0142.
Sala, G., & Gobet, F. (2020). Cognitive and academic benefits of music training with children: A multilevel meta-analysis. Memory & Cognition, 48(8), 1429–1441. https://doi.org/10.3758/s13421-020-01060-2.
Seufert, T. (2020). Building bridges between self-regulation and cognitive load an invitation for a broad and differentiated attempt. Educational Psychology Review, 32(4), 1151–1162. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10648-020-09574-6.
Shin, H. Y., & Hwang, H. J. (2017). Mental health of the people with hearing impairment in Korea: A population-based cross-sectional study. Korean Journal of Family Medicine, 38, 57–63. https://doi.org/10.4082/kjfm.2017.38.2.57.
Silver, I. A., & Nedelec, J. L. (2018). Cognitive abilities and antisocial behavior in prison: A longitudinal assessment using a large state-wide sample of prisoners. Intelligence, 71, 17–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intell.2018.09.004.
Stubberud, J., Huster, R., Hoorelbeke, K., Hammar, Å., & Hagen, B. I. (2021). Improved emotion regulation in depression following cognitive remediation: A randomized controlled trial. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 147(1), 103991. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brat.2021.103991.
Szarkowski, A., & Brice, P. (2018). Positive psychology in research with the deaf community: An idea whose time has come. Journal of Deaf Studies and Deaf Education, 23(2), 111–117. https://doi.org/10.1093/deafed/enx058.
Tunmer, W. E., & Hoover, W. A. (2019). The cognitive foundations of learning to read: A framework for preventing and remediating reading difficulties. Australian Journal of Learning Difficulties, 24(1), 75–93. https://doi.org/10.1080/19404158.2019.1614081.
Vernon, M. (2005). Fifty years of research on the intelligence of deaf and hard-of-hearing children: A review of literature and discussion of implications. Journal of deaf studies and deaf education, 10(3), 225–231. https://doi.org/10.1093/deafed/eni024.
Williams, K. C., Falkum, E., & Martinsen, E. W. (2015). A cognitive therapy program for hearing-impaired employees suffering from mental distress. International Journal of Audiology, 54(4), 227–233. https://doi.org/10.3109/14992027.2014.958621.
Yang, M., Chen, H. J., Liu, B., Huang, Z. C., Feng, Y., Li, J., & Teng, G. J. (2014). Brain structural and functional alterations in patients with unilateral hearing loss. Hearing Research, 316(1), 37–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heares.2014.07.006.
Acknowledgements
The author would like to appreciate the Exceptional Education Organization of Isfahan, Iran. Also, I respectfully appreciate all deaf and hard-of-hearing (DHH) students participated in this study.
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Mohammad Ashori: Conceived and designed the experiments; Performed the experiments; Analyzed and interpreted the data; Contributed reagents, materials, analysis tools or data; Wrote the paper.
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ashori, M. Effect of cognitive remediation on cognitive and behavioral emotion regulation of female deaf and hard-of-hearing students. Curr Psychol 43, 8740–8751 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-023-05027-9
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-023-05027-9