Abstract
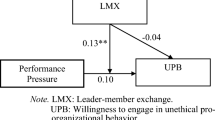
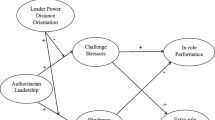
Authoritarian leadership is a stressor that stimulates counterproductive work behaviors (CWB) among employees. Based on affective events theory, this study explored how authoritarian leadership affects employees’ targeted CWB and investigated the mediating role of negative affect. Drawing from social comparison theory, we further explored how relative leader-member exchange (RLMX) plays the role in the model. Through a questionnaire survey of 462 respondents from 93 teams in China, we constructed a cross-level moderated mediation model in Mplus to test our hypothesis. The results showed that (1) authoritarian leadership positively predicted employees’ organizational counterproductive work behaviors (CWB-O) but not interpersonal counterproductive work behaviors (CWB-I). Additionally, (2) RLMX positively moderated the relationship between authoritarian leadership and negative affect, and moderated the mediating effect of negative affect. Specifically, authoritarian leadership had a negative but non-significant influence on negative affect at a high level of RLMX. However, the predictive direction and strength of authoritarian leadership on negative affect turned to significantly positive and stronger under the low level of RLMX, which led to an increase in CWB-I and a decrease in CWB-O. The theoretical implications of these findings for advancing the research, the practical approaches to reduce employees’ CWB, and avenues for future research are discussed.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Notes
Weimob (2022, April 26). Weimob Annual Report 2021. https://cdn2.weimob.com/saas/@assets/saas-fe-website-web-stc/pdf/ijm20madb3cf2k811m21hi20m0a488.pdf
References
Baka, U. (2015). How do negative affects regulate the effects of workplace aggression on counterproductive work behavior? Polish Psychological Bulletin, 46(3), 326–335. https://doi.org/10.1515/ppb-2015-0040
Bennett, R. J., & Robinson, S. L. (2000). Development of a measure of workplace deviance. Journal of Applied Psychology, 85(3), 349–360. https://doi.org/10.1037/0021-9010.85.3.349
Berry, C. M., Carpenter, N. C., & Barratt, C. L. (2012). Do other-reports of counterproductive work behavior provide an incremental contribution over self-reports? A meta-analytic comparison. Journal of Applied Psychology, 97(3), 613–636. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0026739
Biemann, T., Cole, M. S., & Voelpel, S. (2012). Within-group agreement: On the use (and misuse) of rwg and rwg(j) in leadership research and some best practice guidelines. The Leadership Quarterly, 23(1), 66–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.leaqua.2011.11.006
Bodla, A. A., Tang, N., Dick, R. V., & Mir, U. R. (2019). Authoritarian leadership, organizational citizenship behavior, and organizational deviance: Curvilinear relationships. Leadership and Organization Development Journal, 40(5), 583–599. https://doi.org/10.1108/LODJ-08-2018-0313
Braun, S., Aydin, N., Frey, D., & Peus, C. (2018). Leader narcissism predicts malicious envy and supervisor-targeted counterproductive work behavior: Evidence from field and experimental research. Journal of Busssiness Ethics, 151(3), 725–741. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10551-016-3224-5
Brief, A. P., & Weiss, H. M. (2002). Organizational behavior: Affect in the workplace. Annual Review of Psychology, 53(1), 279–307. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.psych.53.100901.135156
Brislin, R. W. (1970). Back-translation for cross-cultural research. Journal of Cross-Cultural Psychology, 1(3), 185–216. https://doi.org/10.1177/135910457000100301
Butts, M. M., Becker, W. J., & Boswell, W. R. (2015). Hot buttons and time sinks: The effects of electronic communication during non-work time on emotions and work-non-work conflict. Academic of Management Journal, 58(3), 763–788. https://doi.org/10.5465/amj.2014.0170
Buunk, A. P., & Gibbons, F. X. (2007). Social comparison: The end of a theory and the emergence of a field. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes, 102(1), 3–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.obhdp.2006.09.007
Chen, X. P., Eberly, M. B., Chiang, T. J., Farh, J. L., & Cheng, B. S. (2014). Affective trust in Chinese leaders: Linking paternalistic leadership to employee performance. Journal of Management, 40(3), 796–819. https://doi.org/10.1177/0149206311410604
Choi, J. N., Sung, S. Y., Lee, K., & Cho, D. S. (2011). Balancing cognition and emotion, innovation implementation as a function of cognitive appraisal and emotional reactions toward innovation. Journal of Organizational Behavior, 32(1), 107–124. https://doi.org/10.1002/job.684
Chou, W. J., Chou, L. F., Cheng, B. S., & Jen, C. K. (2010). Juan-chiuan and shang-yan: The components of authoritarian leadership. Indigenous Psychological Research in Chinese Societies, 34, 223–284. https://doi.org/10.6254/2010.34.223
Christie, R., & Geis, F. L. (1970). Studies in Machiavellianism. Academic Press.
Dalal, R. S., Lam, H., Weiss, H. M., Welch, E. R., & Hulin, C. L. (2009). A within-person approach to work behavior and performance: Concurrent and lagged citizenship-counterproductivity associations, and dynamic relationships with affect and overall job performance. Academy of Management Journal, 52(5), 1051–1066. https://doi.org/10.5465/AMJ.2009.44636148
Dedahanov, A. T., Lee, D. H., Rhee, J., & Yoon, J. (2016). Entrepreneur’s paternalistic leadership style and creativity: The mediating role of employee voice. Management Decision, 54(9), 2310–2324. https://doi.org/10.1108/MD-11-2015-0537
Dulebohn, J. H., Bommer, W. H., Liden, R. C., Brouer, R. L., & Ferris, G. R. (2012). A meta-analysis of antecedents and consequences of leader-member exchange integrating the past with an eye toward the future. Journal of Management, 38(6), 1715–1759. https://doi.org/10.1177/0149206311415280
Eisenberger, R., Armeli, S., Rexwinkel, B., Lynch, P. D., & Rhoades, L. (2001). Reciprocation of perceived organizational support. Journal of Applied Psychology, 86(1), 42–51. https://doi.org/10.1037/0021-9010.86.1.42
Epitropaki, O., Kapoutsis, I., Ellen, B. P., Ferris, G. R., Drivas, K., & Ntotsi, A. (2016). Navigating uneven terrain: The roles of political skill and LMX differentiation in prediction of work relationship quality and work outcomes. Journal of Organizational Behavior, 37(7), 1078–1103. https://doi.org/10.1002/job.2100
Festinger, L. (1954). A theory of social comparison processes. Human Relations, 7, 117–140. https://doi.org/10.1177/001872675400700202
Fida, R., Paciello, M., Tramontano, C., Fontaine, R., Barbaranelli, C., & Farnese, M. (2015). An integrative approach to understanding counterproductive work behavior: The roles of stressors, negative affect, and disengagement. Journal of Business Ethics, 130(1), 131–144. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10551-014-2209-5
Goodman, P. S., & Haisley, E. (2007). Social comparison processes in an organizational context: New directions. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes, 102(1), 109–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.obhdp.2006.10.005
Guo, L., Decoster, S., Babalola, M. T., De Schutter, L., Garba, O. A., & Riisla, K. (2018). Authoritarian leadership and employee creativity: The moderating role of psychological capital and the mediating role of fear and defensive silence. Journal of Business Research, 92, 219–230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2018.07.034
Harms, P. D., Wood, D., Landay, K., Lester, P. B., & Lester, G. V. (2018). Autocratic leaders and authoritarian followers revisited a review and agenda for the future. The Leadership Quarterly, 29, 105–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.leaqua.2017.12.007
Henderson, D. J., Wayne, S. J., Shore, L. M., Bommer, W. H., & Tetrick, L. E. (2008). Leader-member exchange, differentiation, and psychological contract fulfillment: A multilevel examination. Journal of Applied Psychology, 93(6), 1208–1219. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0012678
Hershcovis, M. S., & Reich, T. C. (2013). Integrating workplace aggression research: Relational, contextual, and method considerations. Journal of Organizational Behavior, 34(Supp11), S26–S42. https://doi.org/10.1002/job.1886
Hiller, N. J., Sin, H. P., Ponnapalli, A. R., & Ozgen, S. (2018). Benevolence and authority as weirdly unfamiliar: A multi-language meta-analysis of paternalistic leadership behaviors from 152 studies. The Leadership Quarterly, 30(1), 165–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.leaqua.2018.11.003
Hooper, D. T., & Martin, R. (2008). Beyond personal leader-member exchange (lmx) quality: The effects of perceived lmx variability on employee reactions. The Leadership Quarterly, 19(1), 20–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.leaqua.2007.12.002
Hu, J., & Liden, R. C. (2013). Relative leader-member exchange within team contexts: How and when social comparison impacts individual effectiveness. Personnel Psychology, 66(1), 127–172. https://doi.org/10.1111/peps.12008
Jiang, H., Yang, C., Sun, P., & Yang, J. (2017). The relationship between authoritarian leadership and employees’ deviant workplace behaviors: The mediating effects of psychological contract violation and organizational cynicism. Frontiers in Psychology, 8, 732. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2017.00732
Jiang, H., Chen, Y., Sun, P., & Li, C. (2019). Authoritarian leadership and employees’ unsafe behaviors: The mediating roles of organizational cynicism and work alienation. Current Psychology, 38(6), 1668–1678. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-017-9726-1
Juna-Silva, A., Pombeira, C., & Caetano, A. (2021). Testing the affective events theory: The mediating role of affect and the moderating role of mindfulness. Applied Cognitive Psychology, 35(4), 1075–1081. https://doi.org/10.1002/acp.3843
Kaplan, S., Bradley, J. C., Luchman, J. N., & Haynes, D. (2009). On the role of positive and negative affectivity in job performance: A meta-analytic investigation. Journal of Applied Psychology, 94(1), 162–172. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0013115
Kaplan, S., Cortina, J., Ruark, G., LaPort, K., & Nicolaides, V. (2014). The role of organizational leaders in employee emotion management: A theoretical model. The Leadership Quarterly, 25(3), 563–580. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.leaqua.2013.11.015
Kiazad, K., Restubog, S. L. D., Zagenczyk, T. J., Kiewitz, C., & Tang, R. L. (2010). In pursuit of power: The role of authoritarian leadership in the relationship between supervisors’ Machiavellianism and subordinates’ perceptions of abusive supervisory behavior. Journal of Research in Personality, 44(4), 512–519. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrp.2010.06.004
Koopman, J., Lin, S., Lennard, A. C., Matta, F. K., & Johnson, R. E. (2020). My coworkers are treated more fairly than me! A self-regulatory perspective on justice social comparisons. The Academy of Management Journal, 63(3), 857–880. https://doi.org/10.5465/amj.2016.0586
Krasikova, Dina V.., Green, Stephen G.., & LeBreton, James M.. (2013). Destructive Leadership: A theoretical review, integration, and future research agenda. Journal of Management, 39(5), 1308–1338. https://doi.org/10.1177/0149206312471388
Lam, C. K., Van der Vegt, G. S., Walter, F., & Huang, X. (2011). Harming high performers: A social comparison perspective on interpersonal harming in work teams. Journal of Applied Psychology, 96(3), 588–601. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0021882
Latif, K., Tariq, H., Khan, A. K., Weng, Q. D., & Sarwar, N. (2020). Loaded with knowledge, yet green with envy: Leader-member exchange comparison and coworkers-directed knowledge hiding behavior. Journal of Knowledge Management, 24(7), 1653–1680. https://doi.org/10.1108/JKM-10-2019-0534
LeBreton, J. M., & Senter, J. L. (2008). Answers to 20 questions about interrater reliability and interrater agreement. Organizational Research Methods, 11(4), 815–852. https://doi.org/10.1177/1094428106296642
Lee, J., Rhee, M., & Park, K. M. (2018). Looking backward through the looking glass: Reference groups and social comparison. Journal of Management & Organization, 26(1), 1–22. https://doi.org/10.1017/jmo.2018.58
Lin, T. T., Cheng, B. S., & Chou, L. F. (2019). Paternalistic Leadership: An Indigenous Concept with Global Significance. In: KH Yeh (Eds.), Asian Indigenous Psychologies in the Global Context. Palgrave Macmillan. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-96232-0_6
Ma, B., Liu, S., Lassleben, H., & Ma, G. (2019). The relationships between job insecurity, psychological contract breach and counterproductive workplace behavior: Does employment status matter? Personnel Review, 48(2), 595–610. https://doi.org/10.1108/PR-04-2018-0138
Mackey, J. D., McAllister, C. P., Ellen, B. P., Carson, J., & E. (2021). A meta-analysis of interpersonal and organizational workplace deviance research. Journal of Management, 47(3), 597–622. https://doi.org/10.1177/0149206319862612
Mahd, S., Ibrahim, M., & Armia, S. (2018). The role of negative affects on the relationship of job stress and counterproductive work behavior (research on public senior high school teachers). International Journal of Asian Social Science, 8(2), 77–84. https://doi.org/10.18488/journal.1.2018.82.77.84
Marcus, B., Taylor, O. A., Hastings, S. E., Sturm, A., & Weigelt, O. (2016). The structure of counterproductive work behavior: A review, a structural meta-analysis, and a primary study. Journal of Management, 42(1), 1–31. https://doi.org/10.1177/0149206313503019
Martin, R., Thomas, G., Legood, A., & Russo, S. D. (2018). Leader-member exchange (LMX) differentiation and work outcomes: Conceptual clarification and critical review. Journal of Organizational Behavior, 39(2), 151–168. https://doi.org/10.1002/job.2202
Mawritz, M. B., Dust, S. B., & Resick, C. J. (2014). Hostile climate, abusive supervision, and employee coping: Does conscientiousness matter? Journal of Applied Psychology, 99(4), 734–747. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0035863
Morgan, W. B., Perry, S. J., & Wang, Y. (2018). The angry implications of work-to-family conflict: Examining effects of leadership on an emotion-based model of deviance. Journal of Vocational Behavior, 108, 13–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvb.2018.05.009
Naseer, S., Raja, U., Syed, F., & Baig, M. (2020). When and why organizational cynicism leads to cwbs. Personnel Review, 50(1), 90–107. https://doi.org/10.1108/PR-09-2019-0480
Ng, Thomas W.H.. (2017). Can idiosyncratic deals promote perceptions of competitive climate, felt ostracism, and turnover? Journal of Vocational Behavior, 99, 118–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvb.2017.01.004
Ocel, H. (2018). The relations between authoritarian leadership and counterproductive work behaviors: The role of psychological resilience. Journal of Entrepreneurship & Organization Management, 7(1), 100229. https://doi.org/10.4172/2169-026X.1000229
Podsakoff, P. M., MacKenzie, S. B., & Podsakoff, N. P. (2012). Sources of method bias in social science research and recommendations on how to control it. Annual Review of Psychology, 63(1), 539–569. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-psych-120710-100452
Preacher, K. J., Rucker, D. D., & Hayes, A. F. (2007). Addressing moderated mediation hypotheses: Theory, methods, and prescriptions. Multivariate Behavioral Research, 42(1), 185–227. https://doi.org/10.1080/00273170701341316
Qi, L., Liu, B., & Mao, K. (2020). Spare the rod and spoil the child? Study on employee workplace deviant behavior. Nankai Business Review International, 11(1), 1–22. https://doi.org/10.1108/NBRI-03-2018-0019
Samnani, Al-Karim., Salamon, Sabrina Deutsch, & Singh, Parbudyal. (2014). Negative Affect and Counterproductive Workplace Behavior: The Moderating Role of Moral Disengagement and Gender. Journal of Business Ethics, 119(2), 235–244. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10551-013-1635-0.
Schaubroeck, J. M., Shen, Y., & Chong, S. (2017). A dual-stage moderated mediation model linking authoritarian leadership to follower outcomes. Journal of Applied Psychology, 102(2), 203–214. https://doi.org/10.1037/apl0000165
Schyns, B., & Schilling, J. (2013). How bad are the effects of bad leaders? A meta-analysis of destructive leadership and its outcomes. Leadership Quarterly, 24(1), 138–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.leaqua.2012.09.001
Scott, B. A., Lennard, A. C., Mitchell, R. L., & Johnson, R. E. (2020). Emotions naturally and laboriously expressed: Antecedents, consequences, and the role of valence. Personnel Psychology, 73(4), 587–613. https://doi.org/10.1111/peps.12382
Spector, P. E. (2011). The relationship of personality to counterproductive work behavior (CWB): An integration of perspectives. Human Resource Management Review, 21(4), 342–352. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hrmr.2010.10.002
Spector, P. E., & Fox, S. (2002). An emotion-centered model of voluntary work behavior: Some parallels between counterproductive work behavior and organizational citizenship behavior. Human Resource Management Review, 12(2), 269–292. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1053-4822(02)00049-9
Tremblay, M., Gaudet, M. C., & Parent-Rocheleau, X. (2021). How and when relative leader-member exchange (rlmx) invigorates attendance at work within a context of lmx differentiation. Journal of Leadership and Organizational Studies, 28(2), 1–16. https://doi.org/10.1177/1548051821989289
Tse, H., Lam, C. K., Gu, J., & Lin, X. S. (2018). Examining the interpersonal process and consequence of leader-member exchange comparison: The role of procedural justice climate. Journal of Organizational Behavior, 39(8), 922–940. https://doi.org/10.1002/job.2268
Tu, C. K., & Luo, B. (2020). Paternalistic leadership and pro-social rule breaking: The moderating roles of psychological empowerment and leader-member exchange. Human Systems Management, 39(1), 93–103. https://doi.org/10.3233/HSM-190531
Vidyarthi, P. R., Liden, R. C., Anand, S., Erdogan, B., & Ghosh, S. (2010). Where do I stand? Examining the effects of leader-member exchange social comparison on employee work behaviors. Journal of Applied Psychology, 95(5), 849–861. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0020033
Wang, H., Niu, X. Y., & Kenneth, S. L. (2004). Multi-dimensional leader-member exchange (LMX) and its impact on task performance and contextual performance of employees. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 36(2), 179–185.
Warr, P. (1990). The measurement of well-being and other aspects of mental health. Journal of Occupational and Organizational Psychology, 63(3), 193–210. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.2044-8325.1990.tb00521.x
Wei, F., Lee, J., & Kwan, H. K. (2016). Impact of active constructive leadership and passive corrective leadership on collective organizational commitment. Leadership & Organization Development Journal, 37(7), 822–842. https://doi.org/10.1108/LODJ-08-2014-0150
Weiss, H. M., & Cropanzano, R. (1996). “Affective events theory: A theoretical discussion of the structure, causes and consequences of affective experiences at work,” in Research in Organizational Behavior, eds B. M. Staw and L. L. Cummings (Greenwich, CT: JAI Press), 1–74.
Yam, K. C., Klotz, A. C., He, W., & Reynolds, S. J. (2017). From good soldiers to psychologically entitled: Examining when and why citizenship behavior leads to deviance. Academy of Management Journal, 60(1), 373–396. https://doi.org/10.5465/amj.2014.0234
Yammarino, F. J., Dionne, S. D., Chun, J. U., & Dansereau, F. (2005). Leadership and levels of analysis: A state-of-the-science review. Leadership Quarterly, 16(6), 879–919. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.leaqua.2005.09.002
Yan, M., Xie, Y. P., Zhao, J., Zhang, Y. J., & Liu, Y. (2020). How ingratiation links to counterproductive work behaviors: The roles of emotional exhaustion and power distance orientation. Frontiers in Psychology, 11, 2238. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2020.02238
Yoon, M. H., & Yoon, D. J. (2019). When and why does relative leader-member exchange enhance service performance? The roles of self-efficacy, team commitment, and multifoci team-level differentiation. International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management, 31(7), 2666–2690. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJCHM-07-2018-0592
Yu, H., Lin, R., Wang, Q., & Lian, R. (2021). Effects of victim justice sensitivity on envy: The role of upward social comparison and perceived control. Current Psychology, 1-8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-020-01338-3
Zhang, X., Wu, W., Wu, W., Zhang, Y., & Xia, Y. (2020). Are your gains threat or chance for me? A social comparison perspective on idiosyncratic deals and coworkers' acceptance. Journal of Management & Organization, 1-22. https://doi.org/10.1017/jmo.2020.32
Zou, W. C., Tian, Q., & Liu, J. (2015). Servant leadership, social exchange relationships, and follower’s helping behavior: Positive reciprocity belief matters. International Journal of Hospitality Management, 51, 147–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhm.2015.08.012
Funding
This study is supported by Major Innovation & Planning Interdisciplinary Platform for the “Double-First Class” Initiative (19XNLG20), Renmin University of China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors listed have made a substantial, direct and intellectual contribution to the work. Xinyue Hu conceived the idea of the study and contributed to data analysis, original writing and revision. Mingchao Dong contributed to data analysis. Yingwu Li revised the manuscript. Mengmeng Wang collected the data. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
This study was conducted in accordance with the recommendations of the Ethics Committee of the Department of Psychology, Renmin University of China, and written informed consent was obtained from all the subjects. All participants provided written informed consent in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki declaration and its later amendments. The study protocol was approved by the ethics committee of the Department of Psychology, Renmin University of China.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Competing interests
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as potential conflicts of interest. The authors are responsible for the content and writing of this manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, X., Dong, M., Li, Y. et al. The cross-level influence of authoritarian leadership on counterproductive work behavior: A moderated mediation model. Curr Psychol 42, 23580–23593 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-022-03491-3
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-022-03491-3