Abstract
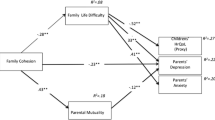
Parents of children with disabilities face more significant economic, psychological, and social pressure, which may impact their subjective well-being (SWB). Conversely, parents’ SWB also contributes to the children’s physical and mental development. However, parents of children with disabilities are a less studied population, and their SWB needs further attention. In this study, we recruited 616 parents of children with disabilities. We used the Family Closeness and Adaptation Scale, Simple Coping Style Questionnaire, Psychological Resistivity Scale, and Subjective Well-being Scale to investigate the influencing mechanism of family adaptability and cohesion on SWB. Structural equation models were built to explore the relationships between variables. Our findings indicate that the family adaptability and cohesion of parents of children with disabilities positively predict SWB, active coping style and resilience partially mediate the relationship between family adaptability and cohesion and SWB, and family adaptability and cohesion indirectly and positively predicated SWB through the chain mediation of resilience and active coping.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
References
Altiere, M. L., & von Kluge, S. (2009). Family functioning and coping behaviors in parents of children with autism. Journal of Child and Family Studies, 18, 83–92. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10826-008-9209-y
Ammari, T., Morris, M. R., & Schoenebeck, S. Y. (2014). Accessing social support and overcoming judgment on social media among parents of children with special needs. In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Weblogs and Social Media, ICWSM (pp. 22–31).
Andrews, F. M., & Withey, S. B. (1976). Evaluating the Measures of Well-Being. In: Social Indicators of Well-Being (pp. 175–217). Springer, Boston. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4684-2253-5_6
Arthaud-Day, M. L., Rode, J. C., Mooney, C. H., & Near, J. P. (2005). The subjective well-being construct: A test of its convergent, discriminant, and factorial validity. Social Indicators Research, 74(3), 445–476. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11205-004-8209-6
Barnes, H. L., & Olson, D. H. (1982). Parent-adolescent communication scale. In D. H. Olson, H. I. McCubbin, H. Barnes, A. Larsen, M. Muxen, & M. Wilson (Eds.), Family inventories: Inventories used in a national survey of families across the family life cycle (pp. 51–63). University of Minnesota.
Beavers, R., & Hampson, R. B. (2000). The beavers systems model of family functioning. Journal of Family Therapy, 22(2), 128–143. https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-6427.00143
Billings, A. G., & Moos, R. H. (1981). The role of coping responses and social resources in attenuating the stress of life events. Journal of Behavioral Medicine, 4(2), 139–157. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00844267
Block, J., & Kremen, A. M. (1996). IQ and ego-resiliency: Conceptual and empirical connections and separateness. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 70(2), 349–361. https://doi.org/10.1037//0022-3514.70.2.349
Campbell-Sills, L., Cohan, S. L., & Stein, M. B. (2006). Relationship of resilience to personality, coping, and psychiatric symptoms in young adults. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 44(4), 585–599. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brat.2005.05.001
Chen, C. (2016). The role of resilience and coping styles in subjective well-being among Chinese university students. The Asia-Pacific Education Researcher, 25(3), 377–387. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40299-016-0274-5
Chen, K., Yang, J., Dong, L., & Xia, Q. (2013). Effect of physical exercise on adolescents’ psychological stress, coping styles and subjective well-being. Journal of Chengdu Sport University, 39(10), 75–79.
Cheng, T., Mauno, S., & Lee, C. (2014). Do job control, support, and optimism help job insecure employees? A three-wave study of buffering effects on job satisfaction, vigor and work-family enrichment. Social Indicators Research, 118(3), 1269–1291. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11205-013-0467-8
Chi, P., Du, H., King, R. B., Zhou, N., Cao, H., & Lin, X. (2019). Well-being contagion in the family: Transmission of happiness and distress between parents and children. Child Indicators Research, 12(6), 2189–2202. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12187-019-09636-4
Cocozza, S., Sacco, P. L., Matarese, G., Maffulli, G. D., Maffulli, N., & Tramontano, D. (2020). Participation to leisure activities and well-being in a group of residents of Naples-Italy: The role of resilience. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(6), 1895. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17061895
Compas, B., Connor-Smith, J., Saltzman, H., Thomsen, A., & Wadsworth, M. (2001). Coping with stress during childhood and adolescence: Problems, progress, and potential in theory and research. Psychological Bulletin, 127, 87–127. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-2909.127.1.87
Connor, K., & Davidson, J. (2003). Development of a new resilience scale: The Connor-Davidson resilience scale (CD-RISC). Depression and Anxiety, 18, 76–82. https://doi.org/10.1002/da.10113
Cui, H., & Zhang, Y. (2013). Mediation role of resilience between family support and subjective well-being. China Journal of Health Psychology, 21(6), 869–872. https://doi.org/10.13342/j.cnki.cjhp.2013.06.010
Dieleman, L. M., Soenens, B., Prinzie, P., De Clercq, L., Ortibus, E., & De Pauw, S. S. W. (2020). Daily parenting of children with cerebral palsy: The role of daily child behavior, parents’ daily psychological needs, and mindful parenting. Development and Psychopathology, 1–17. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0954579419001688
Diener, E. (1984). Subjective well-being. Psychological Bulletin, 95(3), 542–575. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-2909.95.3.542
Diener, E., & Chan, M. Y. (2011). Happy people live longer: Subjective well-being contributes to health and longevity. Applied Psychology: Health and Well-Being, 3(1), 1–43. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1758-0854.2010.01045.x
Diener, E., & Ryan, K. (2009). Subjective well-being: A general overview. South Africa Journal of Psychology, 39(4). https://doi.org/10.1177/008124630903900402
van Dijk, F. A., Schirmbeck, F., Boyette, L. L., de Haan, L., & for Genetic Risk and Outcome of Psychosis (GROUP) Investigators. (2019). Coping styles mediate the association between negative life events and subjective well-being in patients with non-affective psychotic disorders and their siblings. Psychiatry Research, 272, 296–303. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psychres.2018.12.020
Donley, T., King, D., Nyathi, N., Okafor, A., & Mbizo, J. (2018). Socioeconomic status, family functioning and delayed care among children with special needs. Social Work in Public Health, 33(6), 366–381. https://doi.org/10.1080/19371918.2018.1504703
Douma, M., Bouman, C. P., Van Oers, H. A., Maurice-Stam, H., Haverman, L., Grootenhuis, M. A., & Scholten, L. (2020). Matching psychosocial support needs of parents of a child with a chronic illness to a feasible intervention. Maternal and Child Health Journal, 24(10), 1238–1247. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10995-020-02925-3
Dunn, M. E., Burbine, T., Bowers, C. A., & Tantleff-Dunn, S. (2001). Moderators of stress in parents of children with autism. Community Mental Health Journal, 37(1), 39–52. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026592305436
Feder, A., Nestler, E. J., Westphal, M., & Charney, D. S. (2010). Psychobiological mechanisms of resilience to stress. In J. W. Reich, A. J. Zautra, & J. S. Hall (Eds.), Handbook of adult resilience (pp. 35–54). Guilford Press.
Fei, L., Shen, Q., Zhen, Y., Zhao, J., Jiang, S., Wang, L., & Wang, X. (1991). Preliminary evaluation of Chinese version of FACES II and FES: Comparison of normal families and families of schizophrenic patients. Chinese Mental Health Journal, 5, 198-202+238.
Fianco, A., Sartori, R. D. G., Negri, L., Lorini, S., Valle, G., & Fave, A. D. (2015). The relationship between burden and well-being among caregivers of Italian people diagnosed with severe neuromotor and cognitive disorders. Research in Developmental Disabilities, 39, 43–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ridd.2015.01.006
Folkman, S., Lazarus, R. S., Dunkel-Schetter, C., DeLongis, A., & Gruen, R. J. (1986). Dynamics of a stressful encounter: Cognitive appraisal, coping, and encounter outcomes. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 50(5), 992–1003. https://doi.org/10.1037//0022-3514.50.5.992
Garrido, D., Petrova, D., Cokely, E., Carballo, G., & Garcia-Retamero, R. (2021). Parental risk literacy is related to quality of life in spanish families of children with autism spectrum disorder. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 51(7), 2475–2484. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-020-04733-8
Gogineni, R. R. (2019). Posotive phychotherapies for enhancement of resilience and recovery. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 58(10) Supplement, S41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaac.2019.07.174
Goudie, A., Narcisse, M.-R., Hall, D. E., & Kuo, D. Z. (2014). Financial and psychological stressors associated with caring for children with disability. Families, Systems & Health : The Journal of Collaborative Family Healthcare, 32(3), 280. https://doi.org/10.1037/fsh0000027
Greenspoon, P. J., & Saklofske, D. H. (2001). Toward an integration of subjective well-being and psychopathology. Social Indicators Research, 54(1), 81–108. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007219227883
Herbert, H., & Manjula, M. (2017). Stress-coping and factors contributing to resilience in college students: An exploratory study from India. Indian Journal of Clinical Psychology, 44, 26–34.
Hooper, D., Coughlan, J., & Mullen, M. R. (2008). Structural equation modelling: Guidelines for determining model fit., 6(1), 8.
Hsiao, Y.-J. (2018). Parental stress in families of children with disabilities. Intervention in School and Clinic, 53(4), 201–205. https://doi.org/10.1177/1053451217712956
Huang, J., & Huang, Y. (2007). The relationship between social support coping style and subjective well-being of college students. Chinese Journal of Clinical Psychology, 6, 629–631.
Jeon, H.-J. (2003). An application of ecological family welfare model on stress coping strategy and psychological wellbeing. The Korean Society of Community Living Science, 14(2), 107–117.
Jia, D., Li, C., & Liu, J. (2016). Relation of social support to coping styles and life satisfaction in left-behind women. Chinese Mental Health Journal, 30(6), 448–453. Retrieved July 17, 2021, from https://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-ZXWS201606013.htm
Jiang, Q. (1999). The current situation of coping research. Chinese Clinician, 11, 16–18.
Jiang, Q., Huang, L., Lu, K., Lou, Z., Yang, A., Chen, H., & Mao, Z. (1993). Psychological stress: Classification of coping and psychosomatic health. Chinese Mental Health Journal, 4, 145–147+190.
Kim, S., Kim, J. J., Lee, B. J., Yu, J., Lee, K. Y., Won, S., Lee, S., Kim, S., Kang, S., Kim, E., Lee, J., Kim, J., & Chung, Y. C. (2020). Clinical and psychosocial factors associated with depression in patients with psychosis according to stage of illness. Early Intervention in Psychiatry, 14(1), 44–52. https://doi.org/10.1111/eip.12806
Kumpfer, K. L. (2002). Factors and processes contributing to resilience. In M. D. Glantz & J. L. Johnson (Eds.), Resilience and development: Positive life adaptations (pp. 179–224). Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/0-306-47167-1_9
Lazarus, R. S., & Folkman, S. (1991). The concept of coping. In A. Monat & R. Lazarus (Eds.), Stress and coping: An anthology (pp. 189–206). Columbia University Press. https://doi.org/10.7312/mona92982-017
Li, B., & Liu, Q. (2012). On the relationship between college students’ personality , family cohesion and family adaptability. Chinese Journal of Special Education, 1, 81–84.
Li, W., Wang, L., & Yuan, J. (2014). Correlation of family cohesion, family adaptability and subjective well-being in college students. China Journal of Health Psychology, 22(7), 1067–1070. https://doi.org/10.13342/j.cnki.cjhp.2014.07.043.
Li, R., Liu, H., Yao, M., & Chen, Y. (2019). Regulatory focus and subjective well-being: The mediating role of coping styles and the moderating role of gender. The Journal of Psychology, 153(7), 714–731. https://doi.org/10.1080/00223980.2019.1601066
Liang, J., Cui, X., Zuo, C., Wang, Y., & Yue, S. (2018). Social support on subjective well-being among vocational college students: Mediation effect of general self-efficacy and resilience. Modern Preventive Medicine, 45(13), 2383–2386.
Liu, S., Liu, K., Li, T., & Lu, L. (2015). The impact of mindfulness on subjective well-being of college students: The mediating effects of emotion regulation and resilience. Journal of Psychosocial Science, 38(4), 889–895. https://doi.org/10.16719/j.cnki.1671-6981.2015.04.017
Lu, C., Yuan, L., Lin, W., Zhou, Y., & Pan, S. (2017). Depression and resilience mediates the effect of family function on quality of life of the elderly. Archives of Gerontology and Geriatrics, 71, 34–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.archger.2017.02.011
Mak, W., Ng, I., & Wong, C. (2011). Resilience: Enhancing well-being through the positive cognitive triad. Journal of Counseling Psychology, 58, 610–617. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0025195
Mendes, T. P. G. P., Crespo, C. A. M., & Austin, J. K. (2016). Family cohesion and adaptation in pediatric chronic conditions: The missing link of the family’s condition management. Journal of Child and Family Studies, 25(9), 2820–2831. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10826-016-0447-0
Miller, I. W., Ryan, C. E., Keitner, G. I., Bishop, D. S., & Epstein, N. B. (2000). The McMaster approach to families: Theory, assessment, treatment and research. Journal of Family Therapy, 22(2), 168–189. https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-6427.00145
Mo, P., Lau, J., Yu, N. X., & Gu, J. (2014). The role of social support on resilience, posttraumatic growth, hopelessness, and depression among children of HIV-infected parents in mainland China. AIDS Care, 26(12), 1526–1533. https://doi.org/10.1080/09540121.2014.923810
Mota, C. P., & Matos, P. M. (2015). Adolescents in institutional care: Significant adults, resilience and well-being. Child and Youth Care Forum, 44(2), 209–224. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10566-014-9278-6
Newman, R. (2002). Investigating the road to resilience. Monitor on psychology. Retrieved March 21, 2021, from https://www.apa.org/monitor/oct02/pp
Niu, X., Wu, D., Yang, Y., & Lv, F. (2018). Effects of family enviroment on psychologic status of caregivers of children with cerebral palsy: A case control study. Chinese Journal of Rehabilitation Medicine, 33(4), 429–435.
Norlin, D., & Broberg, M. (2013). Parents of children with and without intellectual disability: Couple relationship and individual well-being. Journal of Intellectual Disability Research, 57(6), 552–566. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2788.2012.01564.x
Olson, D. H. (2000). Circumplex model of marital and family systems. Journal of Family Therapy, 22(2), 144–167. https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-6427.00144
Patterson, J. M. (2002). Integrating family resilience and family stress theory. Journal of Marriage and Family, 64(2), 349–360. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1741-3737.2002.00349.x
Proctor, C. L., Linley, P. A., & Maltby, J. (2009). Youth life satisfaction: A review of the literature. Journal of Happiness Studies, 10(5), 583–630. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10902-008-9110-9
Rius-Ottenheim, N., van der Mast, R. C., Zitman, F. G., & Giltay, E. J. (2012). The role of dispositional optimism in physical and mental well-being. In A. Efklides & D. Moraitou (Eds.), A positive psychology perspective on quality of life (pp. 149–173). Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-4963-4_9
Rutter, M. (1987). Psychosocial resilience and protective mechanisms. American Journal of Orthopsychiatry, 57(3), 316–331. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1939-0025.1987.tb03541.x
Rutter, M. (1995). Psychosocial adversity: Risk, Resilience & Recovery. Southern African Journal of Child and Adolescent Mental Health, 7(2), 75–88. https://doi.org/10.1080/16826108.1995.9632442
Sexton, M. B., Byrd, M. R., & Kluge, S. V. (2010). Measuring resilience in women experiencing infertility using the CD-RISC: Examining infertility-related stress, general distress, and coping styles. Journal of Psychiatric Research, 44(4), 236–241. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpsychires.2009.06.007
Shenaar-Golan, V. (2017). Hope and subjective well-being among parents of children with special needs. Child and Family Social Work, 22(1), 306–316. https://doi.org/10.1111/cfs.12241
Skinner, H., Steinhauer, P., & Sitarenios, G. (2000). Family assessment measure (FAM) and process model of family functioning. Journal of Family Therapy, 22(2), 190–210. https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-6427.00146
Vinson, J. (2002). Children with asthma: Initial development of the child resilience model. Pediatric Nursing, 28, 149–158.
Watson, D., Clark, L. A., & Tellegen, A. (1988). Development and validation of brief measures of positive and negative affect: The PANAS scales. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 54(6), 1063–1070. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.54.6.1063
Wei, J. (2014). The relationship between left-at-home rural children’s dispositional optimism, coping styles and life satisfaction. Chinese Journal of Special Education, 11, 58–61.
Werner, E. E. (1995). Resilience in development. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 4(3), 81–85. https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-8721.ep10772327
Wu, S., & Zheng, X. (2020). The effect of family adaptation and cohesion on the well-being of married women: A multiple mediation effect. The Journal of General Psychology, 147(1), 90–107. https://doi.org/10.1080/00221309.2019.1635075
Wu, G., Huang, J., Bao, X., & Li, Y. (2015). Relation of subjective well-being to life-events, social support and coping style in civil servants. Chinese Mental Health Journal, 29(8), 618–622.
Xie, Y. (1998). Preliminary study to the reliability and validity of the simple coping style scale. Chinese Journal of Clinical Psychology, 6, 114–115.
Xu, Q., Fang, Y., Zhang, W., & Diao, Y. (2018). A meta-analysis of the mental health of parents of children with special needs and moderating factors. Chinese. Journal of Special Education, 2, 8-15+25.
Yang, Z., Wan, G., Lin, K., & Tan, R. (2019). Coping styles as a mediator between depression and family function of autism families. China Journal of Health Psychology, 27(6), 834–838. https://doi.org/10.13342/j.cnki.cjhp.2019.06.008
Yu, X., & Zhang, J. (2005). Resilience: The psychological mechanism for recovery and growth during stress. Advances in Psychological Science, 5, 658–665.
Yu, N. X., & Zhang, J. (2007). Factor analysis and psychometric evaluation of the connor-Davidson resilience scale (cd-risc) with chinese people. Social Behavior and Personality: An International Journal, 35, 19–30. https://doi.org/10.2224/sbp.2007.35.1.19
Zhang, Z., Yan, G., Sun, C., & Saklofske, D. H. (2021). Who will adapt best in Antarctica? Resilience as mediator between past experiences in Antarctica and present well-being. Personality and Individual Differences, 169, 109963. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2020.109963
Zhou, Y. (2016). Childhood trauma and subjective well-being in postgraduates: The mediating of coping style. Chinese Journal of Clinical Psychology, 24(3), 509–513. https://doi.org/10.16128/j.cnki.1005-3611.2016.03.028
Zhou, Y., Hu, D., Zhang, K., Mao, J., Teng, F., Yu, T., Xu, K., Tan, R., Ding, X., & Liu, Y. (2020a). The mechanism of family adaptability and cohesion in suicidal ideation among Chinese cancer patients. Journal of Psychosocial Oncology, 38(5), 612–626. https://doi.org/10.1080/07347332.2020.1757799
Zhou, Y., Li, X., Sheng, W., & Chen, Y. (2020b). The influence of empty nest elderly’s participation in physical exercise on their subjective well-being: The intermediary role of psychological resilience. Sichuan Sports Science, 39(2), 63–66.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank all participants of this study and the schools and hospitals that helped us collect data, such as Xi’an Mangya School, Xi’an; Xi’an Qizhi School, Xi’an; Shaanxi Kangfu Hospital, Xi’an; Baoji Special Education School, Baoji; Xi’an Children’s Hospital, Xi’an; Ankang Sunshine School, Ankang; Special Education School of Wugong country, Xianyang; Xi’an Di’er Longya School, Xi’an; Special Education School of Chang’an District, Xi’an; Baoji Children’s Hospital, Baoji. We also thank the Special Education School of Jingbian country, Yulin, and Special Education School of Mei country, Baoji, for their assistance in the design phase of this study.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Social Science Fund of China (grant number: 20BRK038), the Humanities and Social Sciences Fund of the Ministry of Education in China (grant number: 20YJA890019), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities in China (grant number: 2019TS044).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study’s conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by Minjie Ma, Ruiying Gao, and Qianqian Wang. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Minjie Ma and Ruiying Gao. Commentary on the revised manuscript and language polish were carried out by Mingxuan Qi. All authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
This study was approved by the ethics committee of Shaanxi Normal University. All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Consent to Participate
Each participant was presented with an informed consent form, and their written consent was obtained.
Conflict of Interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, M., Gao, R., Wang, Q. et al. Family adaptability and cohesion and the subjective well-being of parents of children with disabilities: the mediating role of coping style and resilience. Curr Psychol 42, 19065–19075 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-022-03094-y
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-022-03094-y