Abstract
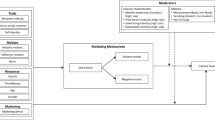
The present study explores the connection between religiosity, beliefs, psychology, and impulsive buying patterns. This study draws strength from two theoretical models:y: Values Attitude and Behavior (VAB) and consistency theory. It was hypothesized that religiosity (intrinsic and extrinsic) predicts beliefs materialism, risk aversion and life satisfaction) that ultimately associated with impulsive buying tendencies. A cross-sectional survey was conducted to collect the data by utilizing the mall intercept approach. A total of 544 valid responses of consumers of apparel products were used to test the model. Data were analyzed through covariance-based structural equation modeling CB-SEM. Empirical findings supported a significant association of religiosity, materialism, risk aversion and life satisfaction. It was also found that beliefs turn into impulsive buying tendencies. Materialism, risk aversion, life satisfaction were found as significant mediators between religiosity and impulsive buying tendencies. The results revealed that the social meaning of religiousness and individual spiritual values enhance life satisfaction, risk aversion and condemn materialistic beliefs. It was found that customers satisfied with their life are less risk-takers and are less inclined towards impulsive tendencies. However, higher-level materialism leads to impulsive tendencies. The study findings offer significant implications of religious values, beliefs and behavioral outcomes for retailers of developing countries. The present study is one of the preliminary studies to examine religiosity, beliefs (materialism, risk aversion, life satisfaction) and impulsive buying tendencies by using VAB and the theory of consistency.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abuznaid, S. A. (2009). Business ethics in Islam: The glaring gap in practice. International Journal of Islamic and Middle Eastern Finance and Management, 2(4), 278–288.
Addo, P. C., Jiaming, F., Kulbo, N. B., & Liangqiang, L. (2020). COVID-19: Fear appeal favoring purchase behavior towards personal protective equipment. The Service Industries Journal, 40(7–8), 471–490.
Adhikari, B. K., & Agrawal, A. (2016). Does local religiosity matter for bank risk-taking? Journal of Corporate Finance, 38, 272–293.
Agag, G. M., & El-Masry, A. A. (2017). Why do consumers trust online travel websites? Drivers and outcomes of consumer trust toward online travel websites. Journal of Travel Research, 56(3), 347–369.
Agarwala, R., Mishra, P., & Singh, R. (2019). Religiosity and consumer behavior: A summarizing review. Journal of Management, Spirituality & Religion, 16(1), 32–54.
Ahn, J., Lee, S. L., & Kwon, J. (2019). Impulsive buying in hospitality and tourism journals. Annals of Tourism Research, 102764.
Ajzen, I., & Fishbein, M. (1988). Theory of reasoned action-theory of planned behavior. University of South Florida.
Akram, U., Hui, P., Kaleem Khan, M., Tanveer, Y., Mehmood, K., & Ahmad, W. (2018). How website quality affects online impulse buying: Moderating effects of sales promotion and credit card use. Asia Pacific Journal of Marketing and Logistics, 30(1), 235–256.
Al-Hyari, K., Alnsour, M., Al-Weshah, G., & Haffar, M. (2012). Religious beliefs and consumer behaviour: From loyalty to boycotts. Journal of Islamic Marketing, 3(2), 155–174.
Allport, G. W., & Ross, J. M. (1967). Personal religious orientation and prejudice. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 5(4), 432–443.
Antaramian, S. P., Huebner, E. S., & Valois, R. F. (2008). Adolescent life satisfaction. Applied Psychology, 57, 112–126.
Arli, D., Gil, L. d. A., & van Esch, P. (2020). The effect of religiosity on luxury goods: The case of Chilean youths. International Journal of Consumer Studies, 44(3), 181–190.
Arli, D. I., & Tjiptono, F. (2018). Consumer ethics, religiosity, and consumer social responsibility: Are they related? Social Responsibility Journal, just-accepted, 14, –320.
Ash, C., & Huebner, E. S. (2001). Environmental events and life satisfaction reports of adolescents: A test of cognitive mediation. School Psychology International, 22(3), 320–336.
Attiq, S. (2015). Attention to social comparison information and compulsive buying behavior: An SOR analysis. Journal of Behavioural Sciences, 25(1).
Bahrainizad, M., & Rajabi, A. (2018). Consumers’ perception of usability of product packaging and impulse buying: Considering consumers’ mood and time pressure as moderating variables. Journal of Islamic Marketing, just-accepted, 00–00.
Battour, M., Ismail, M. N., Battor, M., & Awais, M. (2017). Islamic tourism: An empirical examination of travel motivation and satisfaction in Malaysia. Current Issues in Tourism, 20(1), 50–67.
Bukhari, F., Hussain, S., Ahmed, R. R., Streimikiene, D., Soomro, R. H., & Channar, Z. A. (2020). Motives and role of religiosity towards consumer purchase behavior in Western imported food products. Sustainability, 12(1), 356.
Bukhari, S. F. H., Woodside, F. M., Hassan, R., Shaikh, A. L., Hussain, S., & Mazhar, W. (2019). Is religiosity an important consideration in Muslim consumer behavior: Exploratory study in the context of western imported food in Pakistan. Journal of Islamic Marketing, 10(4), 1288–1307. https://doi.org/10.1108/JIMA-01-2018-0006.
Casabayó, M., Dávila, J. F., & Rayburn, S. W. (2020). Thou shalt not covet: Role of family religiosity in anti-consumption. International Journal of Consumer Studies, 44(5), 445–454.
Chan, T. K., Cheung, C. M., & Lee, Z. W. (2017). The state of online impulse-buying research: A literature analysis. Information & Management, 54(2), 204–217.
Chen-Yu, J. H., & Seock, Y.-K. (2002). Adolescents’ clothing purchase motivations, information sources, and store selection criteria: A comparison of male/female and impulse/nonimpulse shoppers. Family and Consumer Sciences Research Journal, 31(1), 50–77.
Chih, W.-H., Wu, C. H.-J., & Li, H.-J. (2012). The antecedents of consumer online buying impulsiveness on a travel website: Individual internal factor perspectives. Journal of Travel & Tourism Marketing, 29(5), 430–443.
Choi, Y. (2010). Religion, religiosity, and south Korean consumer switching behaviors. Journal of Consumer Behaviour, 9(3), 157–171.
Dekhil, F., Boulebech, H., & Bouslama, N. (2017). Effect of religiosity on luxury consumer behavior: The case of the Tunisian Muslim. Journal of Islamic Marketing, 8(1), 74–94.
Dittmar, H., Beattie, J., & Friese, S. (1995). Gender identity and material symbols: Objects and decision considerations in impulse purchases. Journal of Economic Psychology, 16(3), 491–511.
Essoo, N., & Dibb, S. (2004). Religious influences on shopping behaviour: An exploratory study. Journal of Marketing Management, 20(7–8), 683–712.
Gelfand, M. J. (2012). Culture’s constraints: International differences in the strength of social norms. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 21(6), 420–424.
Ghani, B. A., Harjin, A. A., & Ghani, S. A. (2008). Konsep Penggunaan dari Perspektif Ekonomi Islam. Seminar Keusahawanan Islam II Peringkat Kebangsaan, 1–36.
Habib, M. D., Batool, N., & Hassan, M. (2020). Religiosity and impulsive buying tendencies: A model and empirical application. Journal of Islamic Business and Management, 10(1), 220–240.
Habib, M. D., & Qayyum, A. (2017). Online impulsive buying behavior: A model and empirical investigation. Journal of Managerial Sciences, XI(3), 146–166.
Habib, M. D., & Qayyum, A. (2018). Cognitive emotion theory and emotion-action tendency in online impulsive buying behavior. Journal of Management Sciences, 5(1), 86–99.
Habib, M. D., & Saman, A. (2020). A model and empirical examination of influencing factors of customer satisfaction and service performance through interactional quality., 12(1), 119–138. https://doi.org/10.22547/BER/12.1.6
Hair Jr., J. F., Babin, B. J., & Krey, N. (2017). Covariance-based structural equation modeling in the journal of advertising: Review and recommendations. Journal of Advertising, 46(1), 163–177.
Hair Jr., J. F., Hult, G. T. M., Ringle, C., & Sarstedt, M. (2016). A primer on partial least squares structural equation modeling (PLS-SEM). Sage Publications.
Harmancioglu, N., Zachary Finney, R., & Joseph, M. (2009). Impulse purchases of new products: An empirical analysis. Journal of Product and Brand Management, 18(1), 27–37.
Hausman, A. (2000). A multi-method investigation of consumer motivations in impulse buying behavior. Journal of Consumer Marketing, 17(5), 403–426.
Hayes, A. F., & Preacher, K. J. (2014). Statistical mediation analysis with a multicategorical independent variable. British Journal of Mathematical and Statistical Psychology, 67(3), 451–470.
Homer, P. M., & Kahle, L. R. (1988). A structural equation test of the value-attitude-behavior hierarchy. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 54(4), 638–646.
Hultén, P., & Vanyushyn, V. (2011). Impulse purchases of groceries in France and Sweden. Journal of Consumer Marketing, 28(5), 376–384.
Hwang, H. (2018). Do religion and religiosity affect consumers’ intentions to adopt pro-environmental behaviours? International Journal of Consumer Studies, 42(6), 664–674.
Isaksen, K. J., & Roper, S. (2012). The commodification of self-esteem: Branding and British teenagers. Psychology & Marketing, 29(3), 117–135.
Islam, T., & Chandrasekaran, U. (2020). Religiosity and consumer decision making styles of young Indian Muslim consumers. Journal of Global Scholars of Marketing Science, 30, 1–23.
Jannoo, Z., Yap, B. W., Auchoybur, N., & Lazim, M. A. (2014). The effect of nonnormality on CB-SEM and PLS-SEM path estimates. International Journal of Mathematical, Computational, Physical and Quantum Engineering, 8(2), 285–291.
Ju, J., & Ahn, J.-H. (2016). The effect of social and ambient factors on impulse purchasing behavior in social commerce. Journal of Organizational Computing and Electronic Commerce, 26(4), 285–306.
Kacen, J. J., & Lee, J. A. (2002). The influence of culture on consumer impulsive buying behavior. Journal of Consumer Psychology, 12(2), 163–176.
Karoui, S., & Khemakhem, R. (2019). Factors affecting the Islamic purchasing behavior–a qualitative study. Journal of Islamic Marketing, 10(4), 1104–1127. https://doi.org/10.1108/JIMA-12-2017-0145
Khan, F., Ahmed, W., & Najmi, A. (2019). Understanding consumers’ behavior intentions towards dealing with the plastic waste: Perspective of a developing country. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 142, 49–58.
Kingston, T. (2016). Cute, creepy, or crispy—How values, attitudes, and norms shape human behavior toward bats. Bats in the Anthropocene: Conservation of bats in a changing world. Springer international AG, Cham, 571–588.
Kortt, M. A., Dollery, B., & Grant, B. (2015). Religion and life satisfaction down under. Journal of Happiness Studies, 16(2), 277–293.
Krause, N. (2004). Common facets of religion, unique facets of religion, and life satisfaction among older African Americans. The Journals of Gerontology Series B: Psychological Sciences and Social Sciences, 59(2), S109–S117.
La Barbera, P. A., & Gürhan, Z. (1997). The role of materialism, religiosity, and demographics in subjective well-being. Psychology & Marketing, 14(1), 71–97.
Lee, G. Y., & Yi, Y. (2008). The effect of shopping emotions and perceived risk on impulsive buying: The moderating role of buying impulsiveness trait. 14(2), 68–91
Liang, Y.-P. (2012). The relationship between consumer product involvement, product knowledge and impulsive buying behavior. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences, 57, 325–330.
Liao, S.-L., Shen, Y.-C., & Chu, C.-H. (2009). The effects of sales promotion strategy, product appeal and consumer traits on reminder impulse buying behaviour. International Journal of Consumer Studies, 33(3), 274–284. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1470-6431.2009.00770.x
Lim, C., & Putnam, R. D. (2010). Religion, social networks, and life satisfaction. American Sociological Review, 75(6), 914–933.
Lin, S.-W., & Lo, L. Y.-S. (2016). Evoking online consumer impulse buying through virtual layout schemes. Behaviour & Information Technology, 35(1), 38–56.
Lindridge, A. (2005). Religiosity and the construction of a cultural-consumption identity. Journal of Consumer Marketing, 22(3), 142–151.
Lins, S., Dóka, Á., Bottequin, E., Odabašić, A., Pavlović, S., Merchán, A., Golasa, A., & Hylander, F. (2015). The effects of having, feeling, and thinking on impulse buying in european adolescents. Journal of International Consumer Marketing, 27(5), 414–428.
Mansour, I. H. F., & Diab, D. M. E. (2016). The relationship between celebrities’ credibility and advertising effectiveness. Journal of Islamic Marketing, 7(2), 148–166. https://doi.org/10.1108/JIMA-05-2013-0036.
Markus, H. R., & Kitayama, S. (1991). Culture and the self: Implications for cognition, emotion, and motivation. Psychological Review, 98(2), 224–253.
Mathras, D., Cohen, A. B., Mandel, N., & Mick, D. G. (2016). The effects of religion on consumer behavior: A conceptual framework and research agenda. Journal of Consumer Psychology, 26(2), 298–311.
Matzler, K., Grabner-Kräuter, S., & Bidmon, S. (2008). Risk aversion and brand loyalty: The mediating role of brand trust and brand affect. Journal of Product and Brand Management, 17(3), 154–162.
McCullough, M. E., Emmons, R. A., & Tsang, J.-A. (2002). The grateful disposition: A conceptual and empirical topography. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 82(1), 112–127.
Miao, M., Jalees, T., Qabool, S., & Zaman, S. I. (2019). The effects of personality, culture and store stimuli on impulsive buying behavior. Asia Pacific Journal of Marketing and Logistics, 32(1), 188–204. https://doi.org/10.1108/APJML-09-2018-0377.
Minton, E. A. (2019). Believing is buying: Religiosity, advertising skepticism, and corporate trust. Journal of Management, Spirituality & Religion, 16(1), 54–75.
Minton, E. A., Kahle, L. R., Jiuan, T. S., & Tambyah, S. K. (2016). Addressing criticisms of global religion research: A consumption-based exploration of status and materialism, sustainability, and volunteering behavior. Journal for the Scientific Study of Religion, 55(2), 365–383.
Minton, E. A., & Liu, R. L. (2021). Religiosity and consumer belonging: Influences on product evaluations. Journal of Consumer Behaviour, 20(1), 32–47.
Mishra, H. G., Sinha, P. K., & Koul, S. (2014). Buying impulsive trait. Journal of Management Research, 14(2), 109–120.
Mohd Dali, N. R. S., Yousafzai, S., & Abdul Hamid, H. (2019). Religiosity scale development. Journal of Islamic Marketing, 10(1), 227–248.
Mokhlis, S. (2009). Relevancy and measurement of religiosity in consumer behavior research. International Business Research, 2(3), 75.
Musadik, S. H. S. A., & Azmi, I. A. G. (2019). Impulse buying behaviour from Islamic perspective: A conceptual paper. In Islamic development management (pp. 161–172). Springer.
Nayebzadeh, S., & Jalaly, M. (2014). Investigating Iranian female Muslim consumer impulse buying behaviour used as a form of retail therapy. Journal of Islamic Marketing, 5(2), 302–320.
Neill, C. M., & Kahn, A. S. (1999). The role of personal spirituality and religious social activity on the life satisfaction of older widowed women. Sex Roles, 40(3–4), 319–329.
Ortiz Alvarado, N. B., Rodríguez Ontiveros, M., & Quintanilla Domínguez, C. (2020). Exploring emotional well-being in Facebook as a driver of impulsive buying: A cross-cultural approach. Journal of International Consumer Marketing, 1–16.
Park, E. J., Kim, E. Y., Funches, V. M., & Foxx, W. (2012). Apparel product attributes, web browsing, and e-impulse buying on shopping websites. Journal of Business Research, 65(11), 1583–1589.
Peifer, J. T., & Holbert, R. L. (2016). Appreciation of pro-attitudinal versus counter-attitudinal political humor: A cognitive consistency approach to the study of political entertainment. Communication Quarterly, 64(1), 16–35.
Podsakoff, P. M., MacKenzie, S. B., Lee, J.-Y., & Podsakoff, N. P. (2003). Common method biases in behavioral research: A critical review of the literature and recommended remedies. Journal of Applied Psychology, 88(5), 879–903.
Pollner, M. (1989). Divine relations, social relations, and well-being. Journal of Health and Social Behavior, 30, 92–104.
Pradhan, D., Israel, D., & Jena, A. K. (2018). Materialism and compulsive buying behaviour: The role of consumer credit card use and impulse buying. Asia Pacific Journal of Marketing and Logistics, 30(5), 1239–1258.
Raggiotto, F., Mason, M. C., & Moretti, A. (2018). Religiosity, materialism, consumer environmental predisposition. Some insights on vegan purchasing intentions in Italy. International Journal of Consumer Studies, 42(6), 613–626.
Rahman, M., Albaity, M., & Maruf, B. (2017). The role of religiosity on the relationship between materialism and fashion clothing consumption among Malaysian generation Y consumers. Social Indicators Research, 132(2), 757–783.
Ramazani, A., & Kermani, M. (2021). Spiritualism versus materialism: Can religiosity reduce conspicuous consumption? Journal of Islamic Marketing. Vol. ahead-of-print No. ahead-of-print. https://doi.org/10.1108/JIMA-09-2019-0184.
Razzaq, Z., Razzaq, A., Yousaf, S., & Hong, Z. (2018). The impact of utilitarian and hedonistic shopping values on sustainable fashion consumption: The moderating role of religiosity. Global Business Review, 19(5), 1224–1239.
Rook, D. W., & Fisher, R. J. (1995). Normative influences on impulsive buying behavior. Journal of Consumer Research, 22(3), 305–313.
Ruvio, A. A., & Belk, R. W. (2013). The Routledge companion to identity and consumption. Routledge. https://books.google.com.pk/books?hl=en&lr=&id=rVJCjkLnjOkC&oi=fnd&pg=PP2&dq=Ruvio+and+Belk+(2013)+impulsive+buying&ots=24jX2WvKFW&sig=YtUSGYcZTcOCgHo8FGHxy-gvs5k
Schieman, S., Bierman, A., & Ellison, C. G. (2013). Religion and mental health. In Handbook of the sociology of mental health (pp. 457–478). Springer.
Shah Alam, S., Mohd, R., & Hisham, B. (2011). Is religiosity an important determinant on Muslim consumer behaviour in Malaysia? Journal of Islamic Marketing, 2(1), 83–96.
Sharma, P., Sivakumaran, B., & Marshall, R. (2010). Impulse buying and variety seeking: A trait-correlates perspective. Journal of Business Research, 63(3), 276–283.
Silvera, D. H., Lavack, A. M., & Kropp, F. (2008). Impulse buying: The role of affect, social influence, and subjective wellbeing. Journal of Consumer Marketing, 25(1), 23–33.
Sohn, H.-K., & Lee, T. J. (2017). Tourists’ impulse buying behavior at duty-free shops: The moderating effects of time pressure and shopping involvement. Journal of Travel & Tourism Marketing, 34(3), 341–356. https://doi.org/10.1080/10548408.2016.1170650
Stern, H. (1962). The significance of impulse buying today. Journal of Marketing, 26(2), 59–62.
Stillman, T. F., Fincham, F. D., Vohs, K. D., Lambert, N. M., & Phillips, C. A. (2012). The material and immaterial in conflict: Spirituality reduces conspicuous consumption. Journal of Economic Psychology, 33(1), 1–7.
Strack, F., Werth, L., & Deutsch, R. (2006). Reflective and impulsive determinants of consumer behavior. Journal of Consumer Psychology, 16(3), 205–216. https://doi.org/10.1207/s15327663jcp1603_2
Turkyilmaz, C. A., Erdem, S., & Uslu, A. (2015). The effects of personality traits and website quality on online impulse buying. Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences, 175, 98–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2015.01.1179
Valois, R. F., Zullig, K. J., Huebner, E. S., & Drane, J. W. (2009). Youth developmental assets and perceived life satisfaction: Is there a relationship? Applied Research in Quality of Life, 4(4), 315–331.
Vasconcelos, A. F. (2010). The effects of prayer on organizational life: A phenomenological study. Journal of Management & Organization, 16(3), 369–381.
Verhagen, T., & van Dolen, W. (2011). The influence of online store beliefs on consumer online impulse buying: A model and empirical application. Information & Management, 48(8), 320–327.
Vitell, S., Ramos-Hidalgo, E., & Rodríguez-Rad, C. (2018). A Spanish perspective on the impact on religiosity and spirituality on consumer ethics. International Journal of Consumer Studies, 42(6), 675–686.
Weaver, G. R., & Agle, B. R. (2002). Religiosity and ethical behavior in organizations: A symbolic interactionist perspective. Academy of Management Review, 27(1), 77–97.
Weaver, S. T., Moschis, G. P., & Davis, T. (2011). Antecedents of materialism and compulsive buying: A life course study in Australia. Australasian Marketing Journal; AMJ, 19(4), 247–256.
Wilson, J. A., & Liu, J. (2011). The challenges of Islamic branding: Navigating emotions and halal. Journal of Islamic Marketing, 2(1), 28–42.
Wilson, R. (2006). Islam and business. Thunderbird International Business Review, 48(1), 109–123.
Wolf, E. J., Harrington, K. M., Clark, S. L., & Miller, M. W. (2013). Sample size requirements for structural equation models: An evaluation of power, bias, and solution propriety. Educational and Psychological Measurement, 73(6), 913–934.
Yeniaras, V., & Akkemik, K. A. (2017). Materialism and fashion consciousness: The moderating role of status consumption tendencies and religiosity. Journal for the Scientific Study of Religion, 56(3), 498–513.
Yousaf, S., & Shaukat Malik, M. (2013). Evaluating the influences of religiosity and product involvement level on the consumers. Journal of Islamic Marketing, 4(2), 163–186.
Acknowledgments
Author gratitude is extended to the prospective editor(s) and reviewers that will/have spared time to guide toward a successful publication.
Availability of Data and Materials
The data for this present study are sourced from structured questionnaire. The current data specific data can be made available upon request.
Funding
I hereby declare that there is no form of funding received for this study and we wish to publish our syst as traditional.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval Statement
The current work is original and have not been published elsewhere in any form or language in any other outlet. There is no associated body to the study.
Informed Consent
The data for this present study are sourced from structured questionnaires. The current data specific data can be made available upon request.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent to Publish
Yes
Competing Interests
I wish to disclose here that there are no potential conflicts of interest at any level of this study.
Consent and Already Available Data and/or Biologic Material
Not applicable.
Additional information
The Authors of this article also assures that they follow the springer publishing procedures and agree to publish it as any form of access article confirming to subscribe access standards and licensing.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The data for the study used for this study are sourced from primary survey dataset, made available upon request
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Habib, M.D., Bekun, F.V. Does religiosity matter in impulsive psychology buying behaviors? A mediating model and empirical application. Curr Psychol 42, 9986–9998 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-021-02296-0
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-021-02296-0