Abstract
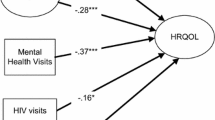
HIV disclosure to family members might be associated with the health-related quality of life (H-QoL) among people living with HIV/AIDS (PLWH). However, previous findings of the association were mixed, and few empirical studies had explored the potential mediating mechanisms underlying the relationship. This study aimed to examine the association between disclosure to family members and H-QoL, and the role of social support in the relationship. A cross-sectional survey was conducted among 1104 PLWH (58.70% male, average age 37.05 years old) in Guangxi, China. Participants provided information on HIV disclosure to family members, perceived social support, H-QoL including physical and mental health dimensions (scored as Physical health score [PHS] and Mental health score [MHS]), and social-demographic characteristics. Descriptive statistics, bivariate analysis, and path analysis were applied to examine our hypotheses. Bivariate analysis demonstrated that HIV disclosure to family members was positively correlated with social support but not with PHS and MHS statistically. Social support was positively correlated with PHS and MHS. Path analysis revealed that the direct effects of disclosure on both physical and mental H-QoL were not significant. In contrast, the indirect effects of disclosure on both mental and physical H-QoL through social support were significant, despite of small effect size. The potential mediating role of social support was highlighted in improving PLWH’s well-being. Future interventions targeting H-QoL promotion might incorporate disclosure management and communication skills that are likely to elicit social support and invite patients’ family members to participate in the interventions as appropriate.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Please contact author for data requests.
References
Basavaraj, K. H., Navya, M. A., & Rashmi, R. (2010). Quality of life in HIV/AIDS. Indian Journal of Sexually Transmitted Diseases and AIDS, 31(2), 75–80. https://doi.org/10.4103/0253-7184.74971.
Bentler, P. M., & Bonett, D. G. (1980). Significance tests and goodness of fit in the analysis of covariance structures. Psychological Bulletin, 88(3), 588–606.
Berger, B. E., Ferrans, C. E., & Lashley, F. R. (2001). Measuring stigma in people with HIV: Psychometric assessment of the HIV stigma scale. Research in Nursing and Health, 24(6), 518–529. https://doi.org/10.1002/nur.10011.
Biraguma, J., Mutimura, E., & Frantz, J. M. (2018). Health-related quality of life and associated factors in adults living with HIV in Rwanda. SAHARA-J: Journal of Social Aspects of HIV/AIDS, 15(1), 110–120. https://doi.org/10.1080/17290376.2018.1520144.
Bunjoungmanee, P., Chunloy, K., Tangsathapornpong, A., Khawcharoenporn, T., & Apisarnthanarak, A. (2014). Quality of life assessment among patients living with HIV/AIDS at a tertiary care hospital in Thailand. Southeast Asian Journal of Tropical Medicine and Public Health, 45(4), 834.
Butler, A. M., Williams, P. L., Howland, L. C., Storm, D., Hutton, N., Seage, G. R., & Grp, P. A. C. T. (2009). Impact of disclosure of HIV infection on health-related quality of life among children and adolescents with HIV infection. Pediatrics, 123(3), 935–943. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2008-1290.
Chandra, P. S., Deepthivarma, S., Jairam, K. R., & Thomas, T. (2003). Relationship of psychological morbidity and quality of life to illness-related disclosure among HIV-infected persons. Journal of Psychosomatic Research, 54(3), 199–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-3999(02)00567-6
Chaudoir, S. R., Fisher, J. D., & Simoni, J. M. (2011). Understanding HIV disclosure: A review and application of the disclosure processes model. Social Science and Medicine, 72(10), 1618–1629. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.socscimed.2011.03.028.
Cui, Z., Lin, M., Nie, S., & Lan, R. (2017). Risk factors associated with Tuberculosis (TB) among people living with HIV/AIDS: A pair-matched case control study in Guangxi, China. PloS one, 12(3), e0173976. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0173976.
Dahourou, D., Raynaud, J. P., & Leroy, V. (2018). The challenges of timely and safe HIV disclosure among perinatally HIV-infected adolescents in sub-Saharan Africa. Current Opinion in HIV and AIDS, 13(3), 220–229. https://doi.org/10.1097/coh.0000000000000462.
Degroote, S., Vogelaers, D., & Vandijck, D. M. (2014). What determines health-related quality of life among people living with HIV: An updated review of the literature. Archives of Public Health, 72(1), 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1186/2049-3258-72-40.
Dempster, A. P., Laird, N. M., & Rubin, D. B. (1977). Maximum likelihood from incomplete data via the EM algorithm. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society: Series B (Methodological), 39(1), 1–22. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.2517-6161.1977.tb01600.x.
Evangeli, M., & Wroe, A. L. (2017). HIV disclosure anxiety: A systematic review and theoretical synthesis. AIDS and Behavior, 21(1), 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10461-016-1453-3.
Go, V. F., Latkin, C., Le Minh, N., Frangakis, C., Ha, T. V., Sripaipan, T., Mo, T. T., Davis, W. W., Vu, P. T., & Quan, V. M. (2016). Variations in the role of social support on disclosure among newly diagnosed HIV-infected people who inject drugs in Vietnam. AIDS and Behavior, 20(1), 155–164. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10461-015-1063-5.
Hair, J. F., Anderson, R. E., Tatham, R. L., & Black, W. C. (1992). Multivariate data analysis with readings, 3-rd edition. Macmillan Publ.
Hsiung, P. C., Fang, C. T., Lee, K. L., Sheng, W. H., Wu, C. Y., Wang, J. D., & Yao, G. (2011). Validation of the medical outcomes study HIV (MOS-HIV) health survey among HIV-infected patients in Taiwan. Quality of Life Research, 20(2), 281–286. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11136-010-9733-2.
Hu, L. T., & Bentler, P. M. (1999). Cutoff criteria for fit indexes in covariance structure analysis: Conventional criteria versus new alternatives. Structural Equation Modeling-a Multidisciplinary Journal, 6(1), 1–55. https://doi.org/10.1080/10705519909540118.
Huang, Z. J., Tian, M., Dai, S. Y., & Ye, D. Q. (2013). Feasibility, reliability and validity of the Chinese simplified version of the MOS-HIV health survey among AIDS patients in China. Quality of Life Research, 22(2), 403–407. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11136-012-0148-0.
Jia, H., Uphold, C. R., Wu, S., Chen, G. J., & Duncan, P. W. (2005). Predictors of changes in health-related quality of life among men with HIV infection in the HAART era. AIDS Patient Care and STDs, 19(6), 395–405. https://doi.org/10.1089/apc.2005.19.395.
Kalichman, S. C., DiMarco, M., Austin, J., Luke, W., & DiFonzo, K. (2003). Stress, social support, and HIV-status disclosure to family and friends among HIV-positive men and women. Journal of Behavioral Medicine, 26(4), 315–332. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1024252926930.
Kamat, R., Woods, S. P., Cameron, M. V., Iudicello, J. E., & Group, H. I. V. N. R. P. (2016). Apathy is associated with lower mental and physical quality of life in persons infected with HIV. Psychology, Health & Medicine, 21(7), 890–901. https://doi.org/10.1080/13548506.2015.1131998.
Ko, N. Y., Lee, H. C., Hsu, S. T., Wang, W. L., Huang, M. C., & Ko, W. C. (2007). Differences in HIV disclosure by modes of transmission in Taiwanese families. AIDS Care, 19(6), 791–798. https://doi.org/10.1080/09540120601095718.
Lan, G., Yuan, Z., Cook, A., Xu, Q., Jiang, H., Zheng, H., Wang, L., Yuan, L., Xie, X., & Lu, Y. (2015). The relationships among social support and quality of life in persons living with HIV/AIDS in Jiangxi and Zhejiang provinces, China. AIDS Care, 27(8), 946–953. https://doi.org/10.1080/09540121.2015.1011072.
Laschober, T. C., Serovich, J. M., Brown, M. J., Kimberly, J. A., & Lescano, C. M. (2019). Mediator and moderator effects on the relationship between HIV-positive status disclosure concerns and health-related quality of life. AIDS Care, 31(8), 994–1000. https://doi.org/10.1080/09540121.2019.1595511.
Lazarus, J. V., Safreed-Harmon, K., Barton, S. E., Costagliola, D., Dedes, N., Del Amo Valero, J., Gatell, J. M., Baptista-Leite, R., Mendão, L., Porter, K., Vella, S., & Rockstroh, J. K. (2016). Beyond viral suppression of HIV - the new quality of life frontier. BMC Medicine, 14(1), 94. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12916-016-0640-4.
Li, X., Stanton, B., Fang, X., & Lin, D. (2006). Social stigma and mental health among rural-to-urban migrants in China: A conceptual framework and future research needs. World Health & Population, 8(3), 14–31. https://doi.org/10.12927/whp.2006.18282.
Li, L., Sun, S., Wu, Z., Wu, S., Lin, C., & Yan, Z. (2007). Disclosure of HIV status is a family matter: Field notes from China. Journal of Family Psychology, 21(2), 307–314. https://doi.org/10.1037/0893-3200.21.2.307.
Lin, X., Chi, P., Zhang, L., Zhang, Y., Fang, X., Qiao, S., & Li, X. (2016). Disclosure of HIV Serostatus and sexual orientation among HIV-positive men who have sex with men in China. Community Mental Health Journal, 52(4), 457–465. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10597-015-9879-z.
Lyimo, R. A., Stutterheim, S. E., Hospers, H. J., de Glee, T., van der Ven, A., & de Bruin, M. (2014). Stigma, disclosure, coping, and medication adherence among people living with HIV/AIDS in northern Tanzania. AIDS Patient Care and STDs, 28(2), 98–105. https://doi.org/10.1089/apc.2013.0306.
Martin, L. A., Vosvick, M., & Riggs, S. A. (2012). Attachment, forgiveness, and physical health quality of life in HIV + adults. AIDS Care, 24(11), 1333–1340. https://doi.org/10.1080/09540121.2011.648598.
Mayfield Arnold, E., Rice, E., Flannery, D., & Rotheram-Borus, M. J. (2008). HIV disclosure among adults living with HIV. AIDS Care, 20(1), 80–92. https://doi.org/10.1080/09540120701449138.
Mi, T., Li, X., Zhou, G., Qiao, S., Shen, Z., & Zhou, Y. (2020). HIV disclosure to family members and medication adherence: Role of social support and self-efficacy. AIDS and Behavior, 24(1), 45–54. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10461-019-02456-1.
Ministry of Health of the People’s Republic of China. (2012). 2012 China AIDS response progress report. Retrieved Oct. 10 from https://www.unaids.org/sites/default/files/country/documents/ce_CN_Narrative_Report[1].pdf
Murri, R., Fantoni, M., Del Borgo, C., Visona, R., Barracco, A., Zambelli, A., Testa, L., Orchi, N., Tozzi, V., Bosco, O., & Wu, A. W. (2003). Determinants of health-related quality of life in HIV-infected patients. AIDS Care, 15(4), 581–590. https://doi.org/10.1080/0954012031000134818.
Qiao, S., Li, X., & Stanton, B. (2013). Theoretical models of parental HIV disclosure: A critical review. AIDS Care, 25(3), 326–336. https://doi.org/10.1080/09540121.2012.712658.
Qiao, S., Li, X., Zhou, Y., Shen, Z., Tang, Z., & Stanton, B. (2015). Factors influencing the decision-making of parental HIV disclosure: A socio-ecological approach. AIDS, 29(Suppl 1), S25–S34. https://doi.org/10.1097/QAD.0000000000000670.
Ray, M., Logan, R., Sterne, J. A. C., Hernandez-Diaz, S., Robins, J. M., Sabin, C., Bansi, L., van Sighem, A., de Wolf, F., Costagliola, D., Lanoy, E., Bucher, H. C., von Wyl, V., Esteve, A., Casabona, J., del Amo, J., Moreno, S., Justice, A., Gouler, J., Lodi, S., Phillips, A., Seng, R., Meyer, L., Perez-Hoyos, S., de Olalla, P. G., Herman, M. A., Phillips, A. N., Gilson, R., Easterbrook, P., Fisher, M., Gazzard, B., Johnson, M., Walsh, J., Leen, C., Orkin, C., Anderson, J., Pillay, D., Delpech, V., Schwenk, A., Dunn, D., Gompels, M., Hill, T., Porter, K., Babiker, A., Sabin, C., & Collaboration, H.-C. (2010). The effect of combined antiretroviral therapy on the overall mortality of HIV-infected individuals. AIDS, 24(1), 123–137. https://doi.org/10.1097/QAD.0b013e3283324283.
Richman, W. L., Kiesler, S., Weisband, S., & Drasgow, F. (1999). A meta-analytic study of social desirability distortion in computer- administered questionnaires, traditional questionnaires, and interviews. Journal of Applied Psychology, 84, 754–775. https://doi.org/10.1037/0021-9010.84.5.754.
Rueda, S., Raboud, J., Mustard, C., Bayoumi, A., Lavis, J. N., & Rourke, S. B. (2011). Employment status is associated with both physical and mental health quality of life in people living with HIV. AIDS Care, 23(4), 435–443. https://doi.org/10.1080/09540121.2010.507952.
Serovich, J. M., Kimberly, J. A., Mosack, K. E., & Lewis, T. L. (2001). The role of family and friend social support in reducing emotional distress among HIV-positive women. AIDS Care, 13(3), 335–341. https://doi.org/10.1080/09540120120043982.
Sethosa, E., & Peltzer, K. (2005). Evaluation of HIV counselling and testing, self-disclosure, social support and sexual behaviour change among a rural sample of HIV reactive patients in South Africa. Curationis, 28(1), 29–41. https://doi.org/10.4102/curationis.v28i1.912.
Sherbourne, C. D., & Stewart, A. L. (1991). The MOS social support survey. Social Science and Medicine, 32(6), 705–714. https://doi.org/10.1016/0277-9536(91)90150-b.
Shrout, P. E., & Bolger, N. (2002). Mediation in experimental and nonexperimental studies: New procedures and recommendations. Psychological Methods, 7(4), 422–445. https://doi.org/10.1037/1082-989X.7.4.422.
Smith, R., Rossetto, K., & Peterson, B. L. (2008). A meta-analysis of disclosure of one's HIV-positive status, stigma and social support. AIDS Care, 20(10), 1266–1275. https://doi.org/10.1080/09540120801926977.
Sowell, R. L., Seals, B. F., Phillips, K. D., & Julious, C. H. (2003). Disclosure of HIV infection: How do women decide to tell? Health Education Research, 18(1), 32–44. https://doi.org/10.1093/her/18.1.32.
Ssali, S. N., Atuyambe, L., Tumwine, C., Segujja, E., Nekesa, N., Nannungi, A., Ryan, G., & Wagner, G. (2010). Reasons for disclosure of HIV status by people living with HIV/AIDS and in HIV care in Uganda: An exploratory study. AIDS Patient Care and STDs, 24(10), 675–681. https://doi.org/10.1089/apc.2010.0062.
Thapa, S., Hannes, K., Buve, A., Bhattarai, S., & Mathei, C. (2018). Theorizing the complexity of HIV disclosure in vulnerable populations: A grounded theory study. BMC Public Health, 18(1), 162–162. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-018-5073-x.
Timberlake, S. (1999). Extrait de «questions and answers on reporting, partner notification and disclosure of HIV Serostatus and/or AIDS». Public Health and Human Rights Implications. Genève: .
UNAIDS. (2019). UNAIDS data 2019. Retrieved Oct. 17 from http://aidsinfo.unaids.org
Vance, D. (2006). The relationship between HIV disclosure and adjustment. Psychological Reports, 99(3), 659–663. https://doi.org/10.2466/Pr0.99.3.659-663.
Vyavaharkar, M., Moneyham, L., Corwin, S., Tavakoli, A., Saunders, R., & Annang, L. (2011). HIV-disclosure, social support, and depression among HIV-infected African American women living in the rural southeastern United States. AIDS Education and Prevention, 23(1), 78–90. https://doi.org/10.1521/aeap.2011.23.1.78.
Wu, A. W. (1999). MOS-HIV health survey users manual. Johns Hopkins University.
Wu, A. W., Hays, R. D., Kelly, S., Malitz, F., & Bozzette, S. A. (1997). Applications of the medical outcomes study health-related quality of life measures in HIV/AIDS. Quality of Life Research, 6(6), 531–554. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018460132567.
Xiao, Z., Li, X., Qiao, S., Zhou, Y., & Shen, Z. (2017). Social support, depression, and quality of life among people living with HIV in Guangxi, China. AIDS Care, 29(3), 319–325. https://doi.org/10.1080/09540121.2016.1224298.
Xu, J.-F., Ming, Z.-Q., Zhang, Y.-Q., Wang, P.-C., Jing, J., & Cheng, F. (2017). Family support, discrimination, and quality of life among ART-treated HIV-infected patients: A two-year study in China. Infectious Diseases of Poverty, 6(1), 152–152. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40249-017-0364-5.
Yen, C. F., Tsai, J. J., Lu, P. L., Chen, Y. H., Chen, T. C., Chen, P. P., & Chen, T. P. (2004). Quality of life and its correlates in HIV/AIDS male outpatients receiving highly active antiretroviral therapy in Taiwan. Psychiatry and Clinical Neurosciences, 58(5), 501–506. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1440-1819.2004.01292.x.
Yoshioka, M. R., & Schustack, A. (2001). Disclosure of HIV status: Cultural issues of Asian patients. AIDS Patient Care and STDs, 15(2), 77–82. https://doi.org/10.1089/108729101300003672.
Yu, D. S., Lee, D. T., & Woo, J. (2004). Psychometric testing of the Chinese version of the medical outcomes study social support survey (MOS-SSS-C). Research in Nursing and Health, 27(2), 135–143. https://doi.org/10.1002/nur.20008.
Zanoni, B. C., Archary, M., Subramony, T., Sibaya, T., Psaros, C., & Haberer, J. E. (2021). Disclosure, social support, and mental health are modifiable factors affecting engagement in Care of Perinatally-HIV infected adolescents: A qualitative dyadic analysis. AIDS and Behavior, 25(1), 237–248. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10461-020-02968-1.
Zea, M. C., Reisen, C. A., Poppen, P. J., Bianchi, F. T., & Echeverry, J. J. (2005). Disclosure of HIV status and psychological well-being among Latino gay and bisexual men. AIDS and Behavior, 9(1), 15–26. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10461-005-1678-z.
Zhang, F., Dou, Z., Ma, Y., Zhao, Y., Liu, Z., Bulterys, M., & Chen, R. Y. (2009). Five-year outcomes of the China national free antiretroviral treatment program. Annals of Internal Medicine, 151(4), 241–251. https://doi.org/10.7326/0003-4819-151-4-200908180-00006.
Zhou, G., Li, X., Qiao, S., Shen, Z., & Zhou, Y. (2017). HIV symptom management self-efficacy mediates the relationship of internalized stigma and quality of life among people living with HIV in China. Journal of Health Psychology, 25(3), 311–321. https://doi.org/10.1177/1359105317715077.
Zimet, G. D., Dahlem, N. W., Zimet, S. G., & Farley, G. K. (1988). The multidimensional scale of perceived social support. Journal of Personality Assessment, 52(1), 30–41. https://doi.org/10.1207/s15327752jpa5201_2.
Funding
The research was supported by National Institutes of Health (NIH) [Grant Nos. R01HD074221, R01AA018090 and R21AI122919], National Nature Science Foundation of China (NSFC) [Grant No.71673146] and National Clinical Research Center for Mental Disorders (Peking University Sixth Hospital) [Grant No. NCRC2021M10]. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the NIH or NSFC.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of Interest/Competing Interests
All authors declare no of conflict of interest.
Ethics Approval
The research protocol was approved by the Institutional Review Boards at both Wayne State University in the United States and Guangxi CDC in China.
Consent to Participate
All participants have given their written consent to participant in the survey.
Consent for Publication
All authors consent to publish our work as journal article.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mi, T., Zhou, G., Li, X. et al. The association between HIV disclosure to family members and quality of life among people living with HIV/AIDS: The indirect effects through social support. Curr Psychol 42, 5755–5764 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-021-01927-w
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-021-01927-w