Abstract
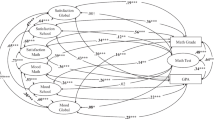
This study examined the relationship between psychological suzhi and academic achievement. Using a two-wave design, data were collected twice with a 6 months’ time lag from a sample of 2735 primary school students in grade 4 to 6. Utilizing cross-lagged analyses, we examined bidirectional effects between psychological suzhi and academic achievement. The results provided support for the positive relationship of psychological suzhi (Time 1) to academic achievement (Time 2), and also provided support for the positive relationship of academic achievement (Time 1) to psychological suzhi (Time 2). The positive effect of psychological suzhi on academic achievement among primary school students should be more prominent than the positive effect of academic achievement on psychological suzhi. Moreover, the cognitive quality, individuality and adaptability of psychological suzhi had a positive bidirectional relationship with academic achievement, respectively. Cognitive quality and individuality played more prominent roles in academic achievement. When compared with the effect of adaptability on academic achievement, the role of academic achievement played a more prominent role in adaptability. Overall, the study highlights the importance of psychological suzhi for academic achievement and academic achievement for psychological suzhi.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boxer, P., Goldstein, S. E., Delorenzo, T., Savoy, S., & Mercado, I. (2011). Educational aspiration-expectation discrepancies: Relation to socioeconomic and academic risk-related factors. Journal of Adolescence, 34(4), 609–617.
Carvalho, R. G. G. (2016). Gender differences in academic achievement: The mediating role of personality. Personality and Individual Differences, 94, 54–58.
Chen, X., Zhang, D. J., Cheng, G., Hu, T. Q., & Liu, G. Z. (2018). The effect of teacher support on middle school students’ academic achievement: The mediating effect of psychological suzhi. Psychological Development and Education, 34(6), 707–714.
Collie, R. J., Holliman, A. J., & Martin, A. J. (2017). Adaptability, engagement and academic achievement at university. Educational Psychology, 37(5), 632–647.
Crockett, L. J., Schulenberg, J. E., & Petersen, A. C. (1987). Congruence between objective and self-report data in a sample of young adolescents. Journal of Adolescent Research, 2(4), 383–392.
Dong, Z. S., & Zhang, D. J. (2015). The relationship between middle school students’ psychological suzhi, emotion regulation strategy and life satisfaction. Journal of Southwest University (Social Sciences Edition), 6, 99–103.
Dornbusch, S. M., Ritter, P. L., Leiderman, P. H., Roberts, D. F., & Fraleigh, M. J. (1987). The relation of parenting style to adolescent school performance. Child Development, 58(5), 1244–1257.
Fang, X. Y., Lin, D. H., Sun, L., & Fang, C. (2004). Parent-adolescent communication and adolescents’ social adjustment. Psychological Development and Education, 20(1), 18–22.
Fonteyne, L., Duyck, W., & Fruyt, F. D. (2017). Program-specific prediction of academic achievement on the basis of cognitive and non-cognitive factors. Learning and Individual Differences, 56, 34–48.
Fuligni, A. J., & Zhang, W. (2004). Attitudes toward family obligation among adolescents in contemporary urban and rural China. Child Development, 75(1), 180–192.
Furlong, M. J., Gilman, R., & Huebner, E. S. (Eds.). (2014). Handbook of positive psychology in schools (2nd ed.). New York: Taylor & Francis.
Gao, B. C., & Liu, R. D. (2011). Types of social support for middle school students: how they influence students' learning. Journal of Psychological Science, 34(3), 608–612.
Gignac, G. E., & Watkins, M. W. (2013). Bifactor modeling and the estimation of model-based reliability in the WAIS-IV. Multivariate Behavioral Research, 48, 639–662.
Gu, H. L., Wen, Z. L., & Fang, J. (2014). Bi-factor models: A new measurement perspective of multidimensional constructs. Journal of Psychological Science, 37(4), 973–979.
Guntern, S., Korpershoek, H., & Werf, G. V. D. (2017). Benefits of personality characteristics and self-efficacy in the perceived academic achievement of medical students. Educational Psychology, 37, 1–12.
Hamaker, E. L., Kuiper, R. M., & Grasman, R. P. (2015). A critique of the cross-lagged panel model. Psychological Methods, 20(1), 102–116.
Hu, T. Q., & Zhang, D. J. (2015). The relationship between psychological suzhi and depression of middle school students: The mediating role of self service attribution bias. Journal of Southwest University (Social Sciences Edition), 41(6), 104–109.
Hu, T. Q., Zhang, D. J., & Cheng, G. (2017). Revision of the psychological suzhi questionnaire of the middle school students (simplified version) and the test of the reliability and validity. Journal of Southwest University (Social Sciences Edition), 10(3), 120–126.
Ji, H. L. (2013). Primary school children’s family learning support, class status and academic performance. Primary and Secondary Mental Health Education, 13, 11–14.
Kuiper, R. M., & Ryan, O. (2018). Drawing conclusions from cross-lagged relationships: Re-considering the role of the time-interval. Structural Equation Modeling: A Multidisciplinary Journal, 25(5), 809–823.
Laidra, K., Pullmann, H., & Allik, J. (2007). Personality and intelligence as predictors of academic achievement: A cross-sectional study from elementary to secondary school. Personality and Individual Differences, 42(3), 441–451.
Lin, C. D. (2009). Developmental psychology (2nd ed.). Bei Jing: People’s Education Press.
Liu, C. X., & Lei, Y. (2015). Thirty years of psychological suzhi research: Looking back and commenting on. Journal of Southwest University (Social Sciences Edition), 41(3), 96–100.
Liu, Y. L., Zhang, D. J., & Guo, C. (2006). A research on the effect of pupils’ psychological suzhi on their academic achievement. Chinese Journal of Special Education, 9, 68–72.
Liu, G., Zhang, D., Pan, Y., Hu, T., He, N., Chen, W., & Wang, Z. (2017a). Self-concept clarity and subjective social status as mediators between psychological suzhi and social anxiety in Chinese adolescents. Personality and Individual Differences, 108, 40–44.
Liu, G., Zhang, D., Pan, Y., Ma, Y., & Lu, X. (2017b). The effect of psychological Suzhi on problem behaviors in Chinese adolescents: The mediating role of subjective social status and self-esteem. Frontiers in Psychology, 8, 1490.
Lu, X. Y., Zhang, D. J., Nie, Q., Zhang, X. Q., Pan, Y. G., & Jin, L. (2018). The relationship between psychological suzhi and the academic self-concept of middle school students: A moderated mediation model. Journal of Southwest University (Natural Science Edition), 40(6), 63–68.
Negru-Subtirica, O., & Pop, E. I. (2016). Longitudinal links between career adaptability and academic achievement in adolescence. Journal of Vocational Behavior, 93, 163–170.
Pan, Y., Hu, Y., Zhang, D., Ran, G., Li, B., Liu, C., Liu, G., Luo, S., & Chen, W. (2017a). Parental and peer attachment and adolescents’ behaviors: The mediating role of psychological suzhi in a longitudinal study. Children and Youth Services Review, 83, 218–225.
Pan, Y. G., Zhang, D. J., & Wu, L. L. (2017b). The development of the brief psychological suzhi questionnaire for primary school students. Journal of Southwest University (Social Sciences Edition), 43(2), 127–133.
Sorić, I., Penezić, Z., & Burić, I. (2017). The big five personality traits, goal orientations, and academic achievement. Learning and Individual Differences, 54, 126–134.
Su, Z. Q., & Zhang, D. J. (2015). The relationship between psychological suzhi anddepression of children aged 8-12: The mediating effect of coping styles. Chinese Journal of Special Education, 2, 72–77.
Vecchione, M., Alessandri, G., Caprara, G. V., & Tisak, J. (2014). Are method effects permanent or ephemeral in nature? Thecase of the revised life orientation test. Structural Equation Modeling: A Multidisciplinary Journal, 21, 117–130.
Wang, X. Q., & Zhang, D. J. (2012). Looking beyond PTH and DFM: The relationship model between psychological suzhi and mental health. Journal of the Southwest University (Social Science Edition), 38(6), 67–74.
Wen, Z. L. (2017). Causal inference and analysis in empirical studies. Journal of Psychological Science, 40(1), 200–208.
Wen, C., Zhang, W., Li, D. P., Yu, C. P., & Dai, W. Z. (2010). Relationship between junior students’ gratitude and academic achievement: With academic engagement as the mediator. Psychological Development and Education, 26(6), 598–605.
Wu, L., Zhang, D., Cheng, G., Hu, T., & Rost, D. H. (2015). Parental emotional warmth and psychological suzhi as mediators between socioeconomic status and problem behaviours in Chinese children. Children and Youth Services Review, 59, 132–138.
Wu, L. L., Zhang, D. J., & Cheng, G. (2017). Preliminary study on bi-factor structure of primary and secondary students’ psychological suzhi. Studies of Psychology and Behavior, 15(1), 26–33.
Wu, L. L., Zhang, D. J., Cheng, G., & Wang, X. Q. (2018). The effect of family socioeconomic status on children’s academic achievements: The mediating role of general psychological suzhi. Journal of Southwest University (Natural Science Edition), 40(6), 56–62.
Ye, B. J., Yang, Q., & Hu, Z. J. (2013). Effect of gratitude on adolescents’ academic achievement: Moderated mediating effect. Psychological Development and Education, 29(2), 192–199.
Yu, G. L., & Chen, S. F. (2001). The relationship of event stress and academic achievement to behavioral adjustment of elementary school students. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 33(4), 344–348.
Zhang, D. J. (2003). On man’s psychological suzhi. Studies of Psychology and Behavior., 1(2), 143–146.
Zhang, D. J., & Liu, Y. L. (2001). Correlative study on psychological suzhi and academic achievement of high school students. Journal of Psychological Science, 24(1), 110–111.
Zhang, D. J., & Wang, X. Q. (2012). An analysis of the relationship between mental health and psychological suzhi: From the perspective of connotation and structure. Journal of the Southwest University (Social Science Edition), 38(3), 69–74.
Zhang, D. J., Feng, Z. Z., Guo, C., & Chen, X. (2000). Problems on research of children psychological suzhi. Journal of Southwest China Normal University (Humanities and Social Sciences Edition), 26, 56–62.
Zhang, D. J., Liu, Y. L., & Guo, C. (2004). Relationship between elementary school student’ psychological suzhi and academic achievement. Psychological Development and Education, 20(1), 64–69.
Zhang, D., Wang, J. L., & Yu, L. (2011). Methods and implementary strategies on cultivating Students’ psychological suzhi. New York: Nova Science Publishers.
Zhang, D. J., Yu, L., & Wang, J. L. (2014). Psychological suzhi training mode and implementation strategy of students. Bei Jing: China Science Press.
Zhang, D. J., Su, Z. Q., & Wang, X. Q. (2017). Thirty-years study on the psychological suzhi of Chinese children and adolescents: Review and prospect. Studies of Psychology and Behavior, 15(1), 3–11.
Funding
This study has been supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. SWU1809354).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
All authors declare that there no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all participants and their parents in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, G., Zhao, Z. & Zhang, D. Cross-lagged relations between psychological suzhi and academic achievement. Curr Psychol 39, 1496–1504 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-019-00184-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-019-00184-2