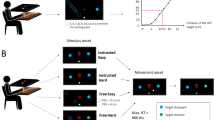
Abstract
Humans can inhibit an action based on external instruction (i.e., reactive inhibition) or internal decision (i.e., intentional inhibition). Although some functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) studies have documented the relationship between reactive and intentional inhibitions, they could not provide pertinent temporal dynamics information due to fMRI’s low temporal resolution. Therefore, in the current study, we explored this issue by extracting the time-domain dynamics and oscillatory-power dynamics from electroencephalographic (EEG) data while participants performed a modified Go/NoGo/Choose task, in which free choices trials were integrated with conventional go/nogo trials. Participants were asked to decide for themselves to either inhibit or execute an action for free choices trials, and to respond properly according to go/nogo signal for conventional go/nogo trials. Two important results were obtained. First, for the reactive condition, nogo trials elicited greater N2 and P3 amplitudes and induced more pronounced delta, theta, and beta band oscillations than go trials, while for the intentional condition, nogo trials only elicited greater P3 amplitudes and triggered pronounced beta band oscillations compared to go trials. Second, while the P3/delta, theta, and beta oscillations were larger for reactive nogo trials than for intentional go/nogo trials, the P3/delta and theta oscillations were larger for intentional go/nogo trials than for reactive go trials. Together, these results suggest that there are both similarities and differences in oscillatory dynamics between reactive and intentional inhibitions. This study is the first to investigate the relationship between reactive and intentional inhibitions at the time-frequency domain, and the current results expand our understanding about different inhibitions.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aron, A. R. (2011). From reactive to proactive and selective control: Developing a richer model for stopping inappropriate responses. Biological Psychiatry, 69(12), e55–e68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2010.07.024.
Bianco, V., Berchicci, M., Perri, R. L., Spinelli, D., & Di Russo, F. (2017a). The proactive self-control of actions: Time-course of underlying brain activities. Neuroimage, 156, 388–393. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2017.05.043.
Bianco, V., Di Russo, F., Perri, R. L., & Berchicci, M. (2017b). Different proactive and reactive action control in fencers’ and boxers’ brain. Neuroscience, 343, 260–268.
Bokura, H., Yamaguchi, S., & Kobayashi, S. (2001). Electrophysiological correlates for response inhibition in a Go/NoGo task. Clinical Neurophysiology, 112(12), 2224–2232.
Brass, M., & Haggard, P. (2007). To do or not to do: The neural signature of self-control. The Journal of Neuroscience, 27(34), 9141–9145. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0924-07.2007.
Brydges, C. R., Fox, A. M., Reid, C. L., & Anderson, M. (2014). Predictive validity of the N2 and P3 ERP components to executive functioning in children: A latent-variable analysis. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 8, 80. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2014.00080.
Cohen, M. X. (2017). Where does EEG come from and what does it mean? Trends in Neurosciences, 40(4), 208–218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tins.2017.02.004.
Di Russo, F., Lucci, G., Sulpizio, V., Berchicci, M., Spinelli, D., Pitzalis, S., & Galati, G. (2016). Spatiotemporal brain mapping during preparation, perception, and action. Neuroimage, 126, 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2015.11.036.
Di Russo, F., Berchicci, M., Bozzacchi, C., Perri, R. L., Pitzalis, S., & Spinelli, D. (2017). Beyond the “Bereitschaftspotential”: Action preparation behind cognitive functions. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 78, 57–81.
Diamond, A. (2013). Executive functions. Annual Review of Psychology, 64, 135–168. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-psych-113011-143750.
Enriquez-Geppert, S., Konrad, C., Pantev, C., & Huster, R. J. (2010). Conflict and inhibition differentially affect the N200/P300 complex in a combined go/nogo and stop-signal task. Neuroimage, 51(2), 877–887. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.02.043.
Faul, F., Erdfelder, E., Lang, A. G., & Buchner, A. (2007). G*Power 3: A flexible statistical power analysis program for the social, behavioral, and biomedical sciences. Behavior Research Methods, 39(2), 175–191.
Filevich, E., Kuhn, S., & Haggard, P. (2012). Intentional inhibition in human action: The power of 'no'. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 36(4), 1107–1118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2012.01.006.
Gajewski, P. D., & Falkenstein, M. (2013). Effects of task complexity on ERP components in go/Nogo tasks. International Journal of Psychophysiology, 87(3), 273–278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpsycho.2012.08.007.
Haggard, P. (2008). Human volition: Towards a neuroscience of will. Nature Reviews. Neuroscience, 9(12), 934–946. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn2497.
Harper, J., Malone, S. M., & Bernat, E. M. (2014). Theta and delta band activity explain N2 and P3 ERP component activity in a go/no-go task. Clinical Neurophysiology, 125(1), 124–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinph.2013.06.025.
Huster, R. J., Enriquez-Geppert, S., Lavallee, C. F., Falkenstein, M., & Herrmann, C. S. (2013). Electroencephalography of response inhibition tasks: Functional networks and cognitive contributions. International Journal of Psychophysiology, 87(3), 217–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpsycho.2012.08.001.
Jiang, J., Zhang, Q., & van Gaal, S. (2015). Conflict awareness dissociates theta-band neural dynamics of the medial frontal and lateral frontal cortex during trial-by-trial cognitive control. Neuroimage, 116, 102–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2015.04.062.
Kalamala, P., Szewczyk, J., Senderecka, M., & Wodniecka, Z. (2018). Flanker task with equiprobable congruent and incongruent conditions does not elicit the conflict N2. Psychophysiology, 55(2). https://doi.org/10.1111/psyp.12980.
Kim, S. G., Richter, W., & Ugurbil, K. (1997). Limitations of temporal resolution in functional MRI. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 37(4), 631–636.
Kramer, U. M., Knight, R. T., & Munte, T. F. (2011). Electrophysiological evidence for different inhibitory mechanisms when stopping or changing a planned response. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 23(9), 2481–2493. https://doi.org/10.1162/jocn.2010.21573.
Krieghoff, V., Waszak, F., Prinz, W., & Brass, M. (2011). Neural and behavioral correlates of intentional actions. Neuropsychologia, 49(5), 767–776. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2011.01.025.
Kuhn, S., Haggard, P., & Brass, M. (2009). Intentional inhibition: How the "veto-area" exerts control. Human Brain Mapping, 30(9), 2834–2843. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.20711.
Lynn, M. T., Muhle-Karbe, P. S., & Brass, M. (2014). Controlling the self: The role of the dorsal frontomedian cortex in intentional inhibition. Neuropsychologia, 65, 247–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2014.09.009.
Maris, E., & Oostenveld, R. (2007). Nonparametric statistical testing of EEG- and MEG-data. Journal of Neuroscience Methods, 164(1), 177–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneumeth.2007.03.024.
Pandey, A. K., Kamarajan, C., Manz, N., Chorlian, D. B., Stimus, A., & Porjesz, B. (2016). Delta, theta, and alpha event-related oscillations in alcoholics during Go/NoGo task: Neurocognitive deficits in execution, inhibition, and attention processing. Progress in Neuro-Psychopharmacology & Biological Psychiatry, 65, 158–171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnpbp.2015.10.002.
Parkinson, J., & Haggard, P. (2015). Choosing to stop: Responses evoked by externally triggered and internally generated inhibition identify a neural mechanism of will. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 27(10), 1948–1956. https://doi.org/10.1162/jocn_a_00830.
Parkinson, J., Garfinkel, S., Critchley, H., Dienes, Z., & Seth, A. K. (2017). Don't make me angry, you wouldn't like me when I'm angry: Volitional choices to act or inhibit are modulated by subliminal perception of emotional faces. Cognitive, Affective, & Behavioral Neuroscience, 17(2), 252–268. https://doi.org/10.3758/s13415-016-0477-5.
Perri, R. L., Berchicci, M., Lucci, G., Spinelli, D., & Di Russo, F. (2015). Why do we make mistakes? Neurocognitive processes during the preparation-perception-action cycle and error-detection. Neuroimage, 113, 320–328. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2015.03.040.
Perri, R. L., Spinelli, D., & Di Russo, F. (2017). Missing the target: The neural processing underlying the omission error. Brain Topography, 30(3), 352–363. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10548-017-0545-3.
Ridderinkhof, K. R., van den Wildenberg, W. P., & Brass, M. (2014). "Dont" versus "wont": Principles, mechanisms, and intention in action inhibition. Neuropsychologia, 65, 255–262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2014.09.005.
Schel, M. A., Kuhn, S., Brass, M., Haggard, P., Ridderinkhof, K. R., & Crone, E. A. (2014a). Neural correlates of intentional and stimulus-driven inhibition: A comparison. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 8, 27. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2014.00027.
Schel, M. A., Ridderinkhof, K. R., & Crone, E. A. (2014b). Choosing not to act: Neural bases of the development of intentional inhibition. Developmental Cognitive Neuroscience, 10, 93–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dcn.2014.08.006.
Schel, M. A., Scheres, A., & Crone, E. A. (2014c). New perspectives on self-control development: Highlighting the role of intentional inhibition. Neuropsychologia, 65, 236–246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2014.08.022.
Verbruggen, F., McLaren, I. P., & Chambers, C. D. (2014). Banishing the control homunculi in studies of action control and behavior change. Perspectives on Psychological Science, 9(5), 497–524. https://doi.org/10.1177/1745691614526414.
Walsh, E., Kuhn, S., Brass, M., Wenke, D., & Haggard, P. (2010). EEG activations during intentional inhibition of voluntary action: An electrophysiological correlate of self-control? Neuropsychologia, 48(2), 619–626. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2009.10.026.
Xu, M., Li, Z., Ding, C., Zhang, J., Fan, L., Diao, L., & Yang, D. (2015). The divergent effects of fear and disgust on inhibitory control: An ERP study. PLoS One, 10(6), e0128932. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0128932.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (SWU1809352), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (71472156). All authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 673 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, M., Fan, L., Li, Z. et al. Neural signatures of reactive and intentional inhibitions: An ERP study. Curr Psychol 39, 1485–1495 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-018-0090-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-018-0090-6