Abstract
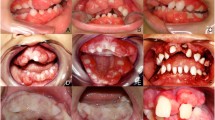
Localized juvenile spongiotic gingival hyperplasia (LJSGH) is a gingival lesion with unique clinicopathologic features that may involve synchronously multiple sites. We present a case with lesions clinically consistent with LJSGH in four jaw quadrants, confirmed by biopsy and review the English literature on multifocal LJSGH cases. A 19 year-old woman presented with circumscribed, erythematous overgrowths on the right and left maxillary and mandibular gingiva. With the provisional diagnosis of multifocal LJSGH, total excision of four maxillary lesions was performed. Clinical, microscopic and immunohistochemical examination with cytokeratin 19 confirmed the diagnosis of LJSGH in multiple sites. The excised lesions showed partial to complete recurrence after 4 months, while spontaneous regression of all but one lesion was observed after 15 months. Twenty cases with synchronous involvement of the gingiva of at least two teeth were previously reported. Their clinical features were comparable to that of solitary LJSGH. Only one case involved all four jaw quadrants. Spontaneous remission has not been documented before. The recognition of multiple lesions with clinicopathologic features diagnostic of LJSGH in the same adult patient argue against the designations “localized” and “juvenile”. Recurrences are common, while remission might occur.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chang JY, Kessler HP, Wright JM. Localized juvenile spongiotic gingival hyperplasia. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2008;106(3):411–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tripleo.2008.04.024.
Darling MR, Daley TD, Wilson A, Wysocki GP. Juvenile spongiotic gingivitis. J Periodontol. 2007;78(7):1235–40. https://doi.org/10.1902/jop.2007.060502.
Argyris PP, Nelson AC, Papanakou S, Merkourea S, Tosios KI, Koutlas IG. Localized juvenile spongiotic gingival hyperplasia featuring unusual p16INK4A labeling and negative human papillomavirus status by polymerase chain reaction. J Oral Pathol Med. 2015;44(1):37–44. https://doi.org/10.1111/jop.12214.
de Freitas Silva BS, Silva Sant’Ana SS, Watanabe S, Vencio EF, Roriz VM, Yamamoto-Silva FP. Multifocal red bands of the marginal gingiva. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2015;119(1):3–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oooo.2014.07.005.
MacNeill SR, Rokos JW, Umaki MR, Satheesh KM, Cobb CM. Conservative treatment of localized juvenile spongiotic gingival hyperplasia. Clin Adv Periodontics. 2011;1(3):199–204. https://doi.org/10.1902/cap.2011.110003.
Nogueira VK, Fernandes D, Navarro CM, Giro EM, de Almeida LY, Leon JE, et al. Cryotherapy for localized juvenile spongiotic gingival hyperplasia: preliminary findings on two cases. Int J Paediatr Dent. 2017;27(3):231–5. https://doi.org/10.1111/ipd.12278.
Solomon LW, Trahan WR, Snow JE. Localized juvenile spongiotic gingival hyperplasia: a report of 3 cases. Paediatr Dent. 2013;35(4):360–3.
Allon I, Lammert KM, Iwase R, Spears R, Wright JM, Naidu A. Localized juvenile spongiotic gingival hyperplasia possibly originates from the junctional gingival epithelium-an immunohistochemical study. Histopathology. 2016;68(4):549–55. https://doi.org/10.1111/his.12774.
Damm DD. Gingival red patch. Juvenile spongiotic gingival hyperplasia. Gen Dent. 2009;57(4):448–51.
Fernandes DT, Wright JM, Lopes SMP, Santos-Silva AR, Vargas PA, Lopes MA. Localized juvenile spongiotic gingival hyperplasia: a report of 4 cases and literature review. Clin Adv Periodontics. 2017. https://doi.org/10.1902/cap.2017.170018.
Flaitz CM, Longoria JM. Oral and maxillofacial pathology case of the month. Localized juvenile spongiotic gingival hyperplasia. Texas Dent J. 2010;127(12):1312.
Kalogirou EM, Chatzidimitriou K, Tosios KI, Piperi EP, Sklavounou A. Localized juvenile spongiotic gingival hyperplasia: report of two cases. J Clini Pediatr Dent. 2017;41(3):228–31. https://doi.org/10.17796/1053-4628-41.3.228.
Noonan V, Lerman MA, Woo SB, Kabani S. Localized juvenile spongiotic gingival hyperplasia. J Massachusetts Dent Soc. 2013;62(2):45.
Rossmann JA. Reactive lesions of the gingiva: diagnosis and treatment options. Open Pathol J. 2011;5:23–32. https://doi.org/10.2174/1874375701105010023.
Decani S, Baruzzi E, Sutera S, Trapani A, Sardella A. A case of juvenile spongiotic gingivitis. Annali di stomatologia. 2013;4(Suppl 2):41.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All Authors declares that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Siamantas, I., Kalogirou, EM., Tosios, K.I. et al. Spongiotic Gingival Hyperplasia Synchronously Involving Multiple Sites: Case Report and Review of the Literature. Head and Neck Pathol 12, 517–521 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12105-018-0903-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12105-018-0903-9