Abstract
Oral submucous fibrosis (OSMF) is a chronic debilitating disease and a premalignant condition of the oral cavity characterized by generalized submucosal fibrosis. Despite its precancerous nature, the molecular biology regarding its malignant potential has not been extensively studied. PTEN, a known tumor suppressor gene is mutated in a majority of human cancers and has also been implicated in several fibrotic disorders. The present study aims to evaluate the expression of PTEN in OSMF and oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) and correlate it with the pathogenesis and malignant transformation of OSMF. 60 cases total of OSMF (30) and OSCC (30) were subjected to immunohistochemistry using PTEN antibody. Ten normal oral mucosa (NOM) specimens were also stained as controls. There was progressive loss of PTEN expression from normal mucosa to OSMF and OSCC (p ≤ 0.001). Significant differences were observed for PTEN expression between NOM and OSMF, OSMF and OSCC as well as NOM and OSCC. Though a progressive loss of PTEN was noticed between early OSMF and advanced OSMF, the variation did not reach statistical significance (p ≥ 0.001). Data suggest that there is a significant loss of PTEN expression in OSMF as compared to normal oral mucosa and that this trend increased from OSMF to OSCC. Thus, alteration of PTEN is likely an important molecular event in OSMF pathogenesis and oral carcinogenesis.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Scully C, Bagan J. Oral squamous cell carcinoma: an overview. Oral Oncol. 2009;45:301–8.
Warnakulasuriya S. Global epidemiology of oral and oropharyngeal cancer. Oral Oncol. 2009;45:309–16.
Van der Waal I. Potentially malignant disorders of the oral and oropharyngeal mucosa: terminology, classification and present concepts of management. Oral Oncol. 2009;45:317–23.
Pindborg JJ, Sirasat SM. Oral Submucous fibrosis. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1966;22:764–9.
Tilakaratne WM, Klinikowski MF, Saku T, Peters TJ, Warnakulasuriya S. Oral submucous fibrosis: review on etiology and pathogenesis. Oral Oncol. 2006;42:561–8.
Rajalalitha P, Vali S. Molecular pathogenesis of oral submucous fibrosis—a collagen metabolic disorder. J Oral Pathol Med. 2005;34:321–8.
Murti PR, Bhonsle RB, Pindborg JJ, Daftary DK, Gupta PC, Mehta FS. Malignant transformation rate in oral submucous fibrosis over a 17 year period. Commun Dent Oral Epidemiol. 1985;13:340–1.
Chen YJ, Chang JT, Liao CT, Wang HM, Yen TC, Chiu CC, Lu YC, Li HF, Cheng AJ. Head and neck cancer in the betel quid chewing area: recent advances in molecular carcinogenesis. Cancer Sci. 2008;99:1507–14.
Dahia PM. PTEN, a unique tumor suppressor gene. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2000;7:115–29.
Yamada KM, Araki M. Tumor suppressor PTEN: modulator of cell signaling, growth, migration and apoptosis. J Cell Sci. 2001;114:2375–82.
Stiles BL. Phosphatase and tensin homologue deleted on chromosome 10: extending its PTENtacles. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2009;41:757–61.
Leslie NR. Downes CP.PTEN function: how normal cells control it and tumor cells lose it. Biochem J. 2004;382:1–11.
Sansal I, Sellers WR. The biology and clinical relevance of the PTEN tumor suppressor pathway. J Clin Oncol. 2004;22:2954–63.
Shao X, Tandon R, Samara G, Kanki H, Yano H, Close LG, Parsons R, Sato T. Mutational analysis of the PTEN gene in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 1998;77:684–8.
Squarize CH, Castilho RM, Declo SPJ. Immunohistochemical evidence of PTEN in oral squamous cell carcinoma and its correlation with the histological malignancy grading system. J Oral Pathol Med. 2002;31:379–89.
Kurusawa Y, Shiba M, Nakamura M, Fushimi K, Ishigami T, Bukawa H, Yokoe H, Uzawa K, Tanzawa H. PTEN expression and methylation status in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 2008;19:1429–34.
Bu S, Asano Y, Bujor A, Highland K, Hant F, Trojanowska M. Dihydrosphingosine 1-phosphate has a potent antifibrotic effect in scleroderma fibroblasts via normalization of phosphatase and tensin homolog levels. Arthr Rheum. 2010;62:2117–26.
Hao LS, Zhang XL, An JY, Karlin J, Tian XP, Dun ZN, Xie SR, Chen S. PTEN expression is down-regulated in liver tissues of rats with hepatic fibrosis induced by biliary stenosis. APMIS. 2009;117:681–91.
Kato M, Putta S, Wang M, Yuan H, Lanting L, Nair I, Gunn A, Nakagawa Y, Shimano H, Todorov I, Rossi JJ, Natarajan R. TGF-beta activates Akt kinase through a microRNA-dependent amplifying circuit targeting PTEN. Nat Cell Biol. 2009;11:881–9.
Xia H, Diebold D, Nho R, Perlman D, Kleidon J, Kahm J, Avdulov S, Peterson M, Nerva J, Bitterman P, Henke C. Pathological integrin signaling enhances proliferation of primary lung fibroblasts from patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. J Exp Med. 2008;205:1659–72.
Kuwano K. PTEN as a new agent in the fight against fibrogenesis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2006;173:5–6.
Teunissen BE, Smeets PJ, Willemsen PH, De Windt LJ, Van der Vusse GJ, Van Bilsen M. Activation of PPAR delta inhibits cardiac fibroblast proliferation and the transdifferentiation into myofibroblasts. Cardiovasc Res. 2007;75:519–29.
Sui L, Dong Y, Watanabe Y, Yamaguchi F, Sugimoto K, Tokuda M. Alteration and clinical relevance of PTEN expression and its correlation with survivin expression in epithelial ovarian tumors. Oncol Rep. 2006;15:773–8.
Dave BJ, Trivedi AH, Adhvaryu SG. Role of areca nut consumption in cause of oral cancers—a cytogenetic assessment. Cancer. 1992;70:1017–23.
Trivedy C, Warnakulasuriya KAAS, Tavasoli M, Ateingrimsdottir H, Penhallow J, Maher R, Johnson NW. p53 aberrations in oral submucous fibrosis and oral squamous cell carcinoma detected by immunohistochemistry and PCR-SSCP. J Oral Pathol Med. 1998;27:72–7.
Cox SC, Walker DM. Epithelial growth fraction and expression of p53 tumor suppressor gene in oral submucous fibrosis. Aust Dent J. 1996;1996(41):91–6.
Teni T, Pawar S, Sanghvi V, Saranath D. Expression of bcl-2 and bax in chewing tobacco induced oral cancers and oral lesions in India. Pathol Oncol Res. 2002;8:109–14.
Liao PH, Lee TL, Yang LC, Yang SH, Chen SL, Chou MY. Adenomatous polyposis coli gene mutation and decreased wild—type p53 protein expression in oral submucous fibrosis: a preliminary investigation. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2001;92:202–7.
Teh TM, Tilakaratne WM, Chaplin T, Young BD, Ariyawardana A, Pitiyage G, et al. Fingerprinting genomic instability in oral submucous fibrosis. J Oral Pathol Med. 2008;37:430–6.
Mutter GL. Diagnosis of premalignant endometrial disease. J Clin Pathol. 2002;55:326–31.
Willis BC, Borok Z. TGF-β induced EMT: mechanisms and implications for fibrotic lung disease. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2007;293:L525–34.
Chaing CP, Lang MJ, Liu BY, Wang JT, Leu JS, Hahn LJ, et al. Expression of proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) in oral submucous fibrosis, oral epithelial hyperkeratosis and oral epithelial dysplasia in Taiwan. Oral Oncol. 2000;36:353–9.
Yanjia H, Xinchun J. The role of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in oral squamous cell carcinoma and oral submucous fibrosis. Clinica Chemica Acta. 2007;383:51–6.
Xia L, Ling TY, Gao YJ, Tang DS, Li WH. Arecoline and keratinocytes may affect the collagen metabolism of fibroblasts. J Oral Pathol Med. 2009;38:422–6.
Lalli A, Tilakaratne WM, Ariyawardana A, Fitchet C, Leigh IM, Hagi-Pavli E, Cruchley AT, Parkinson EK, The MT, Fortune F, Waseem A. An altered keratinocyte phenotype in oral submucous fibrosis: correlation of keratin K17 expression with disease severity. J Oral Pathol Med. 2008;37:211–20.
Ranganathan K, Kavitha R, Sawant SS, Vaidya MM. Cytokeratin expression in oral submucous fibrosis—an immunohistochemical study. J Oral Pathol Med. 2006;35:25–32.
Das RK, Pal M, Barui A, Paul RR, Chakraborthy C, Ray AK, Sengupta S, Chatterjee J. Assessment of malignant potential of oral submucous fibrosis through evaluation of p63, E-cadherin and CD 105 expression. J Clin Pathol. 2010;63(10):894–9.
Angadi PV, Kale AD, Hallikerimath S. Evaluation of myofibroblasts in oral submucous fibrosis: correlation with disease severity. J Oral Pathol Med. 2011;40(3):208–13. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0714.2010.00995.
Moutasim KA, Jenei V, Sapienza K, Marsh D, Weinreb PH, Violette SM, Lewis MP, Marshall JF, Fortune F, Tilakaratne WM, Hart IR, Thomas GJ. Betel-derived alkaloid up-regulates keratinocyte alphavbeta6 integrin expression and promotes oral submucous fibrosis. J Pathol. 2011;223(3):366–77. doi:10.1002/path.2786.
Li X, Ling TY, Gao YJ. Effect of arecoline on the differentiation of myofibroblasts of oral mucosa (Abstract). Zhongua Kuo Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2007;42:423–7.
White ES, Atrasz RG, Hu B, Phan SH, Stambolic V, Mak TW, Hogaboam CM, Flaherty KR, Martinez FJ, Kontos CD, Toews GB. Negative regulation of myofibroblast differentiation by PTEN (phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted on chromosome 10). Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2006;173:112–21.
Thannickal VJ, Lee DY, White ES, Cui Z, Larios JM, Chacon R, Horowitz JC, Day RM, Thomas PE. Myofibroblast differentiation by TGF-β1 is dependent on cell adhesion and integrin signaling via focal adhesion kinase. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:12384–9.
Gu J, Tamura M, Yamada KM. Tumor suppressor PTEN inhibits integrin and growth factor mediated mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase. J Cell Biol. 1998;143:1375–8.
Tamura M, Gu J, Matsumoto K, Aota S, Parsons R, Yamada KM. Inhibition of cell migration, spreading, and focal adhesion by tumor suppressor PTEN. Science. 1998;280:1614–7.
Chen Q, Samaranayake LP, Zhou H, Xiao L. Homozygous deletion of PTEN tumor suppressor gene is not a feature of oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Oncol. 2000;36:95–9.
Mavros A, Hahn M, Weilang I, Koy S, Koufaki ON, Strelocke K, et al. Infrequent genetic alterations of the tumor suppressor gene PTEN/MMAC1 in squamous cell carcinoma of the oral cavity. J Oral Pathol Med. 2002;31:270–6.
Chakraborthy S, Azeem Mohiyuddin SM, Gopinath KS, Kumar A. Involvement of TSC genes and differential expression of other members of the mTOR signaling pathway in oral squamous cell carcinoma. BMC Cancer. 2008;8:163–9.
Lee JI, Soria JC, Hassan KA, El-Naggar AK, Tang X, Lui DD, Homg WK, Mao L. Loss of PTEN expression as a prognostic marker for tongue cancer. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2001;127:1441–5.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Mr. Mallapur for assisting us with statistical analyses, Mr. Justin from Biogenex Company for his technical support and gratefully acknowledge Patricia J. Kelly, Associate Dean for Research, University of Missouri-Kansas City for the assistance in manuscript preparation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.

12105_2012_341_MOESM1_ESM.jpg
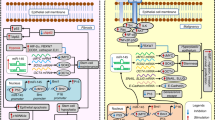
Diagram to demonstrate the possible mechanism of PTEN in the pathogenesis and malignant transformation of OSMF (JPEG 237 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Angadi, P.V., Krishnapillai, R. Evaluation of PTEN Immunoexpression in Oral Submucous Fibrosis: Role in Pathogenesis and Malignant Transformation. Head and Neck Pathol 6, 314–321 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12105-012-0341-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12105-012-0341-z