Abstract
Objectives
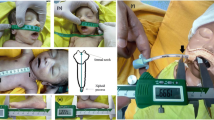
To assess the correct placement of endotracheal tube (ETT) by confirming it with a flexible fiberoptic bronchoscope (FOB), to propose a new formula that would be suitable for Indian children, and to assess the movement of the ETT tip during neck flexion and extension.
Methods
A total of 76 patients were included in the study between the age of 2 and 10 y. Depth of ETT insertion was assessed using FOB. ETT migration due to changes in head and neck position was also assessed.
Results
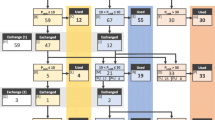
It was observed that 6 out of 76 children had endobronchial/at carina position of ETT after the initial insertion as per the black line guidance in the neutral position. While the incidence was 23, 36, and 36, respectively as per Cole, weight-, and height-based formula.
Conclusion
The existing formulae are not suitable for Indian children as their physical stature is different from other ethnic populations. Therefore, the authors suggest a new formula [(Age/2) + 10 cm] for depth of ETT insertion for children of the authors’ geographical area.
Trial Registration
CTRI/2015/06/005871.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lee SU, Jung JY, Kim DK, et al. New decision formulas for predicting endotracheal tube depth in children: analysis of neck CT images. Emerg Med J. 2018;35:303–8.
Weiss M, Knirsch W, Kretschmar O, et al. Tracheal tube-tip displacement inchildren during head-neck movement–a radiological assessment. Br J Anaesth. 2006;96:486–91.
O’Meara M, Watton D. Advanced Paediatric Life Support: The Practical Approach. 5th ed. London, UK: Wiley; 2012.
Morgan GA, Steward DJ. Linear airway dimensions in children: including those from cleft palate. Can Anaesth Soc J. 1982;29:1–8.
Neunhoeffer F, Wahl T, Hofbeck M, et al. A new method for determining the insertion depth of tracheal tubes in children: a pilot study. Br J Anaesth. 2016;116:393–7.
Lau N, Playfor SD, Rashid A, Dhanarass M. New formulae for predicting tracheal tube length. Paediatr Anaesth. 2006;16:1238–43.
Chowdhry R, Dangman B, Pinheiro JM. The concordance of ultrasound technique versus X-ray to confirm endotracheal tube position in neonates. J Perinatol. 2015;35:481–4.
Kemper M, Dullenkopf A, Schmidt AR, Gerber A, Weiss M. Nasotracheal intubation depth in paediatric patients. Br J Anaesth. 2014;113:840–6.
Penlington GN. Letter: Endotracheal tube sizes for children. Anaesthesia. 1974;29:494–5.
Ho AM, Aun CS, Karmaker MK. The margin of safety associated with the use of cuffed pediatric tracheal tubes. Anaesthesia. 2002;57:173–5.
Tareerath M, Mangmeesri P. Accuracy of Age-Based Formula to Predict the Size and Depth of Cuffed Oral Preformed Endotracheal Tubes in Children Undergoing Tonsillectomy. Ear Nose Throat J. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1177/0145561320980511.
Santos DLS, Andrade PDO, Gomes ELFD. Does the endotracheal tube insertion depth predicted by formulas in children have a good concordance with the ideal position observed by X-ray? Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2020;32:295–300.
Acknowledgements
The authors extend their sincere gratitude to Prof. Umesh Goneppanavar for his invaluable contribution to the contrivance/formulation of this study.
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
PL, MP: Concept; PL: Data collection; PL, AT, RMS, MP drafted and revised the manuscript. All authors approved the final version of manuscript. MP will act as the guarantor for this paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
None.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Logia, P., Theagrajan, A., M.S., R. et al. New Formula for Depth of Insertion of Endotracheal Tube in Children: A Prospective Observational Study. Indian J Pediatr 91, 125–130 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12098-022-04206-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12098-022-04206-z