Abstract
Objective
To compare asthma control by Asthma Control Test (ACT)/Childhood Asthma Control Test (cACT) Questionnaire of Global Initiative for Asthma 2017 (GINA-2017) against spirometry in children, 5–18 y of age, with asthma.
Methods
A prospective observational study was conducted between July 2017 and March 2019 in pulmonology OPD of a tertiary care center. Children with asthma aged 5–18 y, falling under the inclusion criteria had spirometry and cACT/ACT questionnaire before starting inhaled corticosteroids. After 12 wk, symptom control was reassessed by ACT/cACT and spirometry. Chi-square/Fischer exact test and paired t-test/Mann–Whitney U test used for qualitative and quantitative data, respectively.
Results
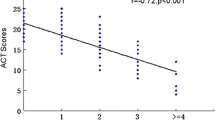
ACT/cACT pretreatment score was 12.76 (2.521), and at follow-up the score was 23.94 (1.941) (p < 0.001). Control by GINA increased from 2.04% to 91.84% at follow-up (p < 0.001). Significant improvement in forced expiratory volume in first second (FEV1), forced expiratory volume/forced vital capacity (FEV1/FVC), forced expiratory flow between 25 and 75% of FVC (FEF25−75) and peak expiratory flow rate (PEFR) between pretreatment and follow-up seen were −71.86%, 106.84%, 101.82%, and 97.51% vs. 82.2%, 109.55%, 110.38%, and 107.00%, respectively. Positive correlation between ACT/cACT and FEV1 (r = 0.26, p ≤ 0.05), PEFR (r = 0.30, p ≤ 0.05).
Conclusions
There is a good correlation of symptom control between ACT/cACT and spirometry with significant positive correlation for FEV1, PEFR.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bateman ED, Hurd SS, Barnes PJ, Bousquet J, Drazen JM, Fitzgerald M, et al. Global strategy for asthma management and prevention: GINA executive summary. Eur Respir J. 2008;31:143–78.
Liu AH, Covar RA, Spahn JD, Sicherer SH. Childhood Asthma. In: Kliegman RM, Stanton BF, St Geme JW, Schor NF, editors. Nelson Textbook of Paediatrics. 20th ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier Inc; 2016. p. 1095–15.
Masoli M, Fabian D, Holt S, Beasley R. Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA) Program. The global burden of asthma: executive summary of the GINA dissemination committee report. Allergy. 2004;59:469–78.
Taylor DR, Bateman ED, Boulet LP, Boushey HA, Busse WW, Casale TB, et al. A new perspective on concepts of asthma severity and control. Eur Respir J. 2008;32:545–54.
Nathan RA, Sorkness CA, Kosinki M, Schatz M, Li JT, Marcus P,et al. Development of asthma control test: a survey for assessing asthma control. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2004;113:59–65.
Schatz M, Kosinki M, Yarlas AS, Hanlon J, Watson ME, Jhingran P. The minimally important difference of the asthma control test. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009;124:719–23.
Chalise SP, Bhatta NK, Singh RR, Prasad MS, Poudel P. Assessment of control of bronchial asthma in children using childhood asthma control test. Indian J Chest Dis Allied Sci. 2014;56:75–8.
Liu AH, Zeiger R, Sorkness C, Mahr R, Ostrom N, Burgess S, et al. Development and cross-sectional validation of the childhood asthma control test. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007;119:817–25.
Koolen BB, Pijnenburg MW, Brackel HJ, Landstra AM, Van den Berg NJ, Merkus PJ, et al. Comparing global initiative for asthma (GINA) criteria with the childhood asthma control test (C-ACT) and asthma control test (ACT). Eur Respir J. 2011;38:561–6.
Cloutier MM, Schatz M, Castro M, Clark N, Kelly HW, Smith RM, et al. Asthma outcomes: composite scores of asthma control. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012;129:24–33.
Schatz M, Sorkness CA, Li JT, Marcus P, Murray JJ, Nathan RA, et al. Asthma control test: reliability, validity, and responsiveness in patients not previously followed by asthma specialists. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2006;117:549–56.
Ito Y, Adachi Y, Itazawa T, Okabe Y, Adachi YS, Higuchi O, et al. Association between the results of the childhood asthma control test and objective parameters in asthmatic children. J Asthma. 2011;48:1076–80.
Melosini L, Dente FL, Bacci E, Bartoli ML, Cianchetti S, Costa F, et al. Asthma control test (ACT): comparison with clinical, functional, and biological markers of asthma control. J Asthma. 2012;49:317–23.
Shirai T, Furuhashi K, Suda T, Chida K. Relationship of the asthma control test with pulmonary function and exhaled nitric oxide. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2008;101:608–13.
Lee MS, Kao JK, Lee CH, Tsao LY, Chiu HY, Tseng YC, et al. Correlations between pulmonary function and childhood asthma control test results in 5-11-year-old children with asthma. Pediatr Neonatol. 2014;55:218–24.
Yoos HL, Kitzman H, McMullen A, Henderson C, Sidora K. Symptom monitoring in childhood asthma: a randomized clinical trial comparing peak expiratory flow rate with symptom monitoring. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2002;88:283–91.
Yuan H, Liu X, Li L, Wang G, Liu C, Zeng Y, Mao R, Du C, Chen Z. Clinical and pulmonary function changes in cough variant asthma with small airway disease. Allergy, Asthma & Clinical Immunology. 2019;15:1–10.
Mitra AD, Ogston S, Crighton A, Mukhopadhyay S. Lung function and asthma symptoms in children: relationships and response to treatment. Acta Paediatr. 2002;91:789–92.
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
GNC conceived the idea and design of the study; JM collected the data and prepared the draft; GNC and NK critically reviewed the draft. GNC will act as the guarantor for this paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
The study was approved by the Institutional Ethics Committee and performed in line with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki (IRB-MCH/22/2017).
Consent to Participate
Informed consent was obtained from the parents of the children.
Conflict of Interest
None.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
M, J., N.C, G. & K, N. Comparison of Asthma Control among Children 5–18 Years of Age by Asthma Control Test Questionnaire of Global Initiative for Asthma 2017 (GINA-2017) Against Spirometry. Indian J Pediatr 90, 770–775 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12098-022-04162-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12098-022-04162-8