Abstract
Objective
To determine the prevalence and spectrum of Connexin 26 (GJB2) mutations in pre-lingual non-syndromic hearing loss (NSHL) patients in authors’ centre and to review the data of Indian patients from the literature.
Methods
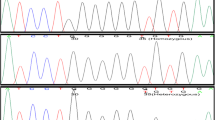
Sanger sequencing of entire coding region contained in single exon (Exon 2) of GJB2 gene in 15 patients of NSHL.
Results
GJB2 mutations were found in 40% (6/15) of NSHL patients, out of which mono-allelic were 33.3% (2/6). Bi-allelic GJB2 mutations were identified in 4 of 6 patients. Most common GJB2 mutation identified was c.71G > A(p.W24X), comprising 30% of the total GJB2 mutant alleles. Six studies involving 1119 patients with NSHL were reviewed and 4 of them have reported c.71G > A(p.W24X) as the commonest mutation while 2 studies found c.35delG as the commonest. GJB2 mutations accounted for 10.9%–36% cases of NSHL. Sixteen other mutations in GJB2 gene were reported in Indian patients out of which 6 mutations other than c.71G > A(p.W24X) viz., c.35delG, c.1A > G(p.M1V), c.127G > A(p.V43 M), c.204C > G(p.Y86X), c.231G > A(p.W77X) and c.439G > A(p.E147K) were identified in the present study.
Conclusions
Connexin 26 (GJB2) mutations are responsible for 19.4% of NSHL in Indian population. The c.71G > A(W24X) and c.35delG were the most prevalent GJB2 mutations accounting for 72.2% (234 of 324 total mutated alleles from 7 studies) and 15.4% (50 of 324 total mutated alleles from 7 studies) respectively. Thus, screening of these two common mutations in GJB2 gene by polymerase chain reaction and restriction fragment length polymorphism (PCR-RFLP) would greatly help in providing easy genetic diagnosis and help in genetic counseling of the families with NSHL.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kemperman MH, Hoefsloot LH, Cremers CW. Hearing loss and connexin 26. J R Soc Med. 2002;95:171–7.
Joseph AY, Rasool TJ. High frequency of connexin 26 (GJB2) mutations associated with nonsyndromic hearing loss in the population of Kerala, India. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2009;73:437–43.
Kelsell DP, Dunlop J, Stevens HP, et al. Connexin 26 mutations in hereditary non-syndromic sensorineural deafness. Nature. 1997;387:80–3.
Denoyelle F, Weil D, Maw MA, Wilcox SA, Lench NJ, Allen-Powell DR. Prelingual deafness: high prevalence of a 30delG mutation in the connexin 26 gene. Hum Mol Genet. 1997;6:2173–7.
Estivill X, Fortina P, Surrey S, et al. Connexin-26 mutations in sporadic and inherited sensorineural deafness. Lancet. 1998;351:394–8.
Kelley PM, Harris DJ, Comer BC, et al. Novel mutations in the connexin 26 gene (GJB2) that cause autosomal recessive (DFNB1) hearing loss. Am J Hum Genet. 1998;62:792–9.
Carrasquillo MM, Zlotogora J, Barges S, Chakravarti A. Two different connexin 26 mutations in an inbred kindred segregating non-syndromic recessive deafness: implications for genetic studies in isolated populations. Hum Mol Genet. 1997;6:2163–72.
Morell RJ, Kim HJ, Hood LJ, et al. Mutations in the connexin 26 gene (GJB2) among Ashkenazi Jews with nonsyndromic recessive deafness. New Engl J Med. 1998;339:1500–5.
Maheshwari M, Vijaya R, Ghosh M, Shastri S, Kabra M, Menon PSN. Screening of families with autosomal recessive non-syndromic hearing impairment (ARNSHL) for mutations in GJB2 gene: Indian scenario. Am J Med Genet. 2003;120A:180–4.
RamShankar M, Girirajan S, Dagan O, et al. Contribution of connexin26 (GJB2) mutations and founder effect to non-syndromic hearing loss in India. J Med Genet. 2003;40:68–74.
Ramchander PV, Nandur VU, Dwarakanath K, Ishnupriya SV, Padma T. Prevalence of Cx26 (GJB2) gene mutations causing recessive nonsyndromic hearing impairment in India. Int J Hum Genet. 2005;5:241–6.
Padma G, Ramchander PV, Nandur UV, Padma T. Indian academy of sciences research article GJB2 and GJB6 gene mutations found in Indian probands with congenital hearing impairment. J Genet. 2009;88:267–72.
Del Castillo I, Moreno-Pelayo MA, Del Castillo FJ, et al. Prevalence and evolutionary origins of the del(GJB6-D13S1830) mutation in the DFNB1 locus in hearing-impaired subjects: a multicenter study. Am J Hum Genet. 2003;73:1452–8.
Pshennikova VG, Barashkov NA, Solovyev AV, et al. Analysis of GJB6 (Сx30) and GJB3 (Сx31) genes in deaf patients with monoallelic mutations in GJB2 (Сx26) gene in the Sakha Republic (Yakutia). Russ J Genet. 2017;53:688–97.
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to all the participants for their kind contribution to this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SM: Conceptualisation, clinical evaluation of patients, data curation, investigation, formal analysis, methodology, validation, writing- original draft; HP and PS: Data curation, conducting laboratory work, formal analysis; KM: Conceptualisation, clinical evaluation of patients, data curation, investigation, methodology, validation, supervision, writing- review and editing; SRP: Conceptualisation, clinical evaluation of patients, funding acquisition, project administration, supervision, writing- review and editing. SRP will act as guarantor for this paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
The study has been approved by the Institute Ethics Committee. All procedures performed in this study involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional committee.
Conflict of Interest
Shubha R Phadke has received a grant from the Indian Council of Medical Research, Government of India, New Delhi, India (Grant number 63/8/2010-BMS). The other authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Source of Funding
This study was funded by Indian Council of Medical Research, Government of India, New Delhi, India (Grant number 63/8/2010-BMS).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mishra, S., Pandey, H., Srivastava, P. et al. Connexin 26 (GJB2) Mutations Associated with Non-Syndromic Hearing Loss (NSHL). Indian J Pediatr 85, 1061–1066 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12098-018-2654-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12098-018-2654-8