Abstract
Objective
To assess the efficacy of temporal artery thermometer in febrile and hypothermic neonates in comparison to axillary thermometer.
Methods
It was a cross sectional observational study. Study participants included 210 neonates admitted in neonatal intensive care unit of a tertiary care teaching hospital, divided into three groups of 70 each, namely normothermic, febrile and hypothermic. Temperatures were measured using temporal artery, axillary and rectal thermometers in each patient.
Results
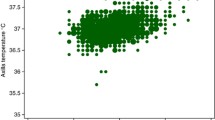
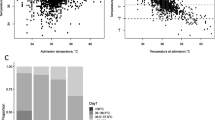
Mean rectal temperature was found to be comparable to mean temporal artery temperature in normothermic babies. Temporal artery thermometer had a better sensitivity to diagnose fever, than hypothermia. Also, temporal artery temperature showed a good correlation with rectal temperature in normothermic and febrile group and not in hypothermic neonates.
Conclusions
Temporal artery thermometer can accurately detect temperature in febrile and normothermic fullterm neonates but not in hypothermic neonates. Further studies are required before advocating temporal artery thermometry as a replacement of rectal thermometry among this group of population.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Duran R, Vatansever U, Acunaş B, Süt N. Comparison of temporal artery, mid-forehead skin and axillary temperature recordings in preterm infants <1500 g of birth weight. J Paediatr Child Health. 2009;45:444–7.
Kai J. Parents’ perception of taking babies’ rectal temperature. BMJ. 1993;307:660–2.
Haddad L, Smith S, Phillips KD, Heidel RE. Comparison of temporal artery and axillary temperatures in healthy newborns. J Obstet Gynecol Neonatal Nurs. 2012;41:383–8.
Lee G, Flannery-Bergey D, Randall-Rollins K, et al. Accuracy of temporal artery thermometry in neonatal intensive care infants. Adv Neonatal Care. 2011;11:62–70.
Batra P, Goyal S. Comparison of rectal, axillary, tympanic, and temporal artery thermometry in the pediatric emergency room. Pediatr Emerg Care. 2013;29:63–6.
Greenes DS, Fleisher GR. Accuracy of a noninvasive temporal artery thermometer for use in infants. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2001;155:376–81.
Callanan D. Detecting fever in young infants: reliability of perceived, pacifier, and temporal artery temperatures in infants younger than 3 months of age. Pediatr Emerg Care. 2003;19:240–3.
Siberry GK, Diener-West M, Schappell E, Karron RA. Comparison of temple temperatures with rectal temperatures in children under two years of age. Clin Pediatr (Phila). 2002;41:405–14.
Omron Thermometers, Omron Healthcare. Australia. Available at: http://omronhealthcare.com.au/pdf/mc-343_omron-thermometer-instructions.pdf. Accessed on 18 Oct 2016.
Exergen Temporal Artery Thermometers, Exergen Corporation. Massachusetts. Available at: http://www.exergen.com/medical/PDFs/tat2000instrev7-rev-ecl.pdf. Accessed on 18 Oct 2016.
Fever. Medline Plus Medical Encyclopaedia. US National library of medicine. Available at: http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/. Accessed on 9 Sept 2016.
Hoffman RJ, Etwaru K, Dreisinger N, Khokhar A, Husk G. Comparison of temporal artery thermometry and rectal thermometry in febrile pediatric emergency department patients. Pediatr Emerg Care. 2013;29:301–4.
Odinaka KK, Edelu BO, Nwolisa CE, Amamilo IB, Okolo SN. Temporal artery thermometry in children younger than 5 years: a comparison with rectal thermometry. Pediatr Emerg Care. 2014;30:867–70.
Al-Mukhaizeem F, Allen U, Komar L, et al. Comparison of temporal artery, rectal and esophageal core temperatures in children: results of a pilot study. Paediatr Child Health. 2004;9:461–5.
Romano MJ, Fortenberry JD, Autrey E, et al. Infrared tympanic thermometry in the pediatric intensive care unit. Crit Care Med. 1993;21:1181–5.
Schmitz T, Bair N, Falk M, Levine C. A comparison of five methods of temperature measurement in febrile intensive care patients. Am J Crit Care. 1995;4:286–92.
Acknowledgments
Authors would like to acknowledge the contributions of Mr. Rajiv Kumar, Department of Biostatistics, University College of Medical Sciences, for helping them in statistical analysis.
Contributions
PB, and EG conceptualized the study. PB, EG and PD designed the protocol. EG and RK collected data. PB, EG, and RK analyzed and interpreted data, searched literature and drafted the manuscript. PB and PD critically analyzed the manuscript. PB will act as guarantor for the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
None.
Source of Funding
None.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Goswami, E., Batra, P., Khurana, R. et al. Comparison of Temporal Artery Thermometry with Axillary and Rectal Thermometry in Full Term Neonates. Indian J Pediatr 84, 195–199 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12098-016-2259-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12098-016-2259-z