Abstract
Objective
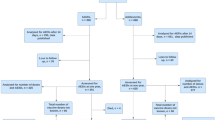
To determine, whether or not intramuscular injection of diphtheria, pertussis and tetanus (DwPT) vaccine should be given first and subcutaneous injection of measles, mumps and rubella (MMR) thereafter or vice versa and can this cause less pain of DwPT vaccine injection.
Methods
In a randomized parallel group clinical trial, seventy 18-mo-old healthy children who were referred for routine vaccination to Akbari Health Care Center, Yazd, Iran from September 2014 through March 2015 were randomly allocated to two groups to receive DwPT and then MMR vaccines or MMR first, and then DwPT. Primary outcomes included pain score during DwPT injection, pain score during MMR injection, overall pain score of vaccination and obtaining a pain score of less than three during DwPT injection. Pain scores were assessed based on Modified Behavioral Pain Scale. Secondary outcome was crying duration during DwPT injection.
Results
Thirty seven girls and 33 boys were evaluated in two groups. Pain scores of DwPT and MMR injections, the frequency of pain score obtained to be less than three during DwPT injection and the crying duration were not different in both groups. But, overall pain score of vaccination was lower when subcutaneous injection of MMR vaccine was given before intramuscular injection of DwPT vaccine. (14.23 ± 1.35 vs. 15.61 ± 2.65; P = 0.04).
Conclusions
Overall pain score of vaccination in multiple vaccine injection at the same visit might be reduced if subcutaneous vaccine is injected before intramuscular one.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schechter NL, Zempsky WT, Cohen LL, McGrath PJ, McMurtry CM, Bright NS. Pain reduction during pediatric immunizations: evidence-based review and recommendations. Pediatrics. 2007;119:e1184–98.
Jacobson RM, Swan A, Adegbenro A, Ludington SL, Wollan PC, Poland GA; Vaccine Research Group. Making vaccines more acceptable— methods to prevent and minimize pain and other common adverse events associated with vaccines. Vaccine. 2001;19:2418–27.
Taddio A, Appleton M, Bortolussi R, et al. Reducing the pain of childhood vaccination: an evidence-based clinical practice guideline (summary). CMAJ. 2010;182:1989–95.
Ozdemir FK, Tüfekci FG. The effect of using musical mobiles on reducing pain in infants during vaccination. J Res Med Sci. 2012;17:662–7.
Young KD. Pediatric procedural pain. Ann Emerg Med. 2005;45:160–71.
Ipp M, Taddio A, Sam J, Gladbach M, Parkin PC. Vaccine-related pain: randomised controlled trial of two injection techniques. Arch Dis Child. 2007;92:1105–8.
Taddio A, Nulman I, Koren BS, Stevens B, Koren G. A revised measure of acute pain in infants. J Pain Symptom Manag. 1995;10:456–63.
Ipp M, Parkin PC, Lear N, Goldbach M, Taddio A. Order of vaccine injection and infant pain response. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2009;163:469–72.
Taddio A, Ilersich AL, Ipp M, Kikuta A, Shah V; HELPinKIDS Team Physical interventions and injection techniques for reducing injection pain during routine childhood immunizations: systematic review of randomized controlled trials and quasi-randomized controlled trials. Clin Ther. 2009;31:S48–76.
Sánchez-Molero Martín Mdel P, Del Cerro Gutiérrez AM, Galán Delgado H, Muñoz Camargo JC. Infant pain response according to vaccine administration. [Article in Spanish] Rev Enferm. 2014;37:50–7.
Ravikiran SR, Kumar PM, Meundi AD. Pain response in newborns to the order of injecting BCG and hepatitis-B vaccines: a randomized trial. Indian J Pediatr. 2011;78:693–7.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the staff of Akbari Health Care Center, Yazd, Iran.
Contributions
All the authors contributed in this research and article preparation. RF will act as guarantor for the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
None.
Source of Funding
This study was funded by a grant from the Deputy for Research of Shahid Sadoughi University of Medical Sciences, Yazd, Iran. The research was also a thesis presented for obtaining the specialty of Pediatrics degree by Hossein Gholami MD.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fallah, R., Gholami, H., Ferdosian, F. et al. Evaluation of Vaccines Injection Order on Pain Score of Intramuscular Injection of Diphtheria, Whole Cell Pertussis and Tetanus Vaccine. Indian J Pediatr 83, 1405–1409 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12098-016-2186-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12098-016-2186-z