Abstract
Objective
To find the value of urine neutrophil gelatinase associated lipocalin (NGAL) in differentiating steroid response in children with idiopathic nephrotic syndrome (INS).
Methods
A total of 52 children with INS (n = 27, steroid resistant; n = 25, steroid responsive) aged 1–16 y, along with 18 healthy control children were enrolled in this study. Urine NGAL as well as urine protein, and serum creatinine were analyzed during active phase of INS.
Results
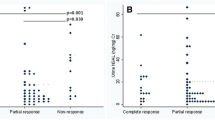
Serum creatinine (P 0.032), and urine NGAL/Cr (P 0.001) were significantly higher in steroid resistant than steroid sensitive patients. The optimal cutoff value for urine NGAL/Cr with the highest sensitivity and specificity was 0.46 ng/mg and cut off value of 0.01 and 1.15 ng/mg had maximum sensitivity and specificity, respectively.
Conclusions
Urine NGAL/Cr could be considered as a marker of steroid resistance in children with idiopathic nephrotic syndrome.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nickavar A, Lahouti Harahdashti A. Is steroid response changing in children with idiopathic nephrotic syndrome. Iran J Kidney Dis. 2014;8:389–93.
Wasilewska A, Zoch-Zwierz W, Taranta-Janusz K, Michaluk-Skutnik J. Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin: a new marker of cyclosporine nephrotoxicity? Pediatr Nephrol. 2010;25:889–97.
Noto A, Cibecchini F, Fanos V, Mussap M. NGAL and metabolomics: the single biomarker to reveal the metabolome alterations in kidney injury. Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:612032.
Wasilewska A, Taranta-Janusz K, Dębek W, Zoch-Zwierz W, Kuroczycka-Saniutycz E. KIM-1 and NGAL: new markers of obstructive nephropathy. Pediatr Nephrol. 2011;26:579–86.
Hirsch R, Dent C, Pfriem H, Allen J, Beekman RH 3rd, Ma Q, et al. NGAL is an early predictive biomarker of contrast-induced nephropathy in children. Pediatr Nephrol. 2007;22:2089–95.
Wheeler DS, Devarajan P, Ma Q, et al. Serum neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) as a marker of acute kidney injury in critically ill children with septic shock. Crit Care Med. 2008;36:1297–303.
Bolignano D, Lacquaniti A, Coppolino G, et al. Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) and progression of chronic kidney disease. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2009;4:337–44.
Bolignano D, Coppolino G, Aloisi C, Romeo A, Nicocia G, Buemi M. Effect of a single intravenous immunoglobulin infusion on neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin levels in proteinuric patients with normal renal function. J Investig Med. 2008;56:997–1003.
Nickolas TL, Forster CS, Sise ME, et al. NGAL (Lcn2) monomer is associated with tubulointerstitial damage in chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2012;82:718–22.
Kim JS, Bellew CA, Silverstein DM, Aviles DH, Boineau FG, Vehaskari VM. High incidence of initial and late steroid resistance in childhood nephrotic syndrome. Kidney Int. 2005;68:1275–81.
Bennett MR, Piyaphanee N, Czech K, Mitsnefes M, Devarajan P. NGAL distinguishes steroid sensitivity in idiopathic nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol. 2012;27:807–12.
Xia H, He QN, Li XY, Shuai LJ, Chen HX, Yi ZW. Expression of urinary neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin and its clinical significance in children with idiopathic nephrotic syndrome. Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2013;15:541–5.
Nishida M, Kawakatsu H, Okumura Y, Hamaoka K. Serum and urinary neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin levels in children with chronic renal diseases. Pediatr Int. 2010;52:563–8.
Korzeniecka-Kozerska A, Wasilewska A, Tenderenda E, Sulik A, Cybulski K. Urinary MMP-9/NGAL ratio as a potential marker of FSGS in nephrotic children. Dis Markers. 2013;34:357–62.
Wen Q, Huang LT, Luo N, Wang YT, Li XY, Mao HP. Proteomic profiling identifies haptoglobin as a potential serum biomarker for steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome. Am J Nephrol. 2012;36:105–13.
Bazzi C, Rizza V, Casellato D, et al. Urinary IgG and α2-macroglobulin are powerful predictors of outcome and responsiveness to steroids and cyclophosphamide in idiopathic focal segmental glomerulosclerosis with nephrotic syndrome. Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:941831.
Youssef DM, El-Shal AA. Urine neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin and kidney injury in children with focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Iran J Kidney Dis. 2012;6:355–60.
Conflict of Interest
None.
Source of Funding
This study was supported by “Children’s and Neonatal Health Center of Gorgan Medical University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nickavar, A., Safaeian, B., Sadeghi-Bojd, S. et al. Urine Neutrophil Gelatinase Associated Lipocalin to Creatinine Ratio: A Novel Index for Steroid Response in Idiopathic Nephrotic Syndrome. Indian J Pediatr 83, 18–21 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12098-015-1809-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12098-015-1809-0