Abstract
Objective
To determine the effect of glucocorticoids on lipid profile, endothelial function and arterial wall mechanics in children.
Methods
Thirty patients who had received glucocorticoids for 4 to 8 wk were compared with 30 age and sex matched healthy controls. Baseline evaluation included weight, height, body mass index (BMI), blood pressure (BP), lipid profile and Ultrasonographic evaluation of brachial artery for endothelial dependant as well as endothelial independent vasodilatation and evaluation of common carotid artery for intima media thickness (IMT) and arterial wall mechanics. All of these parameters were evaluated two more times- after 4 wk of steroid therapy and 2 wk after stopping the drug.
Results
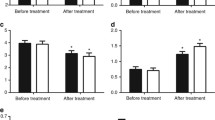
Patients were found to have significant increase in BMI; systolic and diastolic BP; total and LDL cholesterol and carotid IMT and also a decrease in cross sectional compliance (CSC) after 4 wk of steroid therapy (oral prednisolone). However, all these parameters returned towards baseline, 2 wk after stopping the drug. No endothelial dysfunction was observed in these patients.
Conclusions
Four to eight wk of glucocorticoids use in children leads to reversible changes in BMI, systolic and diastolic BP, total and LDL cholesterol, carotid IMT and CSC.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sader MA, Celermajer DS. Endothelial function, vascular reactivity and gender differences in the cardiovascular system. Cardiovasc Res. 2002;53:597–604.
Celermajer DS, Sorensen KE, Gooch VM, et al. Non-invasive detection of endothelial dysfunction in children and adults at risk of atherosclerosis. Lancet. 1992;340:1111–5.
Widlansky ME, Gokce N, Keaney Jr JF, Vita JA. The clinical implications of endothelial dysfunction. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2003;42:1149–60.
Krieger M, Stern DM. Series introduction: Multiligand receptors and human diseases. J Clin Invest. 2001;108:645–7.
Morel DW, DiCorleto PE, Chisolm GM. Endothelial and smooth muscle cells alter low density lipoprotein in vitro by free radical oxidation. Arteriosclerosis. 1984;4:357–64.
Anderson TJ, Uehata A, Gerhard MD, et al. Close relation of endothelial function in the human coronary and peripheral circulations. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1995;26:1235–41.
Gokce N, Keaney Jr JF, Hunter LM, et al. Predictive value of noninvasively determined endothelial dysfunction for long-term cardiovascular events in patients with peripheral vascular disease. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2003;41:1769–75.
Corrado E, Rizzo M, Coppola G, Muratori I, Carella M, Novo S. Endothelial dysfunction and carotid lesions are strong predictors of clinical events in patients with early stages of atherosclerosis; A 24-month follow–up study. Coron Artery Dis. 2008;19:139–44.
Suwaidi JA, Hamasaki S, Higano ST, Nishimura RA, Holmes DR Jr, Lerman A. Long-term follow-up of patients with mild coronary artery disease and endothelial dysfunction. Circulation. 2000;101:948–54.
Schächinger V, Britten MB, Zeiher AM. Prognostic impact of coronary vasodilator dysfunction on adverse long-term outcome of coronary heart disease. Circulation. 2000;101:1899–906.
Iglesias del Sol A, Bots ML, Grobbee DE, Hofman A, Witteman JC. Carotid intima-media thickness at different sites: Relation to incident myocardial infarction; The Rotterdam study. Eur Heart J. 2002;23:934–94.
Tounian P, Aggoun Y, Dubern B, et al. Presence of increased stiffness of the common carotid artery and endothelial dysfunction in severely obese children: A prospective study. Lancet. 2001;358:1400–4.
Aggoun Y, Bonnet D, Sidi D, et al. Arterial mechanical changes in children with familial hypercholesterolemia. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2000;20:2070–5.
Heiss G, Sharrett AR, Barnes R, Chambless LE, Szklo M, Alzola C. Carotid atherosclerosis measured by B-mode ultrasound in populations: Associations with cardiovascular risk factors in the ARIC study. Am J Epidemiol. 1991;134:250–6.
Pignoli P, Tremoli E, Poli A, Oreste P, Paoletti R. Intimal plus medial thickness of the arterial wall: A direct measurement with ultrasound imaging. Circulation. 1986;74:1399–406.
Leeson P, Thorne S, Donald A, Mullen M, Clarkson P, Deanfield J. Non-invasive measurement of endothelial function: Effect on brachial artery dilatation of graded endothelial dependent and independent stimuli. Heart. 1997;78:22–7.
Kumar V, Sachdev HPS, Khalil A. Noninvasive evaluation of endothelial function and arterial mechanics in overweight adolescents. Indian Pediatr. 2004;41:1105–14.
Friedewald WT, Levy RI, Fredrickson DS. Estimation of the concentration of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in plasma, without use of the preparative ultracentrifuge. Clin Chem. 1972;18:499–502.
Park MK. Pediatric Cardiology for Practitioners. India: Mosby Elsevier; 2009. pp. 595. Appendix C.
Thakore AH, Guo CY, Larson MG, et al. Association of multiple inflammatory markers with carotid intimal medial thickness and stenosis (from the Framingham Heart Study). Am J Cardiol. 2007;99:1598–602.
Maxwell SR, Moots RJ, Kendall MJ. Corticosteroids: Do they damage the cardiovascular system? Postgrad Med J. 1994;70:863–70.
Ettinger WH, Klinefelter HF, Kwiterovitch PO. Effect of short-term, low-dose corticosteroids on plasma lipoprotein lipids. Atherosclerosis. 1987;63:167–72.
Zimmerman J, Fainaru M, Eisenberg S. The effects of prednisone therapy on plasma lipoproteins and apolipoproteins: A prospective study. Metabolism. 1984;33:521–6.
Choi HK, Seeger JD. Glucocorticoid use and serum lipid levels in US adults: The Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Arthritis Rheum. 2005;53:528–35.
Lau KK, Tancredi DJ, Perez RV, Butani L. Unusual pattern of dyslipidemia in children receiving steroid minimization immunosuppression after renal transplantation. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2010;5:1506–12.
Boers M, Nurmohamed MT, Doelman CJ, et al. Influence of glucocorticoids and disease activity on total and high density lipoprotein cholesterol in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2003;62:842–5.
Faggiano A, Pivonello R, Spiezia S, et al. Cardiovascular risk factors and common carotid artery calibre and stiffness in patients with Cushing’s disease during active disease and 1 year after disease remission. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2003;88:2527–33.
Chan MK, Varghese Z, Moorhead JF. Lipid abnormalities in uremia, dialysis, and transplantation. Kidney Int. 1981;19:625–37.
Whitworth JA, Williamson PM, Mangos G, Kelly JJ. Cardiovascular consequences of cortisol excess. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2005;1:291–9.
Whitworth JA, Mangos GJ, Kelly JJ. Cushing, cortisol, and cardiovascular disease. Hypertension. 2000;36:912–6.
Contributions
TPY, RA, NS, AC: Conceptualized the study and reviewed literature; TPY, AY, NS, AC, AJ and RA: Collected the data and drafted the manuscript; TPY, AY and AJ: Critically evaluated the paper and finalized the draft.
Conflict of Interest
None.
Role of Funding Source
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Contributions
TPY, RA, NS, AC: Conceptualized the study and reviewed literature; TPY, AY, NS, AC, AJ and RA: Collected the data and drafted the manuscript; TPY, AY and AJ: Critically evaluated the paper and finalized the draft.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yadav, A., Jahan, A., Yadav, T.P. et al. Effect of Glucocorticoids on Serum Lipid Profile and Endothelial Function and Arterial Wall Mechanics. Indian J Pediatr 80, 1007–1014 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12098-013-1035-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12098-013-1035-6