Abstract
Objective
To find usefulness of a package of interventions to improve preschool education through Anganwadi centers on psychosocial development of children.
Methods
A case-control study was undertaken to evaluate an intervention. Eight Anganwadi centers were selected using simple random sampling out of sixteen Anganwadi centers in Talegaon PHC area where intervention was done. Ten children in age group of 4–6 years were selected randomly from each of the eight Anganwadi center in intervention arm. For each child from intervention arm, one agematched child was selected from the matched Anganwadi center. For each subject, Intelligence Quotient and Development Quotient were assessed.
Results
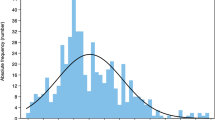
Mean Development Quotient (DQ) and Intelligence Quotient (IQ) values were higher among children in intervention Anganwadi centers (16.2 points for DQ and 10.2 points for IQ). This difference was found statistically significant (p = <0.01). Mean DQ among boys was found 10.1 points higher than that among the girls in control arm, this was statistically significant. According to multivariate linear regression model, the determinants of DQ were: intervention; age of the child; education of mother; sex of child; and PEM grade and the determinants for IQ were: intervention; age of the child; and income.
Conclusion
This study shows that intervention to improve the Early Childhood Education and Development component through Anganwadi centers results in improvement in Developmental and Intelligence Quotient of children.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nair MKC. Pre-school Education (President’s page). Indian Pediatr 2004; 41: 425–427.
Ministry of Health and Family Welfare. Integrated Child Development Services (ICDS). New Delhi: NIPCCD, 1995.
Nair MKC, Radhakrishnan R. Early childhood development in deprived urban settlements: Environmental health project-special article series. Indian Pediatr 2004; 41: 227–237.
Aggarwal A, Kumar R. Long term effects of ICDS services on behaviour and academic achievements of children. Indian J Community Med 2000; 25: 124–128.
Ray SK, Mishra R, Biswas R, Kumar S, Halder A, Chatterjee T. Nutritional status of pavement dweller children of Calcutta City. Indian J Public Health 1999; 43: 49–54.
Morgan CF, King RA, Weisz JR, Schopler J. Introduction to Psychology, 7ed. New York; McGraw Hill, 2004.
Ghai OP, Gupta P, Paul VK. Essential Paediatrics, 6 ed. CBS Publishers New Delhi; Dr.Ghai, 2004.
Raj JB. Know your child’s intelligence and how to improve it. 3ed. Mysore; Swayamsiddha Prakashana, 1998.
EPI INFO 6 [program]. 6.04 version: Centers for Disease Control, Atlanta and World Health Organization, Geneva, 2001.
SPSS for Windows, Rel. 11.0.1. 2001. Chicago: SPSS Inc.
Barnett WS. Long-Term effects of early childhood programs on cognitive and school outcomes. The Future of Children 1995; 5: 25–50.
Powell C, Grantham-McGregor SM. Home visiting of varying frequency and child development. Pediatrics 1989; 84: 157–164.
Hill Z, Kirkwood B, Edmond K. Family and community practices that promote child survival, growth and development. Geneva: WHO, 2004.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ade, A., Gupta, S.S., Maliye, C. et al. Effect of improvement of pre-school education through Anganwadi center on intelligence and development quotient of children. Indian J Pediatr 77, 541–546 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12098-010-0056-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12098-010-0056-7