Abstract
Objective
To determine the relationship of various maternal and neonatal factors with serum vitamin A concentration in matched mother-newborn pairs.
Methods
This is a cross-sectional study on 100 neonate-mother pairs at a tertiary care center at Raipur, C.G., India. Gestational age, birth weight and sex of the neonates as well as maternal parity, hemoglobin (Hb) levels, access to antenatal care (ANC) and presence of toxemia of pregnancy were recorded. Cord and maternal serum vitamin A levels were assayed.
Results
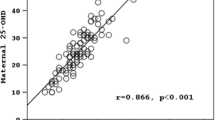
Maternal serum vitamin A levels were not significantly affected by maternal age, parity, Hb level and presence of toxemia. Higher trend of maternal vitamin A concentrations (P=NS) and statistically higher values of cord serum vitamin A levels (P<0.05) were seen in mothers who had received ANC. Significantly higher cord vitamin A levels were seen with increasing weight of the placenta, birth weight of the newborn as well as its gestational age and maturity. Weak but significant positive correlation was present between maternal and cord serum vitamin A levels.
Conclusion
Data from our study show that prematurity and intrauterine growth retardation are associated with low neonatal vitamin A levels. Several factors like lack of ANC, lower maternal Hb levels and reduced placental weight further affect vitamin A status of the newborn rendering them highly susceptible to vitamin A deficiency. We therefore, suggest further studies on vitamin A supplementation in pregnant women and preterm neonates.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gupta M, Jora R, Bhatia R, Pareek A. Keratomalacia in a neonate secondary to maternal vitamin A deficiency. Indian J Pediatr 2005; 72: 881–882.
West KP, Jr, Howard GR, Sommer A. Vitamin A and infection: public health implications. Annu Rev Nutr 1989; 9: 63–86.
Fawzi WW, Chalmers TC, Herrera MG, Mosteller F. Vitamin A supplementation and child mortality. A meta-analysis. JAMA 1993; 269: 898–903.
Hussey GD, Klein M. A randomized, controlled trial of vitamin A in children with severe measles. N Engl J Med 1990; 323: 160–164.
Zile MH. Vitamin A and embryonic development: an overview. J Nutr 1998; 128: 455S–458S.
Laga EM, Driscoll SG, Munro HN. Comparison of placentas from two socioeconomic groups. II. Biochemical characteristics. Pediatrics 1972; 50: 33–39.
Laga EM, Driscoll SG, Munro HN. Comparison of placentas from two socioeconomic groups. I. Morphometry. Pediatrics 1972; 50: 24–32.
Ghebremeskel K, Burns L, Burden TJ, Harbige L, Costeloe K, Powell JJ, Crawford M. Vitamin A and related essential nutrients in cord blood: relationships with anthropometric measurements at birth. Early Hum Dev 1994; 39: 177–188.
Navarro J, Causse MB, Desquilbet N, Herve F, Lallemand D. The vitamin status of low birth weight infants and their mothers. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 1984; 3: 744–748.
Saunders C, Ramalho RA, de Lima AP, Gomes MM, Campos LF, dos Santos Silva BA, Goncalves Soares A, do Carmo Leal M. Association between gestational night blindness and serum retinol in mother/newborn pairs in the city of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Nutrition 2005; 21: 456–461.
Tiews J, Zentz C. [Microdetermination of vitamin A in blood serum and liver biopsies with FeC1-3 in acetyl chloride]. Int Z Vitaminforsch 1967; 37: 307–314.
Vobecky JS, Vobecky J, Shapcott D, Demers PP, Cloutier D, Blanchard R, Fisch C. Biochemical indices of nutritional status in maternal, cord, and early neonatal blood. Am J Clin Nutr 1982; 36: 630–642.
Ibrahim K, Hassan TJ, Jafarey SN. Plasma vitamin A and carotene in maternal and cord blood. Asia Oceania J Obstet Gynaecol 1991; 17: 159–164.
Shah RS, Rajalakshmi R. Vitamin A status of the newborn in relation to gestational age, body weight, and maternal nutritional status. Am J Clin Nutr 1984; 40: 794–800.
Uotila J, Tuimala R, Pyykko K, Ahotupa M. Pregnancyinduced hypertension is associated with changes in maternal and umbilical blood antioxidants. Gynecol Obstet Invest 1993; 36: 153–157.
Gazala E, Sarov B, Hershkovitz E, Edvardson S, Sklan D, Katz M, Friger M, Gorodischer R. Retinol concentration in maternal and cord serum: its relation to birth weight in healthy mother-infant pairs. Early Hum Dev 2003; 71: 19–28.
Shah RS, Rajalakshmi R, Bhatt RV, Hazra MN, Patel BC, Swamy NB, Patel TV. Liver stores of vitamin A in human fetuses in relation to gestational age, fetal size and maternal nutritional status. Br J Nutr 1987; 58: 181–189.
Gebre-Medhin M, Vahlquist A. Vitamin A nutrition in the human foetus. A comparison of Sweden and Ethiopia. Acta Paediatr Scand 1984; 73: 333–340.
Ismadi SD, Olson JA. Vitamin A transport in human fetal blood. Am J Clin Nutr 1975; 28: 967–972.
Panth M, John A, Sivakumar B. Evaluation of a colorimetric method for vitamin A estimation. Indian J Exp Biol 1989; 27: 1044–1047.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Agarwal, K., Dabke, A.T., Phuljhele, N.L. et al. Factors affecting serum vitamin a levels in matched maternal-cord pairs. Indian J Pediatr 75, 443–446 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12098-008-0070-1
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12098-008-0070-1