Abstract
Introduction
ABL2 contributes to the oncogenic potential of cancers, pointing to its inhibition as a possible strategy against malignant diseases. Bioinformatics prediction of upstream effector miR-30a-5p for ABL2 allowed us to hypothesize and then validate mechanistic actions of miR-30a-5p in lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD).
Materials and methods
The ABL2 expression in LUAD was analyzed in the TCGA data, clinical samples, and cell lines. The shRNA-mediated silencing of ABL2 was introduced to illustrate its effect on malignant phenotypes of LUAD cells. The binding affinity between ABL2 and miR-30a-5p was verified by luciferase activity and RNA pull-down assay. Ectopic expression, knockdown methods, and PI3K inhibitor LY294002 were used to investigate their effects on in vitro biological characteristics and in vivo tumor growth of LUAD cells. Using nude mouse lung adenocarcinoma in situ and brain metastasis models to validate the inhibitory effect of miR-30a-5p on LUAD by regulating the ABL2/PI3K/AKT signaling axis.
Results
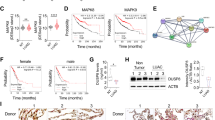
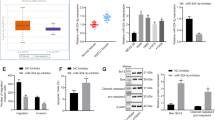
High expression of ABL2 and poor expression of miR-30a-5p were noticed in LUAD tissues and cell lines. Importantly, miR-30a-5p was demonstrated to target and downregulate ABL2, subsequently inactivating the PI3K/AKT pathway. miR-30a-5p inhibited the malignant phenotypes of LUAD cells by inhibiting ABL2 expression and inactivating the PI3K/AKT pathway. For in vivo experiments, miR-30a-5p was substantiated to thwart tumor tumorigenesis by regulating the ABL2/PI3K/AKT axis. In addition, miR-30a-5p suppresses the occurrence and development of in situ lung cancer and brain metastasis via the ABL2/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway.
Conclusion
This study underscores the inhibitory role of miR-30a-5p in LUAD through the ABL2/PI3K/AKT axis, which may be a viable target for LUAD treatment.










Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Hirsch FR, Scagliotti GV, Mulshine JL, Kwon R, Curran WJ Jr, Wu YL, et al. Lung cancer: current therapies and new targeted treatments. Lancet. 2017;389:299–311.
Thai AA, Solomon BJ, Sequist LV, Gainor JF, Heist RS. Lung cancer. Lancet. 2021;398:535–54.
Cancer Genome Atlas Research N. Comprehensive molecular profiling of lung adenocarcinoma. Nature. 2014;511:543–50.
Zengin T, Onal-Suzek T. Analysis of genomic and transcriptomic variations as prognostic signature for lung adenocarcinoma. BMC Bioinformatics. 2020;21:368.
Tammela T, Sanchez-Rivera FJ, Cetinbas NM, Wu K, Joshi NS, Helenius K, et al. A Wnt-producing niche drives proliferative potential and progression in lung adenocarcinoma. Nature. 2017;545:355–9.
Song J, Sun Y, Cao H, Liu Z, Xi L, Dong C, et al. A novel pyroptosis-related lncRNA signature for prognostic prediction in patients with lung adenocarcinoma. Bioengineered. 2021;12:5932–49.
Zhang L, Zhang Z, Yu Z. Identification of a novel glycolysis-related gene signature for predicting metastasis and survival in patients with lung adenocarcinoma. J Transl Med. 2019;17:423.
Kim N, Kim HK, Lee K, Hong Y, Cho JH, Choi JW, et al. Single-cell RNA sequencing demonstrates the molecular and cellular reprogramming of metastatic lung adenocarcinoma. Nat Commun. 2020;11:2285.
Chen J, Zhang K, Zhi Y, Wu Y, Chen B, Bai J, et al. Tumor-derived exosomal miR-19b-3p facilitates M2 macrophage polarization and exosomal LINC00273 secretion to promote lung adenocarcinoma metastasis via Hippo pathway. Clin Transl Med. 2021;11: e478.
Jurisic V, Obradovic J, Pavlovic S, Djordjevic N. Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Gene in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: The Importance of Promoter Polymorphism Investigation. Anal Cell Pathol (Amst). 2018;2018:6192187.
Costa DB. Kinase inhibitor-responsive genotypes in EGFR mutated lung adenocarcinomas: moving past common point mutations or indels into uncommon kinase domain duplications and rearrangements. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2016;5:331–7.
Jurisic V, Vukovic V, Obradovic J, Gulyaeva LF, Kushlinskii NE, Djordjevic N. EGFR Polymorphism and Survival of NSCLC Patients Treated with TKIs: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J Oncol. 2020;2020:1973241.
Obradovic J, Todosijevic J, Jurisic V. Side effects of tyrosine kinase inhibitors therapy in patients with non-small cell lung cancer and associations with EGFR polymorphisms: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Oncol Lett. 2023;25:62.
Ling B, Liao X, Tang Q, Ye G, Bin X, Wang J, et al. MicroRNA-106b-5p inhibits growth and progression of lung adenocarcinoma cells by downregulating IGSF10. Aging (Albany NY). 2021;13:18740–56.
Ishii H, Vodnala SK, Achyut BR, So JY, Hollander MC, Greten TF, et al. miR-130a and miR-145 reprogram Gr-1(+)CD11b(+) myeloid cells and inhibit tumor metastasis through improved host immunity. Nat Commun. 2018;9:2611.
Esquela-Kerscher A, Slack FJ. Oncomirs - microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6:259–69.
Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell. 2009;136:215–33.
Hu J, Sun T, Wang H, Chen Z, Wang S, Yuan L, et al. MiR-215 Is Induced Post-transcriptionally via HIF-Drosha Complex and Mediates Glioma-Initiating Cell Adaptation to Hypoxia by Targeting KDM1B. Cancer Cell. 2016;29:49–60.
Li H, Zhao S, Chen X, Feng G, Chen Z, Fan S. MiR-145 modulates the radiosensitivity of non-small cell lung cancer cells by suppression of TMOD3. Carcinogenesis. 2022;43:288–96.
Shi Q, Ju JG. Circ_0001998 Regulates the Proliferation, Invasion, and Apoptosis of Lung Adenocarcinoma via Sponging miR-145. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022;2022:6446150.
Lin R, Li GS, Gan XY, Peng JX, Feng Y, Wang LT, et al. The clinical significance and mechanism of microRNA-22–3p targeting TP53 in lung adenocarcinoma. Technol Health Care. 2023;
Mo D, Yang D, Xiao X, Sun R, Huang L, Xu J. MiRNA-145 suppresses lung adenocarcinoma cell invasion and migration by targeting N-cadherin. Biotechnol Lett. 2017;39:701–10.
Ma DJ, Zhou XY, Qin YZ, Tian ZH, Liu HS, Li SQ. MiR-22-3p Expression is down-regulated in lung adenocarcinoma. Acta Biochim Pol. 2021;68:667–72.
Deng F, Xu Z, Zhou J, Zhang R, Gong X. ANLN Regulated by miR-30a-5p Mediates Malignant Progression of Lung Adenocarcinoma. Comput Math Methods Med. 2021;2021:9549287.
Chen P, Gu YY, Ma FC, He RQ, Li ZY, Zhai GQ, et al. Expression levels and cotargets of miRNA1263p and miRNA1265p in lung adenocarcinoma tissues: Alphan exploration with RTqPCR, microarray and bioinformatic analyses. Oncol Rep. 2019;41:939–53.
Qin X, Wan Y, Wang S, Xue M. MicroRNA-125a-5p modulates human cervical carcinoma proliferation and migration by targeting ABL2. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2016;10:71–9.
Hoj JP, Mayro B, Pendergast AM. The ABL2 kinase regulates an HSF1-dependent transcriptional program required for lung adenocarcinoma brain metastasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020;117:33486–95.
Liu Y, Shao C, Zhu L, Jiang S, Li G, Zhang W, et al. High Expression of ABL2 Suppresses Apoptosis in Gastric Cancer. Dig Dis Sci. 2018;63:2294–300.
Zeng J, Yang X, Yang L, Li W, Zheng Y. Thymosin beta10 promotes tumor-associated macrophages M2 conversion and proliferation via the PI3K/Akt pathway in lung adenocarcinoma. Respir Res. 2020;21:328.
Liang J, Li H, Han J, Jiang J, Wang J, Li Y, et al. Mex3a interacts with LAMA2 to promote lung adenocarcinoma metastasis via PI3K/AKT pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11:614.
Wu X, Sui Z, Zhang H, Wang Y, Yu Z. Integrated Analysis of lncRNA-Mediated ceRNA Network in Lung Adenocarcinoma. Front Oncol. 2020;10: 554759.
Kun-Peng Z, Xiao-Long M, Chun-Lin Z. LncRNA FENDRR sensitizes doxorubicin-resistance of osteosarcoma cells through down-regulating ABCB1 and ABCC1. Oncotarget. 2017;8:71881–93.
Hoj JP, Mayro B, Pendergast AM. A TAZ-AXL-ABL2 Feed-Forward Signaling Axis Promotes Lung Adenocarcinoma Brain Metastasis. Cell Rep. 2019;29(3421–34): e8.
Miricescu D, Totan A, Stanescu S, II, Badoiu SC, Stefani C, Greabu M. PI3K/AKT/mTOR Signaling Pathway in Breast Cancer: From Molecular Landscape to Clinical Aspects. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;22:
Fattahi S, Amjadi-Moheb F, Tabaripour R, Ashrafi GH, Akhavan-Niaki H. PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling in gastric cancer: Epigenetics and beyond. Life Sci. 2020;262: 118513.
Zhang D, Jiang Q, Ge X, Shi Y, Ye T, Mi Y, et al. RHOV promotes lung adenocarcinoma cell growth and metastasis through JNK/c-Jun pathway. Int J Biol Sci. 2021;17:2622–32.
Zhang G, Xia M, Guo J, Huang Y, Huang J, Wei K, et al. microRNA-1296 Inhibits Glioma Cell Growth by Targeting ABL2. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2021;20:1533033821990009.
Roberts KG, Yang YL, Payne-Turner D, Lin W, Files JK, Dickerson K, et al. Oncogenic role and therapeutic targeting of ABL-class and JAK-STAT activating kinase alterations in Ph-like ALL. Blood Adv. 2017;1:1657–71.
Gu JJ, Rouse C, Xu X, Wang J, Onaitis MW, Pendergast AM. Inactivation of ABL kinases suppresses non-small cell lung cancer metastasis. JCI Insight. 2016;1: e89647.
Hu C, Wu J, Wang L, Liu X, Da B, Liu Y, et al. miR-133b inhibits cell proliferation, migration, and invasion of lung adenocarcinoma by targeting CDCA8. Pathol Res Pract. 2021;223: 153459.
Tao D, Zhang Z, Liu X, Zhang Z, Fu Y, Zhang P, et al. LncRNA HOTAIR promotes the invasion and metastasis of oral squamous cell carcinoma through metastasis-associated gene 2. Mol Carcinog. 2020;59:353–64.
Yang C, Huang T, Liang Y, Xue Y, Liang Y, Wei X, et al. CTHRC1 targeted by miR-30a-5p regulates cell adhesion, invasion and migration in lung adenocarcinoma. J Cardiothorac Surg. 2022;17:46.
Li Y, Zhao J, Zhang W, Wang A, Jiao M, Cai X, et al. LINC02535/miR-30a-5p/GALNT3 axis contributes to lung adenocarcinoma progression via the NF- kappa B signaling pathway. Cell Cycle. 2022;1–16.
Tao K, Liu J, Liang J, Xu X, Xu L, Mao W. Vascular endothelial cell-derived exosomal miR-30a-5p inhibits lung adenocarcinoma malignant progression by targeting CCNE2. Carcinogenesis. 2021;42:1056–67.
Chen X, Zhang W, Xu X. Cyanidin-3-glucoside suppresses the progression of lung adenocarcinoma by downregulating TP53I3 and inhibiting PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. World J Surg Oncol. 2021;19:232.
Lee CH, Hung PF, Liu KJ, Chung HL, Yang WC, Hsu KC, et al. LDOC1 Suppresses Microbe-Induced Production of IL-1beta in Human Normal and Cancerous Oral Cells through the PI3K/Akt/GSK-3beta Axis. Cancers (Basel). 2020;12:
Wang H, Wang L, Zhou X, Luo X, Liu K, Jiang E, et al. OSCC Exosomes Regulate miR-210-3p Targeting EFNA3 to Promote Oral Cancer Angiogenesis through the PI3K/AKT Pathway. Biomed Res Int. 2020;2020:2125656.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
This study was supported by Beijing Life Oasis Charity Service Center (HXKT20221019).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YM designed the study, collected the data and wrote the manuscript. JL checked the whole manuscript, improved the figures and provided funding support. All authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The present study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Affiliated Hospital of Nantong University in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. Written informed consent was obtained from all the participants. All experimental operations were approved by the Laboratory Animal Ethics Committee of Affiliated Hospital of Nantong University.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Miao, Y., Liu, J. Tumor-suppressive action of miR-30a-5p in lung adenocarcinoma correlates with ABL2 inhibition and PI3K/AKT pathway inactivation. Clin Transl Oncol 26, 398–413 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-023-03255-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-023-03255-w