Abstract
Background and objective
This study intended to evaluate the prognostic effects of programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) and tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) in survival and their associations with clinicopathological characteristics in patients with gastric cancer.
Methods
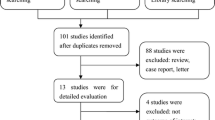
PubMed, Scopus, ProQuest, Web of Science, and Ovid databases were searched to obtain the relevant studies. Eleven studies with 2298 patients were included in this study.
Results
Like the level of TILs, there were no significant associations between PD-L1 expression and TNM stage, lymph node metastasis, vascular invasion, and tumor location (All p values ≥ 0.05). Furthermore, there was no significant association between PD-L1 expression with overall survival (OS) (HR = 0.76, 95% CI: 0.55 to 1.05, p value = 0.10) and disease-free survival (DFS) (HR = 0.62, 95% CI: 0.10 to 3.68, p value = 0.59). In the assessment of TILs presence and survival association, the analysis showed no association between TILs presence and overall survival (OS) (HR = 0.95, 95% CI: 0.62 to 1.45).
Conclusions
In conclusion, the study has revealed no prognostic effect of PD-L1 and TILs in gastric cancer patients.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All the data used in the current study are available from corresponding author under reasonable request.
References
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2019. Cancer J Clin. 2019;69(1):7–34.
Lauren P. The two histological main types of gastric carcinoma: diffuse and so-called intestinal-type carcinoma: an attempt at a histo-clinical classification. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1965;64(1):31–49.
Yakirevich E, Resnick MB. Pathology of gastric cancer and its precursor lesions. Gastroenterol Clin. 2013;42(2):261–84.
Fridman WH, Sautès-Fridman C, Galon J. The immune contexture in human tumours: impact on clinical outcome. Nat Rev Cancer. 2012;12(4):298–306.
Disis ML. Immune regulation of cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28(29):4531.
Galon J, Dieu-Nosjean M, Tartour E, Sautes-Fridman C, Fridman W. Immune infiltration in human tumors: a prognostic factor that should not be ignored. Oncogene. 2010;29(8):1093–102.
Mahmoud SM, Paish EC, Powe DG, Macmillan RD, Grainge MJ, Lee AH, et al. Tumor-infiltrating CD8+ lymphocytes predict clinical outcome in breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29(15):1949–55.
Piersma SJ, Jordanova ES, Van Poelgeest MI, Kwappenberg KM, Van Der Hulst JM, Drijfhout JW, et al. High number of intraepithelial CD8+ tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes is associated with the absence of lymph node metastases in patients with large early-stage cervical cancer. Can Res. 2007;67(1):354–61.
Doroshow DB, Bhalla S, Beasley MB, Sholl LM, Kerr KM, Gnjatic S, et al. PD-L1 as a biomarker of response to immune-checkpoint inhibitors. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2021;18(6):345–62.
Telli TA, Bregni G, Camera S, Deleporte A, Hendlisz A, Sclafani F. PD-1 and PD-L1 inhibitors in oesophago-gastric cancers. Cancer Lett. 2020;469:142–50.
Tran PN, Sarkissian S, Chao J, Klempner SJ. PD-1 and PD-L1 as emerging therapeutic targets in gastric cancer: current evidence. Gastrointest Cancer. 2017;7:1.
Koh J, Ock C-Y, Kim JW, Nam SK, Kwak Y, Yun S, et al. Clinicopathologic implications of immune classification by PD-L1 expression and CD8-positive tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in stage II and III gastric cancer patients. Oncotarget. 2017;8(16):26356.
Wang Y, Zhu C, Song W, Li J, Zhao G, Cao H. PD-L1 expression and CD8+ T cell infiltration predict a favorable prognosis in advanced gastric cancer. J Immunol Res. 2018;2018:4180517.
Liu X, Choi MG, Kim K, Kim K-M, Kim ST, Park SH, et al. High PD-L1 expression in gastric cancer (GC) patients and correlation with molecular features. Pathol Res Pract. 2020;216(4): 152881.
Yu P-C, Long D, Liao C-C, Zhang S. Association between density of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and prognoses of patients with gastric cancer. Medicine. 2018;97(27):e11387.
Zhang M, Dong Y, Liu H, Wang Y, Zhao S, Xuan Q, et al. The clinicopathological and prognostic significance of PD-L1 expression in gastric cancer: a meta-analysis of 10 studies with 1901 patients. Sci Rep. 2016;6(1):1–9.
Zhang L, Qiu M, Jin Y, Ji J, Li B, Wang X, et al. Programmed cell death ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression on gastric cancer and its relationship with clinicopathologic factors. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015;8(9):11084.
Zheng Z, Bu Z, Liu X, Zhang L, Li Z, Wu A, et al. Level of circulating PD-L1 expression in patients with advanced gastric cancer and its clinical implications. Chin J Cancer Res. 2014;26(1):104.
Zhang D, He W, Wu C, Tan Y, He Y, Xu B, et al. Scoring system for tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and its prognostic value for gastric cancer. Front Immunol. 2019;10:71.
Lee H, Chae S, Lee Y, Kim M, Lee H, Lee B, et al. Prognostic implications of type and density of tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes in gastric cancer. Br J Cancer. 2008;99(10):1704–11.
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG. RESEARCH METHODS & REPORTING-Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement-David Moher and colleagues introduce PRISMA, an update of the QUOROM guidelines for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses. BMJ (CR)-print. 2009;338(7716):332.
Hayden JA, Côté P, Bombardier C. Evaluation of the quality of prognosis studies in systematic reviews. Ann Intern Med. 2006;144(6):427–37.
Hardy RJ, Thompson SG. A likelihood approach to meta-analysis with random effects. Stat Med. 1996;15(6):619–29.
Higgins JP, Thompson SG. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat Med. 2002;21(11):1539–58.
Egger M, Smith GD, Schneider M, Minder C. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ. 1997;315(7109):629–34.
Begg CB, Mazumdar M. Operating characteristics of a rank correlation test for publication bias. Biometrics. 1994;50:1088–101.
Yan R, Yang X, Wang X, Wang B, Zhao Y, Huang W, et al. Association between intra-tumoral immune response and programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1) in gastric cancer. Med Sci Monit. 2019;25:6905–10.
Pötzsch M, Berg E, Hummel M, Stein U, von Winterfeld M, Jöhrens K, et al. Better prognosis of gastric cancer patients with high levels of tumor infiltrating lymphocytes is counteracted by PD-1 expression. OncoImmunology. 2020;9(1):1824632.
Ma J, Li J, Hao Y, Nie Y, Li Z, Qian M, et al. Differentiated tumor immune microenvironment of Epstein-Barr virus-associated and negative gastric cancer: Implication in prognosis and immunotherapy. Oncotarget. 2017;8(40):67094–103.
Kang M, Ma X, Shi J, Chen G, Jin X, Wang J, et al. Distinct molecular phenotype and the potential prognostic value of immune prognostic index and tumor infiltrating lymphocytes in hepatoid adenocarcinoma of stomach. Transl Oncol. 2022;19:101380.
Geng Y, Wang H, Lu C, Li Q, Xu B, Jiang J, et al. Expression of costimulatory molecules B7–H1, B7–H4 and Foxp3+ Tregs in gastric cancer and its clinical significance. Int J Clin Oncol. 2015;20(2):273–81.
Svensson MC, Borg D, Zhang C, Hedner C, Nodin B, Uhlén M, et al. Expression of PD-L1 and PD-1 in chemoradiotherapy-Naïve esophageal and gastric adenocarcinoma: relationship with mismatch repair status and survival. Front Oncol. 2019;9(MAR):136.
Kim JH, Kim SY, Shin EY, Jung JH, Choi HJ, Jun KH. Expression patterns of programmed death-1 and programmed death-1 ligand-1 on T cells in gastric cancer. Oncol Lett. 2019;18(3):2661–9.
Liu X, Guo Y, Huang C, Xu D, Zhu C, Xu J, et al. FOXP3+Tregs exhibit different infiltrating status and predict a distinct prognosis in primary lesions and hepatic metastases in stage III&IV advanced gastric cancer. Am J Transl Res. 2020;12(7):3629–44.
Zurlo IV, Schino M, Strippoli A, Calegari MA, Cocomazzi A, Cassano A, et al. Predictive value of NLR, TILs (CD4+/CD8+) and PD-L1 expression for prognosis and response to preoperative chemotherapy in gastric cancer. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2022;71(1):45–55.
Kim JW, Nam KH, Ahn SH, Park DJ, Kim HH, Kim SH, et al. Prognostic implications of immunosuppressive protein expression in tumors as well as immune cell infiltration within the tumor microenvironment in gastric cancer. Gastric Cancer. 2016;19(1):42–52.
Chang H, Jung WY, Kang Y, Lee H, Kim A, Kim HK, et al. Programmed death-ligand 1 expression in gastric adenocarcinoma is a poor prognostic factor in a high CD8+ tumor infiltrating lymphocytes group. Oncotarget. 2016;7(49):80426–34.
Hassen G, Kasar A, Jain N, Berry S, Dave J, Zouetr M, et al. Programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) positivity and factors associated with poor prognosis in patients with gastric cancer: an umbrella meta-analysis. Cureus. 2022;14(4):e23845.
Wang X, Teng F, Kong L, Yu J. PD-L1 expression in human cancers and its association with clinical outcomes. Onco Targets Ther. 2016;9:5023.
Lee JS, Won HS, Hong JH, Ko YH. Prognostic role of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in gastric cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine. 2018;97(32):e11769.
Acknowledgements
This study was done under the kind support of the Department of Gastroenterology, General Hospital of Western Theater Command, Chengdu, China.
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declared no conflict of interest related to this work.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Informed consent
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ren, J., He, Q., Yin, H. et al. Prognostic role and clinical significance of tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte (TIL) and programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression in gastric cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Transl Oncol 25, 1436–1445 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-022-03040-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-022-03040-1