Abstract
Background
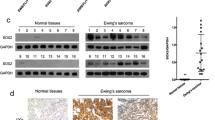
Ewing’s sarcoma is the second most common bone and soft tissue malignancy in children and adolescents. Tumor necrosis factor-α-induced protein 8-like 1 (TIPE1) functions as a tumor suppressor in several cancers. Activation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling in subpopulations of tumor cells contributes to phenotypic heterogeneity and disease progression in Ewing’s sarcoma. The exact role of TIPE1 in Ewing’s sarcoma remains to be elucidated.
Purpose
This study aimed to assess the expression and function of TIPE1 in Ewing’s sarcoma.
Methods
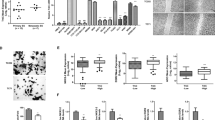
TIPE1 expression in Ewing’s sarcoma cells was determined by qPCR and western blotting. Furthermore, the Ewing’s sarcoma cell line RD-ES was transfected with a lentivirus-based TIPE1 expression system to upregulate the expression of TIPE1. The Cell Counting Kit 8 was used to assess the effect of TIPE1 on cell proliferation. The effects of TIPE1 on cell migration and invasion was detected by Transwell assay. Flow cytometry was performed to detect apoptosis.
Results
Our results suggested lower TIPE1 expression in Ewing’s sarcoma cell lines compared with normal osseous cells. TIPE1 remarkably inhibited the growth and proliferation of Ewing’s sarcoma cell; TIPE1 also induced apoptosis and inhibited invasion in vitro. TIPE1 inhibited Ewing’s sarcoma growth, motility, and survival through regulation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling.
Conclusions
Our results demonstrated the anti-tumor function of TIPE1 in Ewing’s sarcoma and reveal a novel therapeutic target.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data and materials supporting the findings of this study are available within the article.
References
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, Ahmedin Jemal DVM. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65(2):87–108.
Riggi N, Stamenkovic I. The biology of Ewing sarcoma. Cancer Lett. 2007;254(1):1–10.
Gaspar N, Hawkins DS, Dirksen U, Lewis IJ, Ferrari S, Le Deley M-C, et al. Ewing Sarcoma: current management and future approaches through collaboration. J Clin Oncol. 2015;33(27):3036–46.
Ludwig JA. Ewing sarcoma: historical perspectives, current state-of-the-art, and opportunities for targeted therapy in the future. Curr Opin Oncol. 2008;20(4):412–8.
Ladenstein R, Potschger U, Deley MCL, Whelan J, Paulussen M, Oberlin O, et al. Primary disseminated multifocal Ewing sarcoma: results of the Euro-EWING 99 trial. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28(20):3284–91.
Bordoloi D, Banik K, Shabnam B, Padmavathi G, Monisha J, Arfuso F, et al. TIPE family of proteins and its implications in different chronic diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(10):2974.
Cui J, Zhang G, Hao C, Wang Y, Loua Y, Zhang W, et al. The expression of TIPE1 in murine tissues and human cell lines. Mol Immunol. 2011;48(12–13):1548–55.
Padmavathi G, Banik K, Monisha J, Bordoloi D, Bano S, Arfuso F, et al. Novel tumor necrosis factor-alpha induced protein eight (TNFAIP8/TIPE) family: functions and downstream targets involved in cancer progression. Cancer Lett. 2018;432:260–71.
Zhang Z, Liang X, Gao L, Ma H, Liu X, Pan Y, et al. TIPE1 induces apoptosis by negatively regulating Rac1 activation in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Oncogene. 2015;34(20):2566–74.
Xiaocheng Wu, Ma Y, Cheng Ji, Li X, Zheng H, Jiang Li, Zhou R, et al. TIPE1 function as a prognosis predictor and negative regulator of lung cancer. Oncotarget. 2017;8(45):78496–506.
Liu W, Chen Y, Xie H, Guo Y, Ren D, Li Y, et al. TIPE1 suppresses invasion and migration through down-regulating Wnt/β-catenin pathway in gastric cancer. J Cell Mol Medicine. 2017. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.13362.
Chen P, Zhou J, Li J, Zhang Q, Zuo Q. TIPE1 suppresses osteosarcoma tumor growth by regulating macrophage infiltration. Clin Transl Oncol. 2018;21(3):334–41.
Pedersen EA, Menon R, Bailey KM, Thomas DG, Van Noord RA, Tran J, et al. Activation of Wnt/beta-catenin in Ewing sarcoma cells antagonizes EWS/ETS function and promotes phenotypic transition to more metastatic cell states. Cancer Res. 2016;76(17):5040–53.
Hawkins AG, Basrur V, da Veiga F, Leprevost EP, Sperring C, Nesvizhskii AI, et al. The Ewing sarcoma secretome and its response to activation of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2018;17(5):901–12.
Jiang J, Gao Li, Lan Y, Wang Y, Zhao P. TIPE1 promotes cervical cancer cell chemoresistance to cisplatin in a Wild-Type p53-dependent manner. Front Oncol. 2020;10: 593615.
Li F, Zhu X, Yang Y, Huang L, Jinhua Xu. TIPE2 alleviates systemic lupus erythematosus through regulating macrophage polarization. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2016;38(1):330–9.
Fan YuChen, Zhang YuanYuan, Wang Na, Sun YanYan, Wang K. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced protein 8-like 2 (TIPE2) is associated with immune phases of patients with chronic hepatitis B. Oncotarget. 2017;8(19):30781–92.
Day TF, Mewani RR, Starr J, Li X, Chakravarty D, Ressom H, et al. Transcriptome and proteome analyses of TNFAIP8 knockdown cancer cells reveal new insights into molecular determinants of cell survival and tumor progression. Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1513:83–100.
Wang Y, Liu Y, Chunfang Hu, Ni X, Huang X. Tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced protein 8-like 1 promotes apoptosis by regulating B-cell leukemia/lymphoma-2 family proteins in RAW264.7 cells. Oncol Lett. 2016;12(5):3506–12.
Gus-Brautbar Y, Johnson D, Zhang Li, Sun H, Wang P, Zhang S, et al. The anti-inflammatory TIPE2 is an inhibitor of the oncogenic Ras. Mol Cell. 2012;45(5):610–8.
Parrish AB, Freel CD, Kornbluth S. Cellular mechanisms controlling caspase activation and function. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2013;5(6):a008672.
Igney FH, Krammer PH. Death and anti-death: tumour resistance to apoptosis. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002;2(4):277–88.
Carneiro BA, El-Deiry WS. Targeting apoptosis in cancer therapy. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2020;17(7):395–417.
Martinou JC, Youle RJ. Mitochondria in apoptosis: Bcl-2 family members and mitochondrial dynamics. Dev Cell. 2011;21(1):92–101.
Nusse R, Clevers H. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling, disease, and emerging therapeutic modalities. Cell. 2017;169(6):985–99.
Hawkins AG, Pedersen EA, Treichel S, Temprine K, Sperring C, Read JA, et al. Wnt/beta-catenin-activated Ewing sarcoma cells promote the angiogenic switch. JCI Insight. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.135188.
Joo M, Lee HK, Kang YK. Expression of beta-catenin in hepatocellular carcinoma in relation to tumor cell proliferation and cyclin D1 expression. J Korean Med Sci. 2003;18(2):211–7.
Tetsu O, McCormick F. Beta-catenin regulates expression of cyclin D1 in colon carcinoma cells. Nature. 1999;398(6726):422–6.
Shtutman M, Zhurinsky J, Simcha I, Albanese C, D’ amico M, Pestell R, et al. The cyclin D1 gene is a target of the beta-catenin/LEF-1 pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1999;96(10):5522–7.
Lin SY, Xia W, Wang JC, Kwong KY, Spohn B, Wen Y, et al. Beta-catenin, a novel prognostic marker for breast cancer: its roles in cyclin D1 expression and cancer progression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2000;97(8):4262–6.
Kennedy AL, Vallurupalli M, Chen L, Crompton B, Cowley G, Vazquez F, et al. Functional, chemical genomic, and super-enhancer screening identify sensitivity to cyclin D1/CDK4 pathway inhibition in Ewing sarcoma. Oncotarget. 2015;6(30):30178–93.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the postgraduate fund of Taizhou people’s Hospital.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ZCW and LBS were involved in data acquisition. ZCW and SYL were involved in analysis and interpretation of the data. HTJ was involved in the conception and design of the study.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors confirm there is no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Z., Sun, L., Liu, S. et al. TIPE1 inhibits the growth of Ewing’s sarcoma cells by suppressing Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Clin Transl Oncol 25, 1332–1339 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-022-03030-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-022-03030-3